Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of multi-strain probiotics supplementation on gastrointestinal permeability, systemic markers of inflammation and running performance when exercising in the heat.
Methods
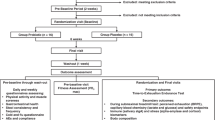
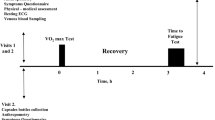
Ten male runners were randomized to 4 weeks of daily supplementation with a probiotics capsule (45 billion CFU of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and Streptococcus strains) or placebo, separated by a washout period (double-blind, cross-over trial). After each treatment, the runners exercised to fatigue at 80 % of their ventilatory threshold at 35 °C and 40 % humidity. To assess gastrointestinal permeability, runners ingested lactulose and rhamnose before exercise and post-exercise urine was collected to measure sugar concentrations. Venous blood samples were collected before, immediately after and 1 h after exercise, and core temperature was monitored during exercise.
Results
Probiotics supplementation significantly increased run time to fatigue (min:s 37:44 ± 2:42 versus 33:00 ± 2:27; P = 0.03, d = 0.54). Average core temperature during exercise was similar between trials (probiotic 38.1 ± 0.2 °C, placebo 38.1 ± 0.1 °C; P = 0.77, d = 0.13). Serum lipopolysaccharide concentration increased post-exercise (P < 0.001), while there was a moderate to large reduction in pre-exercise (d = 0.70) and post-exercise (d = 1.24) concentration following probiotics supplementation. Plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-10 and IL-1ra increased after exercise (P < 0.01), but there was no significant difference between trials (P > 0.05). There was a small to moderate reduction (d = 0.35) in urine lactulose:rhamnose and a small reduction (d = 0.25) in symptoms of gastrointestinal discomfort following probiotics supplementation (both P = 0.25).
Conclusion
Four weeks of supplementation with a multi-strain probiotic increased running time to fatigue in the heat. Further studies are required to elucidate the exact mechanisms for this performance benefit.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenhoefer A, Oswald S, Sonnenborn U, Enders C, Schulze J, Hacker J, Oelschlaeger TA (2004) The probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 interferes with invasion of human intestinal epithelial cells by different enteroinvasive bacterial pathogens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 40(3):223–229
ANSI (2010) Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy. vol ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55–2010. ASHRAE, Atlanta p 11
Borg GA (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14(5):377–381
Bosenberg AT, Brock-Utne JG, Gaffin SL, Wells MT, Blake GT (1988) Strenuous exercise causes systemic endotoxemia. J Appl Physiol 65(1):106–108
Bouchama A, Parhar RS, el-Yazigi A, Sheth K, al-Sedairy S (1991) Endotoxemia and release of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 alpha in acute heatstroke. J Appl Physiol 70(6):2640–2644
Bouchama A, al-Sedairy S, Siddiqui S, Shail E, Rezeig M (1993) Elevated pyrogenic cytokines in heatstroke. Chest 104(5):1498–1502
Camus G, Nys M, Poortmans J, Venneman I, Monfils T, Deby-Dupont G, Juchmes-Ferir A, Deby C, Lamy M, Duchateau J (1998) Endotoxaemia, production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation following strenuous exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 79:62–68
Caputa M, Dokladny K, Kurowicka B (2000) Endotoxaemia does not limit heat tolerance in rats: the role of plasma lipoproteins. Eur J Appl Physiol 82(1–2):142–150
Chapman CM, Gibson GR, Rowland I (2011) Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains? Eur J Nutr 50(1):1–17
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd edn). Lawrence Erlbaum, New Jersey
Cox AJ, Pyne DB, Saunders PU, Fricker PA (2010) Oral administration of the probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum VRI-003 and mucosal immunity in endurance athletes. Br J Sports Med 44(4):222–226
Dill D, Costill D (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Dokladny K, Moseley PL, Ma TY (2006) Physiologically relevant increase in temperature causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290(2):G204–G212
