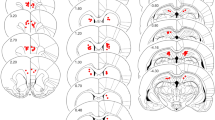
Abstract
Traumatic brain injury results in loss of neurons caused as much by the resulting neuroinflammation as by the injury. Gold salts are known to be immunosuppressive, but their use are limited by nephrotoxicity. However, as we have proven that implants of pure metallic gold release gold ions which do not spread in the body, but are taken up by cells near the implant, we hypothesize that metallic gold could reduce local neuroinflammation in a safe way. Bio-liberation, or dissolucytosis, of gold ions from metallic gold surfaces requires the presence of disolycytes i.e. macrophages and the process is limited by their number and activity. We injected 20–45 μm gold particles into the neocortex of mice before generating a cryo-injury. Comparing gold-treated and untreated cryolesions, the release of gold reduced microgliosis and neuronal apoptosis accompanied by a transient astrogliosis and an increased neural stem cell response. We conclude that bio-liberated gold ions possess pronounced anti-inflammatory and neuron-protective capacities in the brain and suggest that metallic gold has clinical potentials. Intra-cerebral application of metallic gold as a pharmaceutical source of gold ions represents a completely new medical concept that bypasses the blood-brain-barrier and allows direct drug delivery to inflamed brain tissue.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acarin L, Vela JM, Gonzkez B, Castella B (1994) Demonstration of poly-N-acetyl lactosamine residues in ameboid and ramified microglial cells in rat brain by tomato lectin binding. J Histochem Cytochem 42:1033–1041
Alvarez-Buylla A, García-Verdugo JM, Tramontin AD (2001) A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:287–293
Aktas O, Ullrich O, Infante-Duarte C, Nitsch R, Zipp F (2007) Neuronal damage in brain inflammation. Arch Neurol 64:185–189
Aschner M, Sonnewald U, Tan KH (2002) Astrocyte modulation of neurotoxicity. Brain Pathol 12:475–481
Barker RA, Widner H (2004) Immune problems in central nervous system cell therapy. Neurox 1:472–482
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E, Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozak KR, Cahill DP, Chen PJ, Zhu M, Ancukiewicz M, Mrugala MM, Plotkin S, Drappatz JT, Louis DN, Ivy P, Scaddden DT, Benner T, Wen Loefller JS, PY Jain RK (2007) AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 11:83–95
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:57–69
Bondeson J, Sundler R (1995) Auranofin inhibits the induction of interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1753–1759
Butovsky O, Talpalar AE, Ben-Yaakov K, Schwartz M (2005) Activation of microglia by aggregated beta-amyloid or lipopolysaccharide impairs MHC-II expression and renders them cytotoxic whereas IFN-gamma and IL-4 render them protective. Mol Cell Neurosci 29:381–393
Butovsky O, Ziv Y, Schwartz A, Landa G, Talpalar AE, Pluchino S, Martino G, Schwartz M (2006) Microglia activated by IL-4 or IFN-gamma differentially induce neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis from adult stem/progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 31:149–160
Cai J, Wu Y, Mirua T, Pierce JL, Lucero MT, Albertine KH, Spangrude GJ, Rao MS (2002) Properties of a fetal multipotent neural stem cell (NEP Cell). Dev Biol 251:221–240
Chang DM, Baptiste P, Schur PH (1990) The effect of antirheumatic drugs on interleukin (IL-1) activity and IL-1 and IL-1 inhibitor production by human monocytes. J Rheumatol 17:1148–1157
Das S, Basu A (2008) Inflammation: a new candidate in modulating adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci Res 86(6):1199–1208
Danscher G (1981) Localization of gold in biological tissue. A photochemical method for light and electron microscopy. Histochemistry 71:81–88
Danscher G (2002) In vivo liberation of gold ions from gold implants. Autometallographic tracing of gold in cells adjacent to metallic gold. Histochem Cell Biol 117:447–452
Danscher G, Stoltenberg M (2006) Autometallography (AMG) Silver enhancement of quantum dots resulting from (1) metabolism of toxic metals in animals and humans, (2) in vivo, in vitro and immersion created zinc-sulphur/zinc-selenium nanocrystals, (3) metal ions liberated from metal implants and particles. Prog Histochem Cytochem 41:57–139
