Abstract
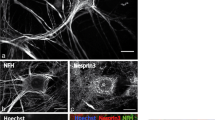
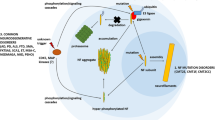
The neuronal cytoskeleton is tightly regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation reactions mediated by numerous associated kinases, phosphatases and their regulators. Defects in the relative kinase and phosphatase activities and/or deregulation of compartment-specific phosphorylation result in neurodegenerative disorders. The largest family of cytoskeletal proteins in mammalian cells is the superfamily of intermediate filaments (IFs). The neurofilament (NF) proteins are the major IFs. Aggregated forms of hyperphosphorylated tau and phosphorylated NFs are found in pathological cell body accumulations in the central nervous system of patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. The precise mechanisms for this compartment-specific phosphorylation of cytoskeletal proteins are not completely understood. In this review, we focus on the mechanisms of neurofilament phosphorylation in normal physiology and neurodegenerative diseases. We also address the recent breakthroughs in our understanding the role of different kinases and phosphatases involved in regulating the phosphorylation status of the NFs. In addition, special emphasis has been given to describe the role of phosphatases and Pin1 in phosphorylation of NFs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerley S, Grierson AJ, Banner S, Perkinton MS, Brownlees J, Byers HL, Ward M, Thornhill P, Hussain K, Waby JS, Anderton BH, Cooper JD, Dingwall C, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, Miller CC (2004) p38alpha stress-activated protein kinase phosphorylates neurofilaments and is associated with neurofilament pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 26:354–364
Angelides KJ, Smith KE, Takeda M (1989) Assembly and exchange of intermediate filament proteins of neurons: neurofilaments are dynamic structures. J Cell Biol 108:1495–1506
Bajaj NP (2000) Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 (CDK5) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:319–327
Beaulieu JM, Robertson J, Julien JP (1999) Interactions between peripherin and neurofilaments in cultured cells: disruption of peripherin assembly by the NF-M and NF-H subunits. Biochem Cell Biol 77:41–45
Bennett GS, Tapscott SJ, Kleinbart FA, Antin PB, Holtzer H (1981) Different proteins associated with 10-nanometer filaments in cultured chick neurons and nonneuronal cells. Science 212:567–569
Black MM, Lee VM (1988) Phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins in intact neurons: demonstration of phosphorylation in cell bodies and axons. J Neurosci 8:3296–3305
Böhmer F, Szedlacsek S, Tabernero L, Ostman A, den Hertog J (2013) Protein tyrosine phosphatase structure-function relationships in regulation and pathogenesis. FEBS J 280(2):413–431
Brettschneider J, Petzold A, Schottle D, Claus A, Riepe M, Tumani H (2006a) The neurofilament heavy chain (NfH) in the cerebrospinal fluid diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 21:291–295
Brettschneider J, Petzold A, Sussmuth SD, Ludolph AC, Tumani H (2006b) Axonal damage markers in cerebrospinal fluid are increased in ALS. Neurology 66:852–856
Butterfield DA, Abdul HM, Opii W, Newman SF, Joshi G, Ansari MA, Sultana R (2006) Pin1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 98(6):1697–1706
Collard JF, Cote F, Julien JP (1995) Defective axonal transport in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 375:61–64
Cote F, Collard JF, Julien JP (1993) Progressive neuronopathy in transgenic mice expressing the human neurofilament heavy gene: a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell 73:35–46
Driver JA, Lu KP (2010) Pin1: a new genetic link between Alzheimer’s disease, cancer and aging. Curr Aging Sci 3(3):158–165
Friede RL, Samorajski T (1970) Axon calibre related to neurofilaments and microtubules in sciatic nerve fibers of rats and mice. Anat Rec 167:379–388
Giasson BI, Mushynski WE (1997) Study of proline-directed protein kinases involved in phosphorylation of the heavy neurofilament subunit. J Neurosci 17:9466–9472
