Abstract
Purpose
The cardiac T-wave peak-to-end interval (Tpe) is thought to reflect dispersion in ventricular repolarisation, with abnormalities in Tpe associated with increased risk of arrhythmia. Extracellular K+ modulates cardiac repolarisation, and since arterial plasma K+ concentration ([K+]) rapidly increases during and declines following exercise, we investigated the relationship between [K+] and Tpe with exercise.
Methods
Serial ECGs (Tpe, Tpe/QT ratio) and [K+] were obtained from 8 healthy, normokalaemic volunteers and 22 patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), at rest, during, and after exhaustive exercise.
Results
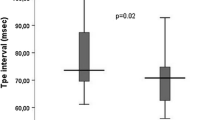
Post-exercise [K+] nadir was 3.1 ± 0.1, 5.0 ± 0.2 and 4.0 ± 0.1 mmol.L−1 (mean ± SEM) for healthy participants and ESRD patients before and after haemodialysis, respectively. In healthy participants, compared to pre-exercise, recovery-induced low [K+] was associated with a prolongation of Tpe (110 ± 8 vs. 87 ± 5 ms, respectively, p = 0.03) and an increase in Tpe/QT ratio (0.28 ± 0.01 vs. 0.23 ± 0.01, respectively, p = 0.01). Analyses of serial data revealed [K+] as a predictor of Tpe in healthy participants (β = -0.54 ±0.05, p < 0.0001), in ESRD patients (β = -0.75 ± 0.06, p < 0.0001) and for all data pooled (β = -0.61 ± 0.04, p < 0.0001). The [K+] was also a predictor of Tpe/QT ratio in healthy participants and ESRD patients.
Conclusions
Tpe and Tpe/QT ratio are predicted by [K+] during exercise. Low [K+] during recovery from exercise was associated with increased Tpe and Tpe/QT, indicating accentuated dispersion of ventricular repolarisation. The findings suggest that variations in [K+] with physical exertion may unmask electrophysiological vulnerabilities to arrhythmia.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials (data transparency)
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to regulations/agreements with the Danish Data Protection Authority, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- [K+]:
-
Plasma potassium concentration
- PVC:
-
Premature ventricular contraction
- QT Interval:
-
ECG interval between Q and T waves
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- Tpe :
-
T-wave peak-to-end interval
- Tpe/QT ratio:
-
Ratio of Tpe interval divided by QT interval
References
Ackerman MJ, Clapham DE (1997) Ion channels–basic science and clinical disease. N Engl J Med 336(22):1575–1586
Albert CM, Mittleman MA, Chae CU, Lee IM, Hennekens CH, Manson JE (2000) Triggering of sudden death from cardiac causes by vigorous exertion. N Engl J Med 343(19):1355–1361. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200011093431902
Altarawneh M, Petersen AC, Smith R, Rouffet DM, Billaut F, Perry BD, Wyckelsma VL, Tobin A, McKenna MJ (2016) Salbutamol effects on systemic potassium dynamics during and following intense continuous and intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 116:2389–2399
Atanasovska T, Petersen AC, Rouffet DM, Billaut F, Ng I, McKenna MJ (2014) Plasma K+ dynamics and implications during and following intense rowing exercise. J Appl Physiol 117:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01027.2013
Atanasovska T, Smith R, Graff C, Tran CT, Melgaard J, Kanters JK, Petersen AC, Tobin A, Kjeldsen KP, McKenna MJ (2018) Protection against severe hypokalemia but impaired cardiac repolarization after intense rowing exercise in healthy humans receiving salbutamol. J Appl Physiol 125(2):624–633. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00680.2017
Bachmann TN, Skov MW, Rasmussen PV, Graff C, Pietersen A, Lind B, Struijk JJ, Olesen MS, Haunso S, Kober L, Svendsen JH, Holst AG, Nielsen JB (2015) Electrocardiographic Tpeak-Tend interval and risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: results from the copenhagen ECG study. Heart Rhythm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.027
Bhuiyan TA, Graff C, Kanters JK, Nielsen J, Melgaard J, Matz J, Toft E, Struijk JJ (2015) The T-peak-T-end interval as a marker of repolarization abnormality: a comparison with the QT interval for five different drugs. Clin Drug Investig 35(11):717–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0328-0
