Abstract
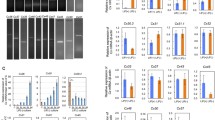
Gap junction proteins are essential for direct intercellular communication but also influence cellular differentiation and migration. The expression of various connexin gap junction proteins has been demonstrated in embryonic stem cells, with Cx43 being the most intensely studied. As Cx43 is the most prominent gap junction protein in the heart, cardiomyocyte-differentiated stem cells have been studied intensely. To date, however, little is known about the expression and the subcellular distribution of Cx43 in undifferentiated stem cells or about the structural arrangement of channels. We, therefore, here investigate expression of Cx43 in undifferentiated human cord-blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (hCBiPS2). For this purpose, we carried out quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. For analysis of Cx43 ultrastructure and protein assembly, we performed freeze-fracture replica immunogold labeling (FRIL). Cx43 expression was detected at mRNA and protein level in hCBIPS2 cells. For the first time, ultrastructural data are presented on gap junction morphology in induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells from cord blood: Our FRIL and electron microscopical analysis revealed the occurrence of gap junction plaques in undifferentiated iPS cells. In addition, these gap junctions were shown to contain the gap junction protein Cx43.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- iPSC:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- Cx43:
-
Connexin 43
- FRIL:
-
Freeze-fracture replica immunogold labeling
- hCBiPS2:
-
Human cord-blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cell clone 2
- hESC:
-
Human embryonic stem cells
References
Beckmann A, Grissmer A, Krause E, Tschernig T, Meier C (2016) Pannexin-1 channels show distinct morphology and no gap junction characteristics in mammalian cells. Cell Tiss Res 363:751–763. doi:10.1007/s00441-015-2281-x
Beyer EC, Paul DL, Goodenough DA (1987) Connexin43: a protein from rat heart homologous to a gap junction protein from liver. J Cell Biol 105:2621–2629
Branton D et al (1975) Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190:54–56
Burridge PW et al (2011) A universal system for highly efficient cardiac differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells that eliminates interline variability. PLoS ONE 6:e18293. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018293
Chen R et al (2012) Cytokine production using membrane adsorbers: human basic fibroblast growth factor produced by Escherichia coli. Eng Life Sci 12:29–38. doi:10.1002/elsc.201100045
Dyce PW, Li D, Barr KJ, Kidder GM (2014) Connexin43 is required for the maintenance of multipotency in skin-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 23:1636–1646. doi:10.1089/scd.2013.0459
Elias LA, Wang DD, Kriegstein AR (2007) Gap junction adhesion is necessary for radial migration in the neocortex. Nature 448:901–907. doi:10.1038/nature06063
Evans WH, De Vuyst E, Leybaert L (2006) The gap junction cellular internet: connexin hemichannels enter the signalling limelight. Biochem J 397:1–14. doi:10.1042/BJ20060175
Flores CE, Nannapaneni S, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Bennett MV, Rash JE, Pereda AE (2012) Trafficking of gap junction channels at a vertebrate electrical synapse in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E573–E582. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121557109
Fujimoto K (1995) Freeze-fracture replica electron microscopy combined with SDS digestion for cytochemical labeling of integral membrane proteins. Application to the immunogold labeling of intercellular junctional complexes. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 11):3443–3449
Fujimoto K (1997) SDS-digested freeze-fracture replica labeling electron microscopy to study the two-dimensional distribution of integral membrane proteins and phospholipids in biomembranes: practical procedure, interpretation and application. Histochem Cell Biol 107:87–96
Gaietta G et al (2002) Multicolor and electron microscopic imaging of connexin trafficking. Science 296:503–507. doi:10.1126/science.1068793
Haase A et al (2009) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood. Cell Stem Cell 5:434–441. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.08.021
Huang GY, Cooper ES, Waldo K, Kirby ML, Gilula NB, Lo CW (1998) Gap junction-mediated cell-cell communication modulates mouse neural crest migration. J Cell Biol 143:1725–1734
Huettner JE, Lu A, Qu Y, Wu Y, Kim M, McDonald JW (2006) Gap junctions and connexon hemichannels in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 24:1654–1667. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0003
