Abstract
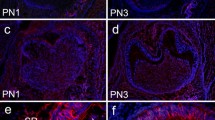
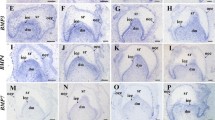
The pattern of gene expression for extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) was revealed in the tooth germ of mouse mandibular molars using quantitative real-time PCR. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical study demonstrated the characteristic distribution of EMMPRIN in the different stages of tooth germ development. To investigate the functional role played by EMMPRIN in tooth germ development, EMMPRIN siRNA interference approach was carried out in cultured mouse mandibles at embryonic day 11.0 (E11.0). The results showed that EMMPRIN siRNA-treated explants exhibited a marked growth inhibition of tooth germ compared to the control and scrambled siRNA-treated explants. Meanwhile, a significant increase in MT1-MMP mRNA expression and a reduction in MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13 and MT2-MMP mRNA expression were observed in the mouse mandibles following EMMPRIN abrogation. The current results indicate that EMMPRIN could thus be involved in the early stage of tooth germ development and morphogenesis, possibly by regulating the expression of MMP genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berditchevski F, Chang S, Bodorova J, Hemler ME (1997) Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin associated proteins. Evidence that alpha3beta1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J Biol Chem 272:29174–29180
Biswas C, Nugent MA (1987) Membrane association of collagenase stimulatory factor(s) from B-16 melanoma cells. J Cell Biochem 35:247–258
Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K (1995) The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 55:434–439
Cao Z, Xiang J, Li C (2009) Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer and enhancement of the production of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:880–885
Chen L, Nakai M, Belton RJ Jr, Nowak RA (2007) Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer and matrix metalloproteinases during mouse embryonic development. Reproduction 133:405–414
Cobourne MT (1999) The genetic control of early odontogenesis. Br J Orthod 26:21–28
Egawa N, Koshikawa N, Tomari T, Nabeshima K, Isobe T, Seiki M (2006) Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP/MMP-14) cleaves and releases a 22-kDa extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) fragment from tumor cells. J Biol Chem 281:37576–37585
Ellis SM, Nabeshima K, Biswas C (1989) Monoclonal antibody preparation and purification of a tumor cell collagenase-stimulatory factor. Cancer Res 49:3385–3391
Goldberg M, Septier D, Bourd K, Hall R, George A, Goldberg H, Menashi S (2003) Immunohistochemical localization of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 in the forming rat incisor. Connect Tissue Res 44:143–153
Guo H, Zucker S, Gordon MK, Toole BP, Biswas C (1997) Stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase production by recombinant extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer from transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem 272:24–27
Guo H, Majmudar G, Jensen TC, Biswas C, Toole BP, Gordon MK (1998) Characterization of the gene for human EMMPRIN, a tumor cell surface inducer of matrix metalloproteinases. Gene 220:99–108
Hanata K, Yamaguchi N, Yoshikawa K, Mezaki Y, Miura M, Suzuki S, Senoo H, Ishikawa K (2007) Soluble EMMPRIN (extra-cellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) stimulates the migration of HEp-2 human laryngeal carcinoma cells, accompanied by increased MMP-2 production in fibroblasts. Arch Histol Cytol 70:267–277
Hori K, Katayama N, Kachi S, Kondo M, Kadomatsu K, Usukura J, Muramatsu T, Mori S, Miyake Y (2000) Retinal dysfunction in basigin deficiency. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3128–3133
Huang Z, Wang C, Wei L, Wang J, Fan Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Chen T (2008) Resveratrol inhibits EMMPRIN expression via P38 and ERK1/2 pathways in PMA-induced THP-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:517–521
Igakura T, Kadomatsu K, Taguchi O, Muramatsu H, Kaname T, Miyauchi T, Yamamura K, Arimura K, Muramatsu T (1996) Roles of basigin, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, in behavior as to an irritating odor, lymphocyte response, and blood-brain barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 224:33–36
