Abstract
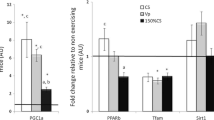
Little is known about the effect of training on genetic markers for mitochondrial biogenesis in elite athletes. We tested the hypothesis that low-volume sprint interval exercise (SIE) would be as effective as high-volume interval exercise (IE). Ten male cyclists competing on national elite level (W max 403 ± 13 W, VO2peak 68 ± 1 mL kg−1 min−1) performed two interval exercise protocols: 7 × 30-s “all-out” bouts (SIE) and 3 × 20-min bouts at ~87% of VO2peak (IE). During IE, the work was eightfold larger (1,095 ± 43 vs. 135 ± 5 kJ) and the exercise duration 17 times longer (60 vs. 3.5 min) than during SIE. Muscle samples were taken before and 3 h after exercise. The mRNA of upstream markers of mitochondrial biogenesis [peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1 (PGC-1α), PGC-1α-related coactivator (PRC) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ (PPARδ)] increased to the same extent after SIE and IE (6-, 1.5- and 1.5-fold increase, respectively). Of the downstream targets of PGC-1α, mitochondrial transcription factor A (Tfam) increased only after SIE and was significantly different from that after IE (P < 0.05), whereas others increased to the same extent (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, PDK4) or was unchanged (nuclear respiratory factor 2, NRF2). We conclude that upstream genetic markers of mitochondrial biogenesis increase in a similar way in elite athletes after one exercise session of SIE and IE. However, since the volume and duration of work was considerably lower during SIE and since Tfam, the downstream target of PGC-1α, increased only after SIE, we conclude that SIE might be a time-efficient training strategy for highly trained individuals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson U, Scarpulla RC (2001) Pgc-1-related coactivator, a novel, serum-inducible coactivator of nuclear respiratory factor 1-dependent transcription in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:3738–3749
Bergstrom J (1962) Muscle electrolytes in man determined by neutron activation analysis on needle biopsy specimens. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 68:1–110
Burgomaster KA, Hughes SC, Heigenhauser GJ, Bradwell SN, Gibala MJ (2005) Six sessions of sprint interval training increases muscle oxidative potential and cycle endurance capacity in humans. J Appl Physiol 98:1985–1990
Burgomaster KA, Heigenhauser GJ, Gibala MJ (2006) Effect of short-term sprint interval training on human skeletal muscle carbohydrate metabolism during exercise and time-trial performance. J Appl Physiol 100:2041–2047
Burgomaster KA, Howarth KR, Phillips SM, Rakobowchuk M, Macdonald MJ, McGee SL, Gibala MJ (2008) Similar metabolic adaptations during exercise after low volume sprint interval and traditional endurance training in humans. J Physiol 586:151–160
Coffey VG, Hawley JA (2007) The molecular bases of training adaptation. Sports Med 37:737–763
Daussin FN, Zoll J, Dufour SP, Ponsot E, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Doutreleau S, Mettauer B, Piquard F, Geny B, Richard R (2008) Effect of interval versus continuous training on cardiorespiratory and mitochondrial functions: relationship to aerobic performance improvements in sedentary subjects. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R264–R272
De Filippis E, Alvarez G, Berria R, Cusi K, Everman S, Meyer C, Mandarino LJ (2008) Insulin-resistant muscle is exercise resistant: evidence for reduced response of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes to exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:E607–E614
Egan B, Carson BP, Garcia-Roves PM, Chibalin AV, Sarsfield FM, Barron N, McCaffrey N, Moyna NM, Zierath JR, O’Gorman DJ (2010) Exercise intensity-dependent regulation of PGC-1{alpha} mRNA abundance is associated with differential activation of upstream signalling kinases in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 588(Pt 10):1779–1790
Gibala MJ, Little JP, van Essen M, Wilkin GP, Burgomaster KA, Safdar A, Raha S, Tarnopolsky MA (2006) Short-term sprint interval versus traditional endurance training: similar initial adaptations in human skeletal muscle and exercise performance. J Physiol 575:901–911
Gibala MJ, McGee SL, Garnham AP, Howlett KF, Snow RJ, Hargreaves M (2009) Brief intense interval exercise activates AMPK and p38MAPK signaling and increases the expression of PGC-1alpha in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 106:929–934
Gleyzer N, Vercauteren K, Scarpulla RC (2005) Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1 M and TFB2 M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 25:1354–1366