Goldstein ME, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA (1987) Phosphorylation protects neurofilaments against proteolysis. J Neuroimmunol 14:149–160
Gou JP, Leterrier JF (1995) Possible involvement of ubiquitination in neurofilament degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217(2):529–538
Grant P, Pant HC (2000) Neurofilament protein synthesis and phosphorylation. J Neurocytol 29(11–12):843–872
Grant P, Zheng Y, Pant HC (2006) Squid (Loligo pealei) giant fiber system: a model for studying neurodegeneration and dementia? Biol Bull 210:318–333
Hamdane M, Dourlen P, Bretteville A, Sambo AV, Ferreira S, Ando K, Kerdraon O, Bégard S, Geay L, Lippens G, Sergeant N, Delacourte A, Maurage CA, Galas MC, Buée L (2006) Pin1 allows for differential tau dephosphorylation in neuronal cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 32(1–2):155–160
Holzer M, Gartner U, Stobe A, Hartig W, Gruschka H, Bruckner MK, Arendt T (2002) Inverse association of Pin1 and tau accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol 104:471–481
Jaffe H, Sharma P, Grant P, Pant H (2001) Characterization of the phosphorylation sites of the squid (Loligo pealei) high-molecular-weight neurofilament protein from giant axon axoplasm. J Neurochem 76:1022–1031
Kesavapany S, Li BS, Amin N, Zheng YL, Grant P, Pant HC (2004) Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5: role in nervous system function and its specific inhibition by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1697(1–2):143–153
Kesavapany S, Patel V, Zheng YL, Pareek TK, Bjelogrlic M, Albers W, Amin N, Jaffe H, Gutkind JS, Strong MJ, Grant P, Pant HC (2007) Inhibition of Pin1 reduces glutamate-induced perikaryal accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilament-H in neurons. Mol Biol Cell 18(9):3645–3655
Landrieu I, Smet-Nocca C, Amniai L, Louis JV, Wieruszeski JM, Goris J, Janssens V, Lippens G (2011) Molecular implication of PP2A and Pin1 in the Alzheimer’s disease specific hyperphosphorylation of tau. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21521
Lee MK, Cleveland DW (1996) Neuronal intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:187–217
Lee MK, Marszalek JR, Cleveland DW (1994) A mutant neurofilament subunit causes massive, selective motor neuron death: implications for the pathogenesis of human motor neuron disease. Neuron 13:975–988
Liou YC, Ryo A, Huang HK, Lu PJ, Bronson R, Fujimori F, Uchida T, Hunter T, Lu KP (2002) Role of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 in protecting against age-dependent neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1335–1340
Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2005a) Contributions of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PP5 to the regulation of tau phosphorylation. Eur J Neurosci 22:1942–1950
Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Rossie S, Gong CX (2005b) Dephosphorylation of tau by protein phosphatase 5: impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 280(3):1790–1796
Liu Q, Xie F, Alvarado-Diaz A, Smith MA, Moreira PI, Zhu X, Perry G (2011) Neurofilamentopathy in neurodegenerative diseases. Open Neurol J 5:58–62
Lu PJ, Wulf G, Zhou XZ, Davies P, Lu KP (1999) The prolyl isomerase Pin1 restores the function of Alzheimer-associated phosphorylated tau protein. Nature 399:784–788
Lu KP, Liou YC, Vincent I (2003) Proline-directed phosphorylation and isomerization in mitotic regulation and in Alzheimer’s disease. BioEssays 25(2):174–181
Nguyen MD, Lariviere RC, Julien JP (2001) Deregulation of Cdk5 in a mouse model of ALS: toxicity alleviated by perikaryal neurofilament inclusions. Neuron 30:135–147
Nixon RA (1993) The regulation of neurofilament protein dynamics by phosphorylation: clues to neurofibrillary pathobiology. Brain Pathol 3:29–38
Nixon RA, Shea TB (1992) Dynamics of neuronal intermediate filaments: a developmental perspective. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 22:81–91