Bleyer AJ, Hartman J, Brannon PC, Reeves-Daniel A, Satko SG, Russell G (2006) Characteristics of sudden death in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 69(12):2268–2273. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5000446
Choy AM, Lang CC, Chomsky DM, Rayos GH, Wilson JR, Roden DM (1997) Normalization of acquired QT prolongation in humans by intravenous potassium. Circulation 96(7):2149–2154
Chua KC, Rusinaru C, Reinier K, Uy-Evanado A, Chugh H, Gunson K, Jui J, Chugh SS (2016) Tpeak-to-Tend interval corrected for heart rate: A more precise measure of increased sudden death risk? Heart Rhythm 13(11):2181–2185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.08.022
Clausen T (2003) Na+-K+ pump regulation and skeletal muscle contractility. Physiol Rev 83(4):1269–1324
Fosser C, Duczynski G, Agin M, Wicker P, Darpo B (2009) Comparison of manual and automated measurements of the QT interval in healthy volunteers: an analysis of five thorough QT studies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 86(5):503–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2009.34
Frolkis JP, Pothier CE, Blackstone EH, Lauer MS (2003) Frequent ventricular ectopy after exercise as a predictor of death. N Engl J Med 348(9):781–790. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa022353
Glitsch HG (2001) Electrophysiology of the sodium-potassium-ATPase in cardiac cells. Physiol Rev 81(4):1791–1826
Goyal A, Spertus JA, Gosch K, Venkitachalam L, Jones PG, Van den Berghe G, Kosiborod M (2012) Serum potassium levels and mortality in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA 307(2):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1967
Gupta P, Patel C, Patel H, Narayanaswamy S, Malhotra B, Green JT, Yan GX (2008) T(p-e)/QT ratio as an index of arrhythmogenesis. J Electrocardiol 41(6):567–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2008.07.016
Harmon KG, Asif IM, Maleszewski JJ, Owens DS, Prutkin JM, Salerno JC, Zigman ML, Ellenbogen R, Rao AL, Ackerman MJ, Drezner JA (2015) Incidence, cause, and comparative frequency of sudden cardiac death in national collegiate athletic association athletes: a decade in review. Circulation 132(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.115.015431
Hnatkova K, Gang Y, Batchvarov VN, Malik M (2006) Precision of QT interval measurement by advanced electrocardiographic equipment. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 29(11):1277–1284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2006.00532.x
Kim JH, Malhotra R, Chiampas G, d’Hemecourt P, Troyanos C, Cianca J, Smith RN, Wang TJ, Roberts WO, Thompson PD, Baggish AL (2012) Cardiac arrest during long-distance running races. N Engl J Med 366(2):130–140. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1106468
Laukkanen JA, Khan H, Kurl S, Willeit P, Karppi J, Ronkainen K, Di Angelantonio E (2014) Left ventricular mass and the risk of sudden cardiac death: a population-based study. J Am Heart Assoc 3(6):e001285. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.114.001285
Letsas KP, Weber R, Astheimer K, Kalusche D, Arentz T (2010) Tpeak-Tend interval and Tpeak-Tend/QT ratio as markers of ventricular tachycardia inducibility in subjects with Brugada ECG phenotype. Europace 12(2):271–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eup357
Lindinger MI, Cairns SP (2021) Regulation of muscle potassium: exercise performance, fatigue and health implications. Eur J Appl Physiol 121(3):721–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04546-8
Lindinger MI, Heigenhauser GJ, McKelvie RS, Jones NL (1990) Role of nonworking muscle on blood metabolites and ions with intense intermittent exercise. Am J Physiol 258(6 Pt 2):R1486-1494
Makar MS, Pun PH (2017) Sudden cardiac death among hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 69(5):684–695. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.12.006
Maury P, Sacher F, Gourraud JB, Pasquie JL, Raczka F, Bongard V, Duparc A, Mondoly P, Sadron M, Chatel S, Derval N, Denis A, Cardin C, Davy JM, Hocini M, Jais P, Jesel L, Carrie D, Galinier M, Haissaguerre M, Probst V, Rollin A (2015) Increased Tpeak-Tend interval is highly and independently related to arrhythmic events in Brugada syndrome. Heart Rhythm 12(12):2469–2476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.07.029
