Abstract
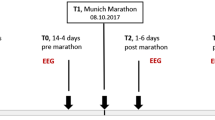
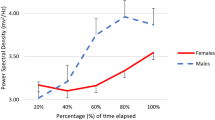
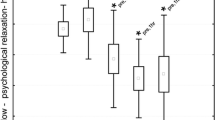
This study was designed to measure the electroencephalogram (EEG) after exercise with increasing intensity. In a field test with increments in running velocity a 2-min EEG was recorded, together with blood lactate concentration and heart rate, after each stage. An individual protocol was used, with up to six stages of running to ensure comparability of exercise intensity among the subjects, in each of 19 athletes (17 men, 2 women) experienced in leisure-time running. The exercise consisted initially of three running stages of aerobic exercise intensity without blood lactate accumulation followed by stages with an increase of lactate concentration. The protocol of the field test led to a progressive increase in cortical activity directly after the stages without blood lactate accumulation mainly in the δ frequency band, followed by θ and α-1 frequency band, and less pronounced in the α-2 and in the β frequency bands. After the stages with an onset and further increase of blood lactate accumulation significant decreases in the β-2, β-1 and α-1 frequency bands occurred predominantly in temporal (T3, T4, T5, and T6) and occipital (O1, and O2) electrode positions, indicating a stage-by-stage decrease of activity. This decrease may be explained by feed-back from working muscle, via afferents to the cortex from intero- and proprio-receptors and affective processes. This could suggest that through a higher running intensity indicated by an onset of blood lactate accumulation metabolic and mechanical changes led to alterations within the afferent systems influencing the level of cortical activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 9 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mechau, D., Mücke, S., Liesen, H. et al. Effect of increasing running velocity on electroencephalogram in a field test. Eur J Appl Physiol 78, 340–345 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050429
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050429