Abstract
Background
The plate–screw interface of an angular stable plate osteosynthesis is very rigid. So far, all attempts to decrease the stiffness of locked plating construct, e.g. the bridged plate technique, decrease primarily the bending stiffness. Thus, the interfragmentary motion increases only on the far cortical side by bending the plate. To solve this problem, the dynamic locking screw (DLS) was developed.
Materials and methods
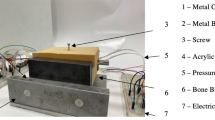
Comparison tests were performed with locking screws (LS) and DLS. Axial stiffness, bending stiffness and interfragmentary motion were compared. For measurements, we used a simplified transverse fracture model, consisting of POM C and an 11-hole LCP3.5 with a fracture gap of 3 mm. Three-dimensional fracture motion was detected using an optical measurement device (PONTOS 5 M/GOM) consisting of two CCD cameras (2,448 × 2,048 pixel) observing passive markers.
Results
The DLS reduced the axial stiffness by approximately 16% while increasing the interfragmentary motion at the near cortical side significantly from 282 µm (LS) to 423 µm (DLS) applying an axial load of 150 N.
Conclusion
The use of DLS reduces the stiffness of the plate–screw interface and thus increases the interfragmentary motion at the near cortical side without altering the advantages of angular stability and the strength.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottlang M, Doornink J, Fitzpatrick DC, Madey SM (2009) Far cortical locking can reduce stiffness of locked plating constructs while retaining construct strength. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:1985–1994
Ramotowski W, Granowski R (1991) Zespol. An original method of stable osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res;67–75
Kolodziej P, Lee FS, Patel A, Kassab SS, Shen KL, Yang KH, and Mast JW (1998) Biomechanical evaluation of the schuhli nut. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 79–85
Ring D, Kloen P, Kadzielski J, Helfet D, Jupiter JB (2004) Locking compression plates for osteoporotic nonunions of the diaphyseal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 425:50–54
Egol KA, Kubiak EN, Fulkerson E, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ (2004) Biomechanics of locked plates and screws. J Orthop Trauma 18:488–493
Perren SM, Allgower M, Cordey J, Russenberger M (1973) Developments of compression plate techniques for internal fixation of fractures. Prog Surg 12:152–179
Claes LE, Heigele CA, Neidlinger-Wilke C, Kaspar D, Seidl W, Margevicius KJ, Augat P (1998) Effects of mechanical factors on the fracture healing process. Clin Orthop Relat Res 355:S132–S147
Duda GN, Sollmann M, Sporrer S, Hoffmann JE, Kassi JP, Khodadadyan C, Raschke M (2002) Interfragmentary motion in tibial osteotomies stabilized with ring fixators. Clin Orthop Relat Res 396:163–172
Goodship AE, Kenwright J (1985) The influence of induced micromovement upon the healing of experimental tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 67:650–655
Wolf S, Janousek A, Pfeil J, Veith W, Haas F, Duda G, Claes L (1998) The effects of external mechanical stimulation on the healing of diaphyseal osteotomies fixed by flexible external fixation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 13:359–364
Kenwright J, Richardson JB, Goodship AE, Evans M, Kelly DJ, Spriggins AJ, Newman JH, Burrough SJ, Harris JD, Rowley DI (1986) Effect of controlled axial micromovement on healing of tibial fractures. Lancet 2:1185–1187
Stoffel K, Dieter U, Stachowiak G, Gachter A, Kuster MS (2003) Biomechanical testing of the LCP—how can stability in locked internal fixators be controlled? Injury 34(Suppl 2):B11–B19
Claes L, Blakytny R, Gockelmann M, Schoen M, Ignatius A, Willie B (2009) Early dynamization by reduced fixation stiffness does not improve fracture healing in a rat femoral osteotomy model. J Orthop Res 27:22–27
Claes LE, Wilke HJ, Augat P, Rubenacker S, Margevicius KJ (1995) Effect of dynamization on gap healing of diaphyseal fractures under external fixation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 10:227–234
Kenwright J,Goodship AE (1989) Controlled mechanical stimulation in the treatment of tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res;36–47
Goodship AE, Watkins PE, Rigby HS, Kenwright J (1993) The role of fixator frame stiffness in the control of fracture healing. An experimental study. J Biomech 26:1027–1035
Brighton CT (1984) The biology of fracture repair. Instr Course Lect 33:60–82
Ahmad M, Nanda R, Bajwa AS, Candal-Couto J, Green S, Hui AC (2007) Biomechanical testing of the locking compression plate: when does the distance between bone and implant significantly reduce construct stability? Injury 38:358–364
Kowalski MJ, Schemitsch EH, Harrington RM, Chapman JR, Swiontkowski MF (1996) A comparative biomechanical evaluation of a noncontacting plate and currently used devices for tibial fixation. J Trauma 40:5–9
Siebenlist S, Kraus T, Burghardt R, Dobele S, Stockle U, Ganslmeier A (2009) Therapy-resistant tibial pseudarthrosis: treatment success with BMP-7 combined with autologous bone. Unfallchirurg 113:59–64
Sturmer KM (1996) Elastic plate osteosynthesis, biomechanics, indications and technique in comparison with rigid osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg 99:816–829
Klaue K, Fengels I, Perren SM (2000) Long-term effects of plate osteosynthesis: comparison of four different plates. Injury 31(Suppl 2):S-B51–S-B62
Uhthoff HK, Poitras P, Backman DS (2006) Internal plate fixation of fractures: short history and recent developments. J Orthop Sci 11:118–126
Uhthoff HK, Finnegan MA (1984) The role of rigidity in fracture fixation. An overview. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 102:163–166
Smith SR, Bronk JT, Kelly PJ (1990) Effect of fracture fixation on cortical bone blood flow. J Orthop Res 8:471–478
Tepic S, Remiger AR, Morikawa K, Predieri M, Perren SM (1997) Strength recovery in fractured sheep tibia treated with a plate or an internal fixator: an experimental study with a two-year follow-up. J Orthop Trauma 11:14–23
Gardner MJ, Nork SE, Huber P, Krieg JC (2009) Stiffness modulation of locking plate constructs using near cortical slotted holes: a preliminary study. J Orthop Trauma 23:281–287
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Best of Abstracts–Chirurgisches Forum 2010, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chirurgie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Döbele, S., Horn, C., Eichhorn, S. et al. The dynamic locking screw (DLS) can increase interfragmentary motion on the near cortex of locked plating constructs by reducing the axial stiffness. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395, 421–428 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0636-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0636-z