Nixon RA, Lewis SE, Mercken M, Sihag RK (1994) [32P]orthophosphate and [35S]methionine label separate pools of neurofilaments with markedly different axonal transport kinetics in mouse retinal ganglion cells in vivo. Neurochem Res 19:1445–1453
Pant HC (1988) Dephosphorylation of neurofilament proteins enhances their susceptibility to degradation by calpain. Biochem J 256:665–668
Pastorino L, Sun A, Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Balastik M, Finn G, Wulf G, Lim J, Li SH, Li X, Xia W, Nicholson LK, Lu KP (2006) The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates amyloid precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta production. Nature 440(7083):528–534
Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402:615–622
Pei JJ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Bogdanovic N, Winblad B, Cowburn RF (1997) Elevated protein levels of protein phosphatases PP-2A and PP-2B in astrocytes of Alzheimer’s disease temporal cortex. J Neural Transm 104(11–12):1329–1338
Pei JJ, Gong CX, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Wu QL, Winblad B, Cowburn RF (1998) Subcellular distribution of protein phosphatases and abnormally phosphorylated tau in the temporal cortex from Alzheimer’s disease and control brains. J Neural Transm 105(1):69–83
Petzold A (2005) Neurofilament phospho forms: surrogate markers for axonal injury, degeneration and loss. J Neurol Sci 233(1–2):183–198
Ramakrishnan P, Dickson DW, Davies P (2003) Pin1 colocalization with phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Neurobiol Dis 14(2):251–264
Rudrabhatla P, Pant HC (2010) Phosphorylation-specific peptidyl-prolyl isomerization of neuronal cytoskeletal proteins by Pin1: implications for therapeutics in neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 19:389–403
Rudrabhatla P, Albers W, Pant HC (2009) Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase 1 regulates protein phosphatase 2A-mediated topographic phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins. J Neurosci 29(47):14869–14880
Rudrabhatla P, Grant P, Jaffe H, Strong MJ, Pant HC (2010) Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of neuronal intermediate filament proteins (NF-M/H) in Alzheimer’s disease by iTRAQ. FASEB J 24(11):4396–4407
Rudrabhatla P, Jaffe H, Pant HC (2011) Direct evidence of phosphorylated neuronal intermediate filament proteins in neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs): phosphoproteomics of Alzheimer’s NFTs. FASEB J 25(11):3896–3905
Ryo A, Togo T, Nakai T, Hirai A, Nishi M, Yamaguchi A, Suzuki K, Hirayasu Y, Kobayashi H, Perrem K, Liou YC, Aoki I (2006) The prolyl-isomerase Pin1 accumulates in the Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease and facilitates the formation of alpha-synuclein inclusions. J Biol Chem 281:4117–4125
Shea TB, Zheng YL, Ortiz D, Pant HC (2004a) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 increases perikaryal neurofilament phosphorylation and inhibits neurofilament axonal transport in response to oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res 76:795–800
Shea TB, Yabe JT, Ortiz D, Pimenta A, Loomis P, Goldman RD, Amin N, Pant HC (2004b) Cdk5 regulates axonaltransport and phosphorylation of neurofilaments in cultured neurons. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 6):933–941
Shea TB, Chan WK, Kushkuley J, Lee S (2009) Organizational dynamics, functions, and pathobiological dysfunctions of neurofilaments. Results Probl Cell Differ 48:29–45
Shetty KT, Link WT, Pant HC (1993) cdc2-like kinase from rat spinal cord specifically phosphorylates KSPXK motifs in neurofilament proteins: isolation and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6844–6848
Sihag RK, Inagaki M, Yamaguchi T, Shea TB, Pant HC (2007) Role of phosphorylation on the structural dynamics and function of types III and IV intermediate filaments. Exp Cell Res 313:2098–2109
Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Ulrich J (1985) Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4274–4276