Hancock CR, Han DH, Chen M, Terada S, Yasuda T, Wright DC, Holloszy JO (2008) High-fat diets cause insulin resistance despite an increase in muscle mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7815–7820
Helgerud J, Hoydal K, Wang E, Karlsen T, Berg P, Bjerkaas M, Simonsen T, Helgesen C, Hjorth N, Bach R, Hoff J (2007) Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve VO2max more than moderate training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:665–671
Hellsten Y, Nielsen JJ, Lykkesfeldt J, Bruhn M, Silveira L, Pilegaard H, Bangsbo J (2007) Antioxidant supplementation enhances the exercise-induced increase in mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA content in human skeletal muscle. Free Radic Biol Med 43:353–361
Holloszy JO (1967) Biochemical adaptations in muscle. Effects of exercise on mitochondrial oxygen uptake and respiratory enzyme activity in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 242:2278–2282
Holloszy JO (2008) Regulation by exercise of skeletal muscle content of mitochondria and GLUT4. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 7):5–18
Irrcher I, Adhihetty PJ, Joseph AM, Ljubicic V, Hood DA (2003) Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle by endurance exercise. Sports Med 33:783–793
Jager S, Handschin C, St-Pierre J, Spiegelman BM (2007) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12017–12022
Kanki T, Ohgaki K, Gaspari M, Gustafsson CM, Fukuoh A, Sasaki N, Hamasaki N, Kang D (2004) Architectural role of mitochondrial transcription factor A in maintenance of human mitochondrial DNA. Mol Cell Biol 24:9823–9834
Kramer DK, Ahlsen M, Norrbom J, Jansson E, Hjeltnes N, Gustafsson T, Krook A (2006) Human skeletal muscle fibre type variations correlate with PPAR alpha, PPAR delta and PGC-1 alpha mRNA. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 188:207–216
Kubukeli ZN, Noakes TD, Dennis SC (2002) Training techniques to improve endurance exercise performances. Sports Med 32:489–509
Kuhl JE, Ruderman NB, Musi N, Goodyear LJ, Patti ME, Crunkhorn S, Dronamraju D, Thorell A, Nygren J, Ljungkvist O, Degerblad M, Stahle A, Brismar TB, Andersen KL, Saha AK, Efendic S, Bavenholm PN (2006) Exercise training decreases the concentration of malonyl-CoA and increases the expression and activity of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase in human muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1296–E1303
Laursen PB, Shing CM, Peake JM, Coombes JS, Jenkins DG (2002) Interval training program optimization in highly trained endurance cyclists. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:1801–1807
Laursen PB, Shing CM, Peake JM, Coombes JS, Jenkins DG (2005) Influence of high-intensity interval training on adaptations in well-trained cyclists. J Strength Cond Res 19:527–533
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Luquet S, Lopez-Soriano J, Holst D, Fredenrich A, Melki J, Rassoulzadegan M, Grimaldi PA (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta controls muscle development and oxidative capability. FASEB J 17:2299–2301
Mathai AS, Bonen A, Benton CR, Robinson DL, Graham TE (2008) Rapid exercise-induced changes in PGC-1alpha mRNA and protein in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 105:1098–1105
Mortensen OH, Plomgaard P, Fischer CP, Hansen AK, Pilegaard H, Pedersen BK (2007) PGC-1beta is downregulated by training in human skeletal muscle: no effect of training twice every second day vs. once daily on expression of the PGC-1 family. J Appl Physiol 103:1536–1542
Narkar VA, Downes M, Yu RT, Embler E, Wang YX, Banayo E, Mihaylova MM, Nelson MC, Zou Y, Juguilon H, Kang H, Shaw RJ, Evans RM (2008) AMPK and PPARdelta agonists are exercise mimetics. Cell 134:405–415
Nordsborg NB, Lundby C, Leick L, Pilegaard H (2010) Relative workload determines exercise induced increases in PGC-1alpha mRNA. Med Sci Sports Exerc. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181d2d21c
Norrbom J, Sundberg CJ, Ameln H, Kraus WE, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2004) PGC-1alpha mRNA expression is influenced by metabolic perturbation in exercising human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 96:189–194
Padilla S, Mujika I, Orbananos J, Angulo F (2000) Exercise intensity during competition time trials in professional road cycling. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:850–856
Pilegaard H, Ordway GA, Saltin B, Neufer PD (2000) Transcriptional regulation of gene expression in human skeletal muscle during recovery from exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E806–E814
