Abstract
Background
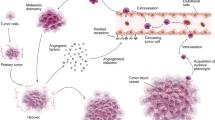
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels from the endothelium of the existing vasculature, is fundamental in tumor growth, progression, and metastasis. Inhibiting tumor angiogenesis is a promising strategy for treatment of cancer and has been successfully transferred from preclinical to clinical application in recent years. Whereas conventional therapeutic approaches, e.g. chemotherapy and radiation, are focussing on tumor cells, antiangiogenic therapy is directed against the tumor supplying blood vessels.
Materials and methods
This review will summarize important molecular mechanisms of tumor angiogenesis and advances in the design of antiangiogenic drugs. Furthermore, clinical implications of antiangiogenic therapy in surgical oncology will be discussed.
Results
First antiangiogenic drugs have been approved for treatment of advanced solid tumors in several countries. Leading antiangiogenic drugs are designed to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated tumor angiogenesis. Combining antiangiogenic agents with conventional chemotherapy or radiation is currently investigated clinically with great emphasis to realize a multimodal tumor therapy, targeting both the tumor cell and tumor vascular compartment.
Conclusion
Antiangiogenic tumor therapy represents a promising strategy for treatment of cancer and will most likely exhibit its clinical potential in combination with established standard tumor therapies in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (1990) What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82:4–6
Algire GH, Chalkley HW (1945) Vascular reactions of normal and malignant tissue in vivo. J Natl Cancer Inst 6:73–85
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G et al (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335–2342
Folkman J, Kalluri R (2004) Cancer without disease. Nature 427:787
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS (2005) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438:967–974
O’Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS, Cao Y, Sage EH, Folkman J (1994) Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell 79:315–328
Pinedo HM, Verheul HM, D’Amato RJ, Folkman J (1998) Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet 352:1775–1777
Browder T, Folkman J, Pirie-Shepherd S (2000) The hemostatic system as a regulator of angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:1521–1524
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N (1989) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246:1306–1309
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Bielenberg DR, Pettaway CA, Takashima S, Klagsbrun M (2006) Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation, and function. Exp Cell Res 312:584–593
Plank MJ, Sleeman BD, Jones PF (2004) The role of the angiopoietins in tumour angiogenesis. Growth Factors 22:1–11
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S et al (1997) Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277:55–60
Szebenyi G, Fallon JF (1999) Fibroblast growth factors as multifunctional signaling factors. Int Rev Cytol 185:45–106
Tonini T, Rossi F, Claudio PP (2003) Molecular basis of angiogenesis and cancer. Oncogene 22:6549–6556
Sargiannidou I, Zhou J, Tuszynski GP (2001) The role of thrombospondin-1 in tumor progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226:726–733
Kerbel R, Folkman J (2002) Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2:727–739
Kleespies A, Guba M, Jauch KW, Bruns CJ (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor in esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol 87:95–104
Guba M, Seeliger H, Kleespies A, Jauch KW, Bruns C (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 19:510–517
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, Ferrara N (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 362:841–844
Warren RS, Yuan H, Matli MR, Gillett NA, Ferrara N (1995) Regulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of human colon cancer tumorigenesis in a mouse model of experimental liver metastasis. J Clin Invest 95:1789–1797
Fernando NH, Hurwitz HI (2003) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol 30:39–50
Prewett M, Huber J, Li Y, Santiago A, O’Connor W, King K, Overholser J, Hooper A, Pytowski B, Witte L, Bohlen P, Hicklin DJ (1999) Antivascular endothelial growth factor receptor (fetal liver kinase 1) monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth of several mouse and human tumors. Cancer Res 59:5209–5218
Posey JA, Ng TC, Yang B, Khazaeli MB, Carpenter MD, Fox F, Needle M, Waksal H, LoBuglio AF (2003) A phase I study of anti-kinase insert domain-containing receptor antibody, IMC-1C11, in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:1323–1332
Holash J, Davis S, Papadopoulos N, Croll SD, Ho L, Russell M, Boland P, Leidich R, Hylton D, Burova E, Ioffe E, Huang T et al (2002) VEGF-Trap: a VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:11393–11398
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N, Bergsland E, Hanahan D (2003) Benefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest 111:1287–1295