McKenna MJ, Gissel H, Clausen T (2003) Effects of electrical stimulation and insulin on Na+, K+-ATPase ([3H]-ouabain binding) in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 547(2):567–580
McKenna MJ, Bangsbo J, Renaud J-ME (2008) Muscle K+, Na+, Cl- Disturbances and Na+, K+-pump inactivation: implications for fatigue. J Appl Physiol 104:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01037.2007
McMahon LP, McKenna MJ, Sangkabutra T, Mason K, Sostaric S, Skinner SL, Burge C, Murphy B, Crankshaw D (1999) Physical performance and associated electrolyte changes after haemoglobin normalization: a comparative study in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(5):1182–1187
Medbo JI, Sejersted OM (1990) Plasma potassium changes with high intensity exercise. J Physiol 421:105–122
Medbo JI, Sejersted OM (1994) Plasma K+ changes during intense exercise in endurance-trained and sprint-trained subjects. Acta Physiol Scand 151(3):363–371
Modesto KM, Moller JE, Freeman WK, Shub C, Bailey KR, Pellikka PA (2006) Safety of exercise stress testing in patients with abnormal concentrations of serum potassium. Am J Cardiol 97(8):1247–1249
Mugnai G, Benfari G, Fede A, Rossi A, Chierchia GB, Vassanelli F, Menegatti G, Ribichini FL (2016) Tpeak-to-Tend/QT is an independent predictor of early ventricular arrhythmias and arrhythmic death in anterior ST elevation myocardial infarction patients. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 5(6):473–480. https://doi.org/10.1177/2048872615598616
Nielsen OB, Clausen T (1997) Regulation of Na+, K+-pump activity in contracting rat muscle. J Physiol 503(3):571–581
Paterson DJ (1996) Antiarrhythmic mechanisms during exercise. J Appl Physiol 80(6):1853–1862
Petersen AC, Leikis MJ, McMahon LP, Kent AB, McKenna MJ (2009) Effects of endurance training on extrarenal potassium regulation and exercise performance in patients on haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(9):2882–2888. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfp157
Petersen AC, Leikis MJ, McMahon LP, Kent AB, Murphy KT, Gong X, McKenna MJ (2012) Impaired exercise performance and muscle Na(+), K(+)-pump activity in renal transplantation and haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant 27(5):2036–2043. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr586
Porthan K, Viitasalo M, Toivonen L, Havulinna AS, Jula A, Tikkanen JT, Vaananen H, Nieminen MS, Huikuri HV, Newton-Cheh C, Salomaa V, Oikarinen L (2013) Predictive value of electrocardiographic T-wave morphology parameters and T-wave peak to T-wave end interval for sudden cardiac death in the general population. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 6(4):690–696. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.113.000356
Prenner SB, Shah SJ, Goldberger JJ, Sauer AJ (2016) Repolarization heterogeneity: beyond the QT interval. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.116.003607
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen K, Kuck KH, Hernandez-Madrid A, Nikolaou N, Norekvål TM, Spaulding C, Van Veldhuisen DJ (2015) 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur Heart J 36(41):2793–2867. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv316
Sangkabutra T, Crankshaw DP, Schneider C, Fraser SF, Sostaric S, Mason K, Burge CM, Skinner SL, McMahon LP, McKenna MJ (2003) Impaired K+ Regulation Contributes to Exercise Limitation In End-stage Renal Failure. Kidney Int 63:283–290
Santoro A, Mancini E, London G, Mercadal L, Fessy H, Perrone B, Cagnoli L, Grandi E, Severi S, Cavalcanti S (2008) Patients with complex arrhythmias during and after haemodialysis suffer from different regimens of potassium removal. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23(4):1415–1421. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm730
Saour BM, Wang JH, Lavelle MP, Mathew RO, Sidhu MS, Boden WE, Sacco JD, Costanzo EJ, Hossain MA, Vachharanji T, Alrefaee A, Asif A (2019) TpTe and TpTe/QT: novel markers to predict sudden cardiac death in ESRD? J Bras Nefrol 41(1):38–47. https://doi.org/10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2017-0021