Pilegaard H, Saltin B, Neufer PD (2003) Exercise induces transient transcriptional activation of the PGC-1alpha gene in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 546:851–858
Pilegaard H, Osada T, Andersen LT, Helge JW, Saltin B, Neufer PD (2005) Substrate availability and transcriptional regulation of metabolic genes in human skeletal muscle during recovery from exercise. Metabolism 54:1048–1055
Rantanen A, Jansson M, Oldfors A, Larsson NG (2001) Downregulation of Tfam and mtDNA copy number during mammalian spermatogenesis. Mamm Genome 12:787–792
Russell AP, Feilchenfeldt J, Schreiber S, Praz M, Crettenand A, Gobelet C, Meier CA, Bell DR, Kralli A, Giacobino JP, Deriaz O (2003) Endurance training in humans leads to fiber type-specific increases in levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 52:2874–2881
Russell AP, Hesselink MK, Lo SK, Schrauwen P (2005) Regulation of metabolic transcriptional co-activators and transcription factors with acute exercise. FASEB J 19:986–988
Scarpulla RC (2008) Nuclear control of respiratory chain expression by nuclear respiratory factors and PGC-1-related coactivator. Ann NY Acad Sci 1147:321–334
Short KR, Vittone JL, Bigelow ML, Proctor DN, Rizza RA, Coenen-Schimke JM, Nair KS (2003) Impact of aerobic exercise training on age-related changes in insulin sensitivity and muscle oxidative capacity. Diabetes 52:1888–1896
Stepto NK, Hawley JA, Dennis SC, Hopkins WG (1999) Effects of different interval-training programs on cycling time-trial performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:736–741
Stepto NK, Coffey VG, Carey AL, Ponnampalam AP, Canny BJ, Powell D, Hawley JA (2009) Global gene expression in skeletal muscle from well-trained strength and endurance athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:546–565
Talmadge RJ, Roy RR (1993) Electrophoretic separation of rat skeletal muscle myosin heavy-chain isoforms. J Appl Physiol 75:2337–2340
Tarnopolsky MA, Rennie CD, Robertshaw HA, Fedak-Tarnopolsky SN, Devries MC, Hamadeh MJ (2007) Influence of endurance exercise training and sex on intramyocellular lipid and mitochondrial ultrastructure, substrate use, and mitochondrial enzyme activity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R1271–R1278
Terada S, Tabata I (2004) Effects of acute bouts of running and swimming exercise on PGC-1alpha protein expression in rat epitrochlearis and soleus muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286:E208–E216
Tonkonogi M, Sahlin K (1997) Rate of oxidative phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria from human skeletal muscle: effect of training status. Acta Physiol Scand 161:345–353
Tonkonogi M, Walsh B, Svensson M, Sahlin K (2000) Mitochondrial function and antioxidative defence in human muscle: effects of endurance training and oxidative stress. J Physiol 528(Pt 2):379–388
Wacker MJ, Tehel MM, Gallagher PM (2008) Technique for quantitative RT-PCR analysis directly from single muscle fibers. J Appl Physiol 105:308–315
Wang YX, Zhang CL, Yu RT, Cho HK, Nelson MC, Bayuga-Ocampo CR, Ham J, Kang H, Evans RM (2004) Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARdelta. PLoS Biol 2:e294
Wang L, Psilander N, Tonkonogi M, Ding S, Sahlin K (2009) Similar expression of oxidative genes after interval and continuous exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:2136–2144
Watt MJ, Southgate RJ, Holmes AG, Febbraio MA (2004) Suppression of plasma free fatty acids upregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and delta and PPAR coactivator 1alpha in human skeletal muscle, but not lipid regulatory genes. J Mol Endocrinol 33:533–544
Wu Z, Puigserver P, Andersson U, Zhang C, Adelmant G, Mootha V, Troy A, Cinti S, Lowell B, Scarpulla RC, Spiegelman BM (1999) Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98:115–124
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by grants from the Swedish Research Council (project 20654), the Swedish National Centre for Research in Sport, and GIH, the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences. The authors wish to sincerely thank all of our subjects participating in this study and Magnus Knutsson and Charlotte Schönbeck for their helpful assistance. None of the authors had any potential financial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan Ward.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1581-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niklas, P., Li, W., Jens, W. et al. Mitochondrial gene expression in elite cyclists: effects of high-intensity interval exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 110, 597–606 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1544-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1544-1