Cabebe E, Wakelee H (2006) Sunitinib: a newly approved small-molecule inhibitor of angiogenesis. Drugs Today (Barc) 42:387–398
Hahn O, Stadler W (2006) Sorafenib. Curr Opin Oncol 18:615–621
Longo R, Sarmiento R, Fanelli M, Capaccetti B, Gattuso D, Gasparini G (2002) Anti-angiogenic therapy: rationale, challenges and clinical studies. Angiogenesis 5:237–256
Overall CM, Kleifeld O (2006) Towards third generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 94:941–946
Smith JW (2003) Cilengitide Merck. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 4:741–745
Guba M, Yezhelyev M, Eichhorn ME, Schmid G, Ischenko I, Papyan A, Graeb C, Seeliger H, Geissler EK, Jauch KW, Bruns CJ (2005) Rapamycin induces tumor-specific thrombosis via tissue factor in the presence of VEGF. Blood 105:4463–4469
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M, Koehl G, Flegel S, Hornung M, Bruns CJ, Zuelke C, Farkas S, Anthuber M, Jauch KW, Geissler EK (2002) Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by antiangiogenesis: involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat Med 8:128–135
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Redman BG, Hudes GR, Wilding G, Figlin RA, Ginsberg MS, Kim ST, Baum CM, DePrimo SE, Li JZ, Bello CL et al (2006) Activity of SU11248, a multitargeted inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:16–24
Giantonio B, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ et al (2005) High-dose bevacizumab in combination with FOLFOX-4 improves survival in patients with previously treated advanced colorectal cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Group (ECOG) study E2300. J Clin Oncol 23(16S):2
Kerbel RS (2006) Antiangiogenic therapy: a universal chemosensitization strategy for cancer? Science 312:1171–1175
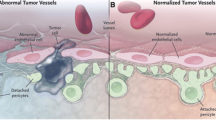
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7:987–989
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E, Munn LL, Jain RK (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6:553–563
Webb T (2005) Vascular normalization: study examines how antiangiogenesis therapies work. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:336–337
Willett CG, Boucher Y, Di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, Mino M, Cohen KS et al (2004) Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 10:145–147
Hudis CA (2005) Clinical implications of antiangiogenic therapies. Oncology (Willist Park N Y) 19:26–31
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J (2000) Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res 60:1878–1886
Belotti D, Vergani V, Drudis T, Borsotti P, Pitelli MR, Viale G, Giavazzi R, Taraboletti G (1996) The microtubule-affecting drug paclitaxel has antiangiogenic activity. Clin Cancer Res 2:1843–1849
O’Leary JJ, Shapiro RL, Ren CJ, Chuang N, Cohen HW, Potmesil M (1999) Antiangiogenic effects of camptothecin analogues 9-amino-20(S)-camptothecin, topotecan, and CPT-11 studied in the mouse cornea model. Clin Cancer Res 5:181–187
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA (2004) The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4:423–436
Kerbel RS, Klement G, Pritchard KI, Kamen B (2002) Continuous low-dose anti-angiogenic/metronomic chemotherapy: from the research laboratory into the oncology clinic. Ann Oncol 13:12–15
Bottini A, Generali D, Brizzi MP, Fox SB, Bersiga A, Bonardi S, Allevi G, Aguggini S, Bodini G, Milani M, Dionisio R, Bernardi C et al (2006) Randomized phase II trial of letrozole and letrozole plus low-dose metronomic oral cyclophosphamide as primary systemic treatment in elderly breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 24:3623–3628
Young SD, Whissell M, Noble JC, Cano PO, Lopez PG, Germond CJ (2006) Phase II clinical trial results involving treatment with low-dose daily oral cyclophosphamide, weekly vinblastine, and rofecoxib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 12:3092–3098
Scappaticci FA, Fehrenbacher L, Cartwright T, Hainsworth JD, Heim W, Berlin J, Kabbinavar F, Novotny W, Sarkar S, Hurwitz H (2005) Surgical wound healing complications in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with bevacizumab. J Surg Oncol 91:173–180
Gruenberger T, Gruenberger B, Scheithauer W (2006) Neoadjuvant therapy with bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 24:2592–2593
Shimizu H, Mitsuhashi N, Ohtsuka M, Ito H, Kimura F, Ambiru S, Togawa A, Yoshidome H, Kato A, Miyazaki M (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins regulate sinusoidal regeneration and remodeling after partial hepatectomy in rats. World J Gastroenterol 11:7254–7260
Ellis LM, Curley SA, Grothey A (2005) Surgical resection after downsizing of colorectal liver metastasis in the era of bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 23:4853–4855
Acknowledgment
The authors thank C. Conrad and M. Dellian for helpful suggestions and critical comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eichhorn, M.E., Kleespies, A., Angele, M.K. et al. Angiogenesis in cancer: molecular mechanisms, clinical impact. Langenbecks Arch Surg 392, 371–379 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0150-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0150-0