DuBose DA, Basamania K, Maglione L, Rowlands J (1983) Role of bacterial endotoxins of intestinal origin in rat heat stress mortality. J Appl Physiol 54(1):31–36
Ewaschuk J, Endersby R, Thiel D, Diaz H, Backer J, Ma M, Churchifl T, Madsen K (2007) Probiotic bacteria prevent hepatic damage and maintain colonic barrier function in a mouse model of sepsis. Hepatology 46(3):841–850
Hall DM, Buettner GR, Oberley LW, Xu L, Matthes RD, Gisolfi CV (2001) Mechanisms of circulatory and intestinal barrier dysfunction during whole body hyperthermia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280(2):H509–H521
Ikari A, Nakano M, Suketa Y, Harada H, Takagi K (2005) Reorganization of ZO-1 by sodium-dependent glucose transporter activation after heat stress in LLC-PK1 cells. J Cell Physiol 203(3):471–478
Jeukendrup AE, Vet-Joop K, Sturk A, Stegen J, Senden J, Saris WHM, Wagenmakers AJM (2000) Relationship between gastro-intestinal complaints and endotoxaemia, cytokine release and the acute-phase reaction during and after a long-distance triathlon in highly trained men. Clin Sci 98(1):47–55
Karczewski J, Troost FJ, Konings I, Dekker J, Kleerebezem M, Brummer RJ, Wells JM (2010) Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298(6):G851–G859
Kenney WL, Ho CW (1995) Age alters regional distribution of blood flow during moderate-intensity exercise. J Appl Physiol 79(4):1112–1119
Kerasioti E, Stagos D, Jamurtas A, Kiskini A, Koutedakis Y, Goutzourelas N, Pournaras S, Tsatsakis AM, Kouretas D (2013) Anti-inflammatory effects of a special carbohydrate-whey protein cake after exhaustive cycling in humans. Food Chem Toxicol. pii: S0278-6915(13)00061-6
Lambert GP (2004) Role of gastrointestinal permeability in exertional heatstroke. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 32(4):185–190
Lambert GP, Broussard LJ, Mason BL, Mauermann WJ, Gisolfi CV (2001) Gastrointestinal permeability during exercise: effects of aspirin and energy-containing beverages. J Appl Physiol 90(6):2075–2080
Lambert GP, Lang J, Bull A, Pfeifer PC, Eckerson J, Moore G, Lanspa S, O’Brien J (2008) Fluid restriction during running increases GI permeability. Int J Sports Med 29(3):194–198
Lamprecht M, Bogner S, Schippinger G, Steinbauer K, Fankhauser F, Hallstroem S, Schuetz B, Greilberger JF (2012) Probiotic supplementation affects markers of intestinal barrier, oxidation, and inflammation in trained men; a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 9(1):45. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-9-45
Leon LR, Helwig BG (2010) Heat stroke: role of the systemic inflammatory response. J Appl Physiol 109(6):1980–1988
Lim CL, Mackinnon LT (2006) The roles of exercise-induced immune system disturbances in the pathology of heat stroke : the dual pathway model of heat stroke. Sports Med 36(1):39–64
Lim C, Pyne D, Horn P, Kalz A, Saunders P, Peake J, Suzuki K, Wilson G, Mackinnon L (2009) The effects of increased endurance training load on biomarkers of heat intolerance during intense exercise in the heat. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 34(6):616–624
Marchbank T, Davison G, Oakes JR, Ghatei MA, Patterson M, Moyer MP, Playford RJ (2011) The nutriceutical bovine colostrum truncates the increase in gut permeability caused by heavy exercise in athletes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300(3):G477–G484
Mennigen R, Nolte K, Rijcken E, Utech M, Loeffler B, Senninger N, Bruewer M (2009) Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296(5):G1140–G1149
Montalto M, Maggiano N, Ricci R, Curigliano V, Santoro L, Di Nicuolo F, Vecchio FM, Gasbarrini A, Gasbarrini G (2004) Lactobacillus acidophilus protects tight junctions from aspirin damage in HT-29 cells. Digestion 69(4):225–228
Oliver SR, Phillips NA, Novosad VL, Bakos MP, Talbert EE, Clanton TL (2012) Hyperthermia induces injury to the intestinal mucosa in the mouse: evidence for an oxidative stress mechanism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302(7):R845–R853
Otte JM, Podolsky DK (2004) Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286(4):G613–G626
Pals KL, Chang RT, Ryan AJ, Gisolfi CV (1997) Effect of running intensity on intestinal permeability. J Appl Physiol 82(2):571–576
