Abstract
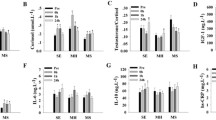
Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) in the circulation are thought to modulate the activation of growth factors, cytokines, and angiogenesis, facilitating physiological adaptations to exercise training. The purpose of this work was to characterize serum MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9 concentrations pre- and post-eight weeks of exercise training. We tested the hypothesis that exercise training would influence serum MMP concentrations in response to an acute resistance exercise test (ARET). Participants were randomized into an 8-week training program (5 days per week) that emphasized callisthenic (CT, N = 8) or resistance (RT, N = 8) exercise. Serum MMP concentrations (MMP-1, -2, -3, -9) were assessed in men (N = 16) in response to an acute bout of high-intensity resistance exercise (six sets of 10-RM squats with 2-min inter-set rest periods) both before and after 8 weeks of training. Training resulted in a temporal shift in the peak MMP-1 concentration from post-ARET to mid-ARET in both groups. Post-training, MMP-9 concentrations were increased immediately after the ARET in the CT group as compared to pre-training ARET concentrations. RT did not alter MMP-3 and -9 concentrations. These data suggest that the mode of exercise training influences the MMP response to an acute bout of exercise, revealing a possible role of MMPs in initiating training-specific adaptations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACSM (2005) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Carmeli E, Moas M, Lennon S, Powers SK (2005) High intensity exercise increases expression of matrix metalloproteinases in fast skeletal muscle fibres. Exp Physiol 90:613–619. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2004.029462
Carmeli E, Haimovitz T, Nemcovsky EC (2007) Cathepsin D and MMP-9 activity increase following a high intensity exercise in hind limb muscles of young rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 18:79–86
Coppock HA, White A, Aplin JD, Westwood M (2004) Matrix metalloprotease-3 and -9 proteolyze insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. Biol Reprod 71:438–443. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.103.023101
Fowlkes JL, Thrailkill KM, Serra DM, Suzuki K, Nagase H (1995) Matrix metalloproteinases as insulin-like growth factor binding protein-degrading proteinases. Prog Growth Factor Res 6:255–263. doi:10.1016/0955-2235(95)00017-8
Fowlkes JL, Serra DM, Bunn RC, Thrailkill KM, Enghild JJ, Nagase H (2004) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I action by matrix metalloproteinase-3 involves selective disruption of IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 complexes. Endocrinology 145:620–626. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0636
Giannelli G, De Marzo A, Marinosci F, Antonaci S (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase imbalance in muscle disuse atrophy. Histol Histopathol 20:99–106
Harman EA, Gutekunst DJ, Frykman PN, Nindl BC, Alemany JA, Mello RP, Sharp MA (2008) Effects of two different eight-week training programs on military physical performance. J Strength Cond Res Natl Strength Cond Assoc 22:524–534
Hashimoto G, Inoki I, Fujii Y, Aoki T, Ikeda E, Okada Y (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases cleave connective tissue growth factor and reactivate angiogenic activity of vascular endothelial growth factor 165. J Biol Chem 277:36288–36295. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201674200
Heinemeier KM, Olesen JL, Haddad F, Langberg H, Kjaer M, Baldwin KM, Schjerling P (2007) Expression of collagen and related growth factors in rat tendon and skeletal muscle in response to specific contraction types. J Physiol 582:1303–1316. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.127639
Kai H, Ikeda H, Yasukawa H, Kai M, Seki Y, Kuwahara F, Ueno T, Sugi K, Imaizumi T (1998) Peripheral blood levels of matrix metalloproteases-2 and -9 are elevated in patients with acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:368–372. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00250-2
Kasahara A, Hayashi N, Mochizuki K, Oshita M, Katayama K, Kato M, Masuzawa M, Yoshihara H, Naito M, Miyamoto T, Inoue A, Asai A, Hijioka T, Fusamoto H, Kamada T (1997) Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 as serum markers of fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Relationship to interferon response. J Hepatol 26:574–583. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(97)80423-0
Kjaer M (2004) Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading. Physiol Rev 84:649–698. doi:10.1152/physrev.00031.2003
