Abstract
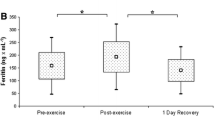
Serum soluble transferrin receptor (sTfR) has been proposed as a more stable index of iron status than serum ferritin in athletes. However, the variation in sTfR concentration during recovery from acute exercise is unknown. The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of prolonged moderate exercise on ferritin and sTfR concentrations, as well as on several hematologic variables up to 24 h post-exercise. Fifteen young, untrained men exercised on a cycle ergometer for 45 min at a heart rate of 150–155 beats min−1 and provided blood samples before as well as immediately, 6 h, and 24 h after exercise. Ferritin and sTfR values did not change significantly with time. sTfR levels exhibited lower variation during the observation period, the median intra-individual coefficient of variation being 5.2%, as opposed to 10.9% for ferritin. In conclusion, serum ferritin concentration is not affected by prolonged moderate exercise and can be used as a reliable index of iron status, at least for athletes not involved in extreme physical activities. Serum sTfR concentration seems to be more stable and could replace ferritin as the preferred index of iron stores if problems associated with the novelty of the assay were overcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volume of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Fallon KE (2001) The acute phase response and exercise: the ultramarathon as prototype exercise. Clin J Sport Med 11:38–43
Gonzalez F, Manas M, Seiquer I, Quiles J, Mataix FJ, Huertas JR, Martinez-Victoria E (1996) Blood platelet function in healthy individuals of different ages. Effects of exercise and exercise conditioning. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 36:112–116
Gray AB, Telford RD, Weidemann MJ (1993) The effect of intense interval exercise on iron status parameters in trained men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:778–782
Hoffman-Goetz L (1998) Immunocompetence in physical activity and sport. In: Wolinski I (ed) Nutrition in exercise and sport. CRC, New York, pp 645–657
Malczewska J, Blach W, Stupnicki R (2000) The effects of physical exercise on the concentrations of ferritin and transferrin receptor in plasma of female judoists. Int J Sports Med 21:175–179
Ricci G, Masotti M, De Paoli Vitali E, Vedovato M, Zanotti G (1988) Effects of exercise on haematologic parameters, serum iron, serum ferritin, red cell 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and creatine contents, and serum erythropoietin in long-distance runners during basal training. Acta Haematol 80:95–98
Schumacher YO, Schmid A, Konig D, Berg A (2002) Effects of exercise on soluble transferrin receptor and other variables of the iron status. Br J Sports Med 36:195–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolaidis, M.G., Michailidis, Y. & Mougios, V. Variation of soluble transferrin receptor and ferritin concentrations in human serum during recovery from exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 89, 500–502 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-003-0839-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-003-0839-x