Dheen ST, Kaur C, Ling EA (2007) Microglia activation and its implications in brain diseases. Curr Med Chem 14:1189–1197
Ekdahl CT, Claasen JH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2003) Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13632–13637
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Meenan RF (1990) The comparative efficacy and toxicity of second-line drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Results of two metaanalyses. Arthritis Rheum 34:1342–1343
Ferre N, Claria J (2006) New insight into the regulation of liver inflammation and oxidative stress. Mini Rev Med Chem 6:1321–1330
Futami T, Ohnishi H, Taguchi N, Kusakari H, Oshima H, Maeda T (2000) Tissue response to titanium implants in the rat maxilla: ultrastructural and histochemical observations of the bone-titanium interface. J Periodontol 71:287–298
Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287:1433–1438
Gilbertson RJ, Rich JW (2007) Making a tumour’s bed: glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat Rev Cancer 7:733–736
Ihrie RA, Alvarez-Buylla A (2008) Cells in the astroglial lineage are neural stem cells. Cell Tissue Res 331:179–191
Kang MK, Hur BI KOMH, Kim CH, Cha SH, Kang SK (2008) Potential identity of multi-potential cancer stem-like subpopulation after radiation of cultured brain glioma. BMC Neurosci 9:15
Koike R, Miki I, Otoshi M, Totsuki T, Inoue H, Kase H, Saito I, Miyasuka N (1994) Gold sodium thiomalate down-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression on vascular endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol 46:599–604
Larsen A, Stoltenberg M, Danscher G (2007) In vitro liberation of charged gold atoms. Autometallographic tracing of gold ions released by macrophages grown on metallic gold surfaces. Histochem Cell Biol 128:1–6
Mhatre M, Floyd RA, Hensley K (2004) Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and amylotrophic lateral sclerosis: common links and potential therapeutic targets. J Alzheimer Dis 6:147–157
Mogilnicka E, Webb M (1982) Comparative studies on the distribution of gold, copper and zinc in the livers and kidneys of rats and hamsters after treatment with sodium [195Au]-aurothiomalate. Chem Biol Interact 40:247–256
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 302:1760–1765
Morshead CM, Garcia AD, Sofroniew MV, Der Kooy D (2003) The ablation of glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive cells from the adult central nervous system results in the loss of forebrain neural stem cells but not retinal stem cells. Eur J NeuroSci 18:76–84
Myers D, Gurkoff GG, Lee GM, Hovda DA, Sofroniew MV (2006) Essential protective roles of reactive astrocytes in traumatic brain injury. Brain 129:2761–2772
Okano H, Sakaguchi M, Ohki K, Suzuki N, Sawamoto K (2007) Regeneration of the central nervous system using endogenous repair mechanisms. J Neurochem 102:1459–1465
Parent JM (2003) Injury-induced neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Neuroscientist 9:261–272
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Elsevier Science, USA
Penkowa M, Moos T (1995) Disruption of the blood-brain interface in neonatal rat neocortex induces a transient expression of metallothionein in reactive astrocytes. Glia 13:217–227
Penkowa M, Moos T, Carrasco J, Hadberg H, Molinero A, Bluethmann H, Hidalog J (1999) Strongly compromised inflammatory response to brain injury in interleukin-6 deficient mice. Glia 25:343–357
Penkowa M, Giralt M, Carrasco J, Hadberg H, Hidalgo J (2000) Impaired inflammatory response and increased oxidative stress and neurodegeneration after brain injury in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Glia 32:271–285
Penkowa M, Camats S, Hadberg H, Quintana A, Rojos S, Giralt M, Molinero A, Campelll IL, Hidalogo J (2003) Astrocyte-targeted expression of IL-6 protects the CNS against a focal brain injury. Exp Neurol 181:130–148
Penkowa M, Quintanta A, Carrasco J, Giralt M, Molinero A, Hidalgo J (2004) Methallothionein prevents neurodegeneration and central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 77:35–53
Penkowa M, Tio L, Giralt M, Quintana A, Molinero A, Atrian S, Vasak M, Hidalgo J (2006) Specificity and divergence in the neurobiological effects of different metallothioneines after brain injury. