Abstract
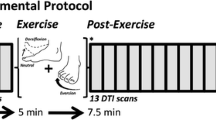
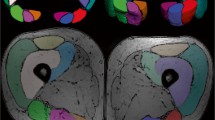
The aim of this study was to examine the diffusive properties of adjacent muscles at rest, and to determine the relationship between diffusive and architectural properties, which are task-specific to muscles. The principle, second, and third eigenvalues, trace of the diffusion tensor, and two anisotropic parameters, ellipsoid eccentricity (e) and fractional anisotropy (FA), of various muscles in the human calf were calculated by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Linear correlations of the calculated parameters to the muscle physiological cross-sectional area (PCSA), which is proportional to maximum muscle force, were performed to ascertain any linear relation between muscle architecture and diffusivity. Images of the left calf were acquired from six healthy male volunteers. Seven muscles were investigated in this study. These comprised the soleus, lateral gastrocnemius, medial gastrocnemius, posterior tibialis, anterior tibialis, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneus longus. All data were presented as the mean and standard error of the mean (SEM). In general, differences in diffusive parameter values occurred primarily between functionally different muscles. A strong correlation was also found between PCSA and the third eigenvalue, e, and FA. A mathematical derivation revealed a linear relationship between PCSA and the third eigenvalue as a result of their dependence on the average radius of all fibers within a single muscle. These findings demonstrated the ability of DTI to differentiate between functionally different muscles in the same region of the body on the basis of their diffusive properties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JL (2003) Muscle fibre type adaptation in the elderly human muscle. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13:40–47
Basser PJ, Jones DK (2002) Diffusion-tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:456–467
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1998) A simplified method to measure the diffusion tensor from seven MR images. Magn Reson Med 39:928–934
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66:259–267
Basser PJ, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C, Duda J, Aldroubi A (2000) In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn Reson Med 44:625–632
Bassett DR Jr (2002) Scientific contributions of A. V. Hill: exercise physiology pioneer. J Appl Physiol 93:1567–1582
Belton PS, Jackson RR, Packer KJ (1972) Pulsed NMR studies of water in striated muscle. I. Transverse nuclear spin relaxation times and freezing effects. Biochim Biophys Acta 286:16–25
Bonny JM, Renou JP (2002) Water diffusion features as indicators of muscle structure ex vivo. Magn Reson Imaging 20:395–400
Campos GE, Luecke TJ, Wendeln HK, Toma K, Hagerman FC, Murray TF, Ragg KE, Ratamess NA, Kraemer WJ, Staron RS (2002) Muscular adaptations in response to three different resistance-training regimens: specificity of repetition maximum training zones. Eur J Appl Physiol 88:50–60
Cercignani M, Horsfield MA, Agosta F, Filippi M (2003) Sensitivity-encoded diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1254–1256
Chow RS, Medri MK, Martin DC, Leekam RN, Agur AM, McKee NH (2000) Sonographic studies of human soleus and gastrocnemius muscle architecture: gender variability. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:236–244
Damon BM, Ding Z, Anderson AW, Freyer AS, Gore JC (2002) Validation of diffusion tensor MRI-based muscle fiber tracking. Magn Reson Med 48:97–104
Fukunaga T, Kawakami Y, Kuno S, Funato K, Fukashiro S (1997) Muscle architecture and function in humans. J Biomech 30:457–463
Gibbs SJ (1997) Observations of diffusive diffraction in a cylindrical pore by PFG NMR. J Magn Reson 124:223–226
Gosker HR, Wouters EF, van der Vusse GJ, Schols AM (2000) Skeletal muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic heart failure: underlying mechanisms and therapy perspectives. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1033–1047
Hsu EW, Muzikant AL, Matulevicius SA, Penland RC, Henriquez CS (1998) Magnetic resonance myocardial fiber-orientation mapping with direct histological correlation. Am J Physiol 274:H1627–H1634
Hsu EW, Buckley DL, Bui JD, Blackband SJ, Forder JR (2001) Two-component diffusion tensor MRI of isolated perfused hearts. Magn Reson Med 45:1039–1045
Jaermann T, Crelier G, Pruessmann KP, Golay X, Netsch T, van Muiswinkel AM, Mori S, van Zijl PC, Valavanis A, Kollias S, Boesiger P (2004) SENSE-DTI at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 51:230–236
Jarvinen TA, Jozsa L, Kannus P, Jarvinen TL, Jarvinen M (2002) Organization and distribution of intramuscular connective tissue in normal and immobilized skeletal muscles. An immunohistochemical, polarization and scanning electron microscopic study. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23:245–254