Sejersted OM, Sjogaard G (2000) Dynamics and consequences of potassium shifts in skeletal muscle and heart during exercise. Physiol Rev 80(4):1411–1481
Shimizu W, Antzelevitch C (2000) Effects of a K(+) channel opener to reduce transmural dispersion of repolarization and prevent torsade de pointes in LQT1, LQT2, and LQT3 models of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation 102(6):706–712. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.6.706
Sutherland GR (2017) Sudden cardiac death: the pro-arrhythmic interaction of an acute loading with an underlying substrate. Eur Heart J 38(40):2986–2994. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw449
Takenaka K, Ai T, Shimizu W, Kobori A, Ninomiya T, Otani H, Kubota T, Takaki H, Kamakura S, Horie M (2003) Exercise stress test amplifies genotype-phenotype correlation in the LQT1 and LQT2 forms of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation 107(6):838–844
Tran CT, Kjeldsen K (2011) Protection against beta adrenoceptor agonist reduction of plasma potassium in severe but not in moderate hypokalemia. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 25(4):452–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2011.00937.x
Tran CT, Bundgaard H, Ladefoged SD, Haunso S, Kjeldsen K (2013) Potassium dynamics are attenuated in hyperkalemia and a determinant of QT adaptation in exercising hemodialysis patients. J Appl Physiol 115(4):498–504. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01019.2012
Vollestad NK, Hallen J, Sejersted OM (1994) Effect of exercise intensity on potassium balance in muscle and blood of man. J Physiol 475(2):359–368
Wu Y, Roden DM, Anderson ME (1999) Calmodulin kinase inhibition prevents development of the arrhythmogenic transient inward current. Circ Res 84(8):906–912. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.84.8.906
Xue J, Gao W, Chen Y, Han X (2008) Study of repolarization heterogeneity and electrocardiographic morphology with a modeling approach. J Electrocardiol 41(6):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2008.07.027
Yan GX, Antzelevitch C (1998) Cellular basis for the normal T wave and the electrocardiographic manifestations of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation 98(18):1928–1936. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.98.18.1928
Yang T, Roden DM (1996) Extracellular potassium modulation of drug block of IKr. Implications for torsade de pointes and reverse use-dependence. Circulation 93(3):407–411. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.93.3.407
Yellen G (2002) The voltage-gated potassium channels and their relatives. Nature 419(6902):35–42
Zumhagen S, Zeidler EM, Stallmeyer B, Ernsting M, Eckardt L, Schulze-Bahr E (2016) Tpeak-Tend interval and Tpeak-Tend/QT ratio in patients with Brugada syndrome. Europace 18(12):1866–1872. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw033
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any external organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CTT, KPK, and MJM conceived and designed the research. CTT, TA, KPK, and MJM conducted the experiments. CTT, TA, CG, JM, JKK, CTT, TA, KPK, and MJM analysed data. CTT and MJM performed the statistical analyses. CTT wrote the initial manuscript draft. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
The studies were approved by the respective ethics committees governing the institutions involved (Copenhagen Regional Committee for Health Research Ethics: KF 01 319759; and Human Research Ethics Committee at Victory University). The study conforms to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
All participants gave written informed consent to participate in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Michael I Lindinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, C.T., Atanasovska, T., Graff, C. et al. Plasma potassium concentration and cardiac repolarisation markers, Tpeak–Tend and Tpeak–Tend/QT, during and after exercise in healthy participants and in end-stage renal disease. Eur J Appl Physiol 122, 691–702 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04870-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04870-7