Johnson RG et al (2012) Gap junction assembly: roles for the formation plaque and regulation by the C-terminus of connexin43. Mol Biol Cell 23:71–86. doi:10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0141
Kar R, Batra N, Riquelme MA, Jiang JX (2012) Biological role of connexin intercellular channels and hemichannels. Arch Biochem Biophys 524:2–15. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.008
Ke Q et al (2013) Connexin 43 is involved in the generation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Mol Genet 22:2221–2233. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt074
Meier C, Dermietzel R, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Rash JE (2004) Connexin32-containing gap junctions in Schwann cells at the internodal zone of partial myelin compaction and in Schmidt-Lanterman incisures. J Neurosci 24:3186–3198. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5146-03.2004
Naus CC, Aftab Q, Sin WC (2016) Common mechanisms linking connexin43 to neural progenitor cell migration and glioma invasion. Semin Cell Dev Biol 50:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.12.008
Oyamada M, Takebe K, Endo A, Hara S, Oyamada Y (2013) Connexin expression and gap-junctional intercellular communication in ES cells and iPS cells. Front Pharmacol 4:85. doi:10.3389/fphar.2013.00085
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucl Acid Res 29:e45
Rash JE, Yasumura T (1999) Direct immunogold labeling of connexins and aquaporin-4 in freeze-fracture replicas of liver, brain, and spinal cord: factors limiting quantitative analysis. Cell Tiss Res 296:307–321
Rash JE, Duffy HS, Dudek FE, Bilhartz BL, Whalen LR, Yasumura T (1997) Grid-mapped freeze-fracture analysis of gap junctions in gray and white matter of adult rat central nervous system, with evidence for a “panglial syncytium” that is not coupled to neurons. J Comp Neurol 388:265–292
Rash JE, Yasumura T, Hudson CS, Agre P, Nielsen S (1998) Direct immunogold labeling of aquaporin-4 in square arrays of astrocyte and ependymocyte plasma membranes in rat brain and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11981–11986
Rash JE, Staines WA, Yasumura T, Patel D, Furman CS, Stelmack GL, Nagy JI (2000) Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7573–7578
Rash JE, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Furman CS (2004) Freeze-fracture and immunogold analysis of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) square arrays, with models of AQP4 lattice assembly. Neuroscience 129:915–934. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.076
Robenek H, Severs NJ (2008) Recent advances in freeze-fracture electron microscopy: the replica immunolabeling technique. Biol Proced Onl 10:9–19. doi:10.1251/bpo138
Segretain D, Falk MM (2004) Regulation of connexin biosynthesis, assembly, gap junction formation, and removal. Biochim Biophys Acta 1662:3–21. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.01.007
Sohl G, Willecke K (2004) Gap junctions and the connexin protein family. Cardiovasc Res 62:228–232. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.013
Sosinsky GE, Nicholson BJ (2005) Structural organization of gap junction channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1711:99–125. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.04.001
Worsdorfer P et al (2008) Connexin expression and functional analysis of gap junctional communication in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell 26:431–439. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0482
Xu C, Inokuma MS, Denham J, Golds K, Kundu P, Gold JD, Carpenter MK (2001) Feeder-free growth of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 19:971–974. doi:10.1038/nbt1001-971
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Andrea Rabung and Alexander Grissmer for excellent technical assistance. They also thank Ann Soether for linguistic editing and Alina Mattheis for the schematic illustrations. The authors are very grateful to Prof. Dr. John E. Rash for his continuous support and expert advice on the manuscript. The authors acknowledge financial support by the German Research Foundation and the Saarland, who funded the freeze-fracture unit. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that research was done without any potential conflict of interest. No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beckmann, A., Schubert, M., Hainz, N. et al. Ultrastructural demonstration of Cx43 gap junctions in induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood. Histochem Cell Biol 146, 529–537 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1469-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1469-9