Patel RM, Myers LS, Kurundkar AR, Maheshwari A, Nusrat A, Lin PW (2012) Probiotic bacteria induce maturation of intestinal claudin 3 expression and barrier function. Am J Pathol 180(2):626–635
Peters HP, Bos M, Seebregts L, Akkermans LM, van Berge Henegouwen GP, Bol E, Mosterd WL, de Vries WR (1999) Gastrointestinal symptoms in long-distance runners, cyclists, and triathletes: prevalence, medication, and etiology. Am J Gastroenterol 94(6):1570–1581
Qiao H, Duffy LC, Griffiths E, Dryja D, Leavens A, Rossman J, Rich G, Riepenhoff-Talty M, Locniskar M (2002) Immune responses in rhesus rotavirus-challenged BALB/c mice treated with bifidobacteria and prebiotic supplements. Pediatr Res 51(6):750–755
Resta-Lenert S, Barrett KE (2003) Live probiotics protect intestinal epithelial cells from the effects of infection with enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC). Gut 52(7):988–997
Schwartz AE, Vanagunas A, Kamel PL (1990) Endoscopy to evaluate gastrointestinal bleeding in marathon runners. Ann Intern Med 113(8):632–633
Selkirk GA, McLellan TM, Wright HE, Rhind SG (2008) Mild endotoxemia, NF-kappaB translocation, and cytokine increase during exertional heat stress in trained and untrained individuals. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295(2):R611–R623
Seth A, Yan F, Polk DB, Rao RK (2008) Probiotics ameliorate the hydrogen peroxide-induced epithelial barrier disruption by a PKC- and MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294(4):G1060–G1069
Shing CM, Peake J, Suzuki K, Okutsu M, Pereira R, Stevenson L, Jenkins DG, Coombes JS (2007) Effects of bovine colostrum supplementation on immune variables in highly trained cyclists. J Appl Physiol 102(3):1113–1122
ter Steege RW, Van der Palen J, Kolkman JJ (2008) Prevalence of gastrointestinal complaints in runners competing in a long-distance run: an internet-based observational study in 1281 subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol 43(12):1477–1482
van Wijck K, Lenaerts K, van Loon LJ, Peters WH, Buurman WA, Dejong CH (2011) Exercise-induced splanchnic hypoperfusion results in gut dysfunction in healthy men. PLoS One 6(7):e22366
van Wijck K, Lenaerts K, Grootjans J, Wijnands K, Poeze M, van Loon LJ, Dejong CH, Buurman WA (2012) Physiology and pathophysiology of splanchnic hypoperfusion and intestinal injury during exercise: strategies for evaluation and prevention. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303(2):155–168
Wang Y, Liu Y, Sidhu A, Ma Z, McClain C, Feng W (2012) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG culture supernatant ameliorates acute alcohol-induced intestinal permeability and liver injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303(1):G32–G41
Wind RD, Tolboom H, Klare I, Huys G, Knol J (2010) Tolerance and safety of the potentially probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus PRSF-L477: a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial in healthy volunteers. Br J Nutr 104(12):1806–1816
Xu DZ, Lu Q, Kubicka R, Deitch EA (1999) The effect of hypoxia/reoxygenation on the cellular function of intestinal epithelial cells. J Trauma 46(2):280–285
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr Michael Leveritt for his assistance with dietary prescription for the runners, and the runners for their commitment to the study. The authors have no competing interests to declare. A portion of this work was funded by the BioCeuticals™, Sydney, Australia and the University of Tasmania. The authors do not have any professional relationships with the company. Luis Vitetta has received National Institute of Complementary Medicine and National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia competitive funding and Industry support for research into probiotics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Fischetti.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shing, C.M., Peake, J.M., Lim, C.L. et al. Effects of probiotics supplementation on gastrointestinal permeability, inflammation and exercise performance in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 93–103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2748-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2748-y