Jones DK, Horsfield MA, Simmons A (1999a) Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 42:515–525
Jones DK, Simmons A, Williams SC, Horsfield MA (1999b) Non-invasive assessment of axonal fiber connectivity in the human brain via diffusion tensor MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:37–41
Kawakami Y, Muraoka Y, Kubo K, Suzuki Y, Fukunaga T (2000) Changes in muscle size and architecture following 20 days of bed rest. J Gravit Physiol 7:53–59
Kawakami Y, Akima H, Kubo K, Muraoka Y, Hasegawa H, Kouzaki M, Imai M, Suzuki Y, Gunji A, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2001) Changes in muscle size, architecture, and neural activation after 20 days of bed rest with and without resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:7–12
Kinsey ST, Locke BR, Penke B, Moerland TS (1999) Diffusional anisotropy is induced by subcellular barriers in skeletal muscle. NMR Biomed 12:1–7
Latour LL, Svoboda K, Mitra PP, Sotak CH (1994) Time-dependent diffusion of water in a biological model system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1229–1233
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:534–546
Lieber RL, Friden J (2000) Functional and clinical significance of skeletal muscle architecture. Muscle Nerve 23:1647–1666
Maganaris CN (2001) Force-length characteristics of in vivo human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 172:279–285
Maganaris CN (2003) Force-length characteristics of the in vivo human gastrocnemius muscle. Clin Anat 16:215–223
Mitra PP, Sen PN, Schwartz LM, Le Doussal P (1992) Diffusion propagator as a probe of the structure of porous media. Phys Rev Lett 68:3555–3558
Mori S, van Zijl PC (2002) Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:468–480
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC (1999) Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45:265–269
Napadow VJ, Chen Q, Mai V, So PT, Gilbert RJ (2001) Quantitative analysis of three-dimensional-resolved fiber architecture in heterogeneous skeletal muscle tissue using NMR and optical imaging methods. Biophys J 80:2968–2975
Poonawalla AH, Zhou XJ (2004) Analytical error propagation in diffusion anisotropy calculations. J Magn Reson Imaging 19:489–498
Powell PL, Roy RR, Kanim P, Bello MA, Edgerton VR (1984) Predictability of skeletal muscle tension from architectural determinations in guinea pig hindlimbs. J Appl Physiol 57:1715–1721
Rassier DE, MacIntosh BR, Herzog W (1999) Length dependence of active force production in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 86:1445–1457
Ries M, Jones RA, Basseau F, Moonen CT, Grenier N (2001) Diffusion tensor MRI of the human kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:42–49
Roy RR, Wilson R, Edgerton VR (1997) Architectural and mechanical properties of the rat adductor longus: response to weight-lifting training. Anat Rec 247:170–178
Staron RS, Kraemer WJ, Hikida RS, Fry AC, Murray JD, Campos GE (1999) Fiber type composition of four hindlimb muscles of adult Fisher 344 rats. Histochem Cell Biol 111:117–123
Stieltjes B, Kaufmann WE, van Zijl PC, Fredericksen K, Pearlson GD, Solaiyappan M, Mori S (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging and axonal tracking in the human brainstem. Neuroimage 14:723–735
Tseng WY, Reese TG, Weisskoff RM, Brady TJ, Wedeen VJ (2000) Myocardial fiber shortening in humans: initial results of MR imaging. Radiology 216:128–139
Tseng WY, Wedeen VJ, Reese TG, Smith RN, Halpern EF (2003) Diffusion tensor MRI of myocardial fibers and sheets: correspondence with visible cut-face texture. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:31–42
Van Donkelaar CC, Kretzers LJ, Bovendeerd PH, Lataster LM, Nicolay K, Janssen JD, Drost MR (1999) Diffusion tensor imaging in biomechanical studies of skeletal muscle function. J Anat 194:79–88
Wagenmakers AJM (2000) Muscle function in critically ill patients. Clin Nutr 20:451–454
Wedeen VJ, Reese TG, Napadow VJ, Gilbert RJ (2001) Demonstration of primary and secondary muscle fiber architecture of the bovine tongue by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Biophys J 80:1024–1028
Wickiewicz TL, Roy RR, Powell PL, Edgerton VR (1983) Muscle architecture of the human lower limb. Clin Orthop 179:275–283
Yamada K, Kizu O, Mori S, Ito H, Nakamura H, Yuen S, Kubota T, Tanaka O, Akada W, Sasajima H, Mineura K, Nishimura T (2003) Brain fiber tracking with clinically feasible diffusion-tensor MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 227:295–301
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry for Science and Research of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galbán, C.J., Maderwald, S., Uffmann, K. et al. Diffusive sensitivity to muscle architecture: a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging study of the human calf. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 253–262 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1186-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1186-2