Strack S, Westphal RS, Colbran RJ, Ebner FF, Wadzinski BE (1997) Protein serine/threonine phosphatase 1 and 2A associate with and dephosphorylate neurofilaments. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 49(1–2):15–28
Sundaram JR, Poore CP, Sulaimee NH, Pareek T, Asad AB, Rajkumar R, Cheong WF, Wenk MR, Dawe GS, Chuang KH, Pant HC, Kesavapany S (2013). Specific inhibition of p25/Cdk5 activity by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces neurodegeneration in vivo. J Neurosci 33(1):334–343
Tortarolo M, Veglianese P, Calvaresi N, Botturi A, Rossi C, Giorgini A, Migheli A, Bendotti C (2003) Persistent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis correlates with disease progression. Mol Cell Neurosci 23:180–192
Toyoshima I, Kato K, Sugawara M, Wada C, Masamune O (1998) Kinesin accumulation in chick spinal axonal swellings with beta, beta’-iminodipropionitrile (IDPN) intoxication. Neurosci Lett 249:103–106
Veeranna S, Shetty KT, Link WT, Jaffe H, Wang J, Pant HC (1995) Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase-5 phosphorylation sites in neurofilament protein (NF-H) are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A. J Neurochem 64:2681–2690
Veeranna S, Amin ND, Ahn NG, Jaffe H, Winters CA, Grant P, Pant HC (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1, 2) phosphorylate Lys-Ser-Pro (KSP) repeats in neurofilament proteins NF-H and NF-M. J Neurosci 18(11):4008–40021
Veeranna S, Shetty KT, Takahashi M, Grant P, Pant HC (2000) Cdk5 and MAPK are associated with complexes of cytoskeletal proteins in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76:229–236
Veeranna S, Yang DS, Lee JH, Vinod KY, Stavrides P, Amin ND, Pant HC, Nixon RA (2011) Declining phosphatases underlie aging-related hyperphosphorylation of neurofilaments. Neurobiol Aging 32(11):2016–2029
Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Schuck T, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2001) PP2A mRNA expression is quantitatively decreased in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Exp Neurol 168(2):402–412
Xiao S, McLean J, Robertson J (2006) Neuronal intermediate filaments and ALS: a new look at an old question. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:1001–1012
Xu Z, Cork LC, Griffin JW, Cleveland DW (1993) Increased expression of neurofilament subunit NF-L produces morphological alternations that resemble the pathology of human motor neuron disease. Cell 73:23–33
Xu Z, Dong DL, Cleveland DW (1994) Neuronal intermediate filaments: new progress on an old subject. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4:655–661
Yuan A, Rao MV, Sasaki T, Chen Y, Kumar A, Veeranna LRK, Eyer J, Peterson AC, Julien JP, Nixon RA (2006) Alphainternexin is structurally and functionally associated with the neurofilament triplet proteins in the mature CNS. J Neurosci 26:10006–10019
Zheng YL, Li BS, Veeranna S, Pant HC (2003) Phosphorylation of the head domain of neurofilament protein (NF-M): a factor regulating topographic phosphorylation of NF-M tail domain KSP sites in neurons. J Biol Chem 278:24026–24032
Zheng YL, Kesavapany S, Gravell M, Hamilton RS, Schubert M, Amin N, Albers W, Grant P, Pant HC (2005) A Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in neurons. EMBO J 24(1):209–220
Zhou J, Wang H, Feng Y, Chen J (2010) Increased expression of cdk5/p25 in N2a cells leads to hyperphosphorylation and impaired axonal transport of neurofilament proteins. Life Sci 86:532–537
Zhu Q, Couillard-Despre′s S, Julien J-P (1997) Delayed maturation of regenerating myelinated axons in mice lacking neurofilaments. Exp Neurol 148:299–316
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Programs of the NIH, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binukumar, B.K., Shukla, V., Amin, N.D. et al. Topographic regulation of neuronal intermediate filaments by phosphorylation, role of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase 1: significance in neurodegeneration. Histochem Cell Biol 140, 23–32 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1108-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1108-7