Koskinen SO, Hoyhtya M, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Martikkala V, Makinen TT, Oksa J, Rintamaki H, Lofberg M, Somer H, Takala TE (2001) Serum concentrations of collagen degrading enzymes and their inhibitors after downhill running. Scand J Med Sci Sports 11:9–15. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0838.2001.011001009.x
Mackey AL, Donnelly AE, Swanton A, Murray F, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T (2006) The effects of impact and non-impact exercise on circulating markers of collagen remodelling in humans. J Sports Sci 24:843–848. doi:10.1080/02640410500231470
Nakamura M, Miyamoto S, Maeda H, Ishii G, Hasebe T, Chiba T, Asaka M, Ochiai A (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-7 degrades all insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and facilitates insulin-like growth factor bioavailability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:1011–1016. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.010
Nishimura T, Nakamura K, Kishioka Y, Kato-Mori Y, Wakamatsu J, Hattori A (2008) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases suppresses the migration of skeletal muscle cells. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 29:37–44. doi:10.1007/s10974-008-9140-2
Pierce JR, Tuckow AP, Alemany JA, Rarick KR, Staab JS, Harman EA, Nindl BC (2009) Effects of acute and chronic exercise on disulfide-linked growth hormone variants. Med Sci Sports Exerc, pp 581–587. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e31818c6d93
Ribbens C, Martin y Porras M, Franchimont N, Kaiser MJ, Jaspar JM, Damas P, Houssiau FA, Malaise MG (2002) Increased matrix metalloproteinase-3 serum levels in rheumatic diseases: relationship with synovitis and steroid treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 61:161–166. doi:10.1136/ard.61.2.161
Roberts CK, Won D, Pruthi S, Kurtovic S, Sindhu RK, Vaziri ND, Barnard RJ (2006) Effect of a short-term diet and exercise intervention on oxidative stress, inflammation, MMP-9, and monocyte chemotactic activity in men with metabolic syndrome factors. J Appl Physiol 100:1657–1665. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01292.2005
Rullman E, Rundqvist H, Wagsater D, Fischer H, Eriksson P, Sundberg CJ, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2007) A single bout of exercise activates matrix metalloproteinase in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 102:2346–2351. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00822.2006
Saenz AJ, Lee-Lewandrowski E, Wood MJ, Neilan TG, Siegel AJ, Januzzi JL, Lewandrowski KB (2006) Measurement of a plasma stroke biomarker panel and cardiac troponin T in marathon runners before and after the 2005 Boston marathon. Am J Clin Pathol 126:185–189. doi:10.1309/D7QUF0HJMCYYYY5A
Suhr F, Brixius K, de Marees M, Bolck B, Kleinoder H, Achtzehn S, Bloch W, Mester J (2007) Effects of short-term vibration and hypoxia during high-intensity cycling exercise on circulating levels of angiogenic regulators in humans. J Appl Physiol 103:474–483. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01160.2006
Tayebjee MH, Lip GY, Blann AD, Macfadyen RJ (2005) Effects of age, gender, ethnicity, diurnal variation and exercise on circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and -9, and their inhibitors, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP)-1 and -2. Thromb Res 115:205–210. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2004.08.023
Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92:827–839. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000070112.80711.3D
Volkov NI, Shirkovets EA, Borilkevich VE (1975) Assessment of aerobic and anaerobic capacity of athletes in treadmill running tests. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 34:121–130. doi:10.1007/BF00999924
Woessner JF Jr (1991) Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J 5:2145–2154
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author(s) and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the Army or the Department of Defense. Citations of commercial organizations and trade names in this report do not constitute an official Department of the Army endorsement or approval of the products or services of these organizations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urso, M.L., Pierce, J.R., Alemany, J.A. et al. Effects of exercise training on the matrix metalloprotease response to acute exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 106, 655–663 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1063-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1063-0