Igakura T, Kadomatsu K, Kaname T, Muramatsu H, Fan QW, Miyauchi T, Toyama Y, Kuno N, Yuasa S, Takahashi M, Senda T, Taguchi O, Yamamura K, Arimura K, Muramatsu T (1998) A null mutation in basigin, an immunoglobulin superfamily member, indicates its important roles in peri-implantation development and spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 194:152–165
Jo Y, Yeon J, Kim HJ, Lee ST (2000) Analysis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 effect on pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase using baculovirus/insect-cell expression system. Biochem J 3:511–519
Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T (2002) Basigin (CD147) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer 99:520–528
Kataoka H, DeCastro R, Zucker S, Biswas C (1993) Tumor cell-derived collagenase-stimulatory factor increases expression of interstitial collagenase, stromelysin, and 72-kDa gelatinase. Cancer Res 53:3154–3158
Kirk P, Wilson MC, Heddle C, Brown MH, Barclay AN, Halestrap AP (2000) CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 facilitates their cell surface expression. EMBO J 19:3896–3904
Kirsch AH, Diaz LA Jr, Bonish B, Antony PA, Fox DA (1997) The pattern of expression of CD147/neurothelin during human T-cell ontogeny as defined by the monoclonal antibody 8D6. Tissue Antigens 50:147–152
Lelongt B, Trugnan G, Murphy G, Ronco PM (1997) Matrix metalloproteinases MMP2 and MMP9 are produced in early stages of kidney morphogenesis but only MMP9 is required for renal organogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol 136:1363–1373
Li R, Huang L, Guo H, Toole BP (2001) Basigin (murine EMMPRIN) stimulates matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 186:371–379
Li H, Cui D, Tong X, Ma N, Gao Y, Cui X, Lu L, Wang D, Liang Y (2002) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in extracellular matrix remodelling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rat models. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 41:393–398
Mina M, Kollar EJ (1987) The induction of odontogenesis in non-dental mesenchyme combined with early murine mandibular arch epithelium. Arch Oral Biol 32:123–127
Sameshima T, Nabeshima K, Toole BP, Yokogami K, Okada Y, Goya T, Koono M, Wakisaka S (2000) Glioma cell extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) (CD147) stimulates production of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases and activated gelatinase A in co-cultures with brain-derived fibroblasts. Cancer Lett 157:177–184
Schwab W, Harada H, Goetz W, Nowicki M, Witt M, Kasper M, Barth K (2007) Immunocytochemical and biochemical detection of EMMPRIN in the rat tooth germ: differentiation-dependent co-expression with MMPs and co-localization with caveolin-1 in membrane rafts of dental epithelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 128:195–203
Sun J, Hemler ME (2001) Regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-2 production through CD147/extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer interactions. Cancer Res 61:2276–2281
Tang W, Chang SB, Hemler ME (2004a) Links between CD147 function, glycosylation, and caveolin-1. Mol Biol Cell 15:4043–4050
Tang Y, Kesavan P, Nakada MT, Yan L (2004b) Tumor-stroma interaction: positive feedback regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) expression and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent generation of soluble EMMPRIN. Mol Cancer Res 2:73–80
Taylor PM, Woodfield RJ, Hodgkin MN, Pettitt TR, Martin A, Kerr DJ, Wakelam MJ (2002) Breast cancer cell-derived EMMPRIN stimulates fibro-blast MMP2 release through a phospholipase A(2) and 5-lipoxygenase catalyzed pathway. Oncogene 21:5765–5772
Yurchenko V, Pushkarsky T, Li JH, Dai WW, Sherry B, Bukrinsky M (2005) Regulation of CD147 cell surface expression: involvement of the proline residue in the CD147 transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem 280:17013–17019
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30900848), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (Grant No. 09DZ2271100), Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Grant No. T0202), Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (Grant No. 2008-0890-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Jiao, T., Chen, Y. et al. EMMPRIN (basigin/CD147) is involved in the morphogenesis of tooth germ in mouse molars. Histochem Cell Biol 133, 585–594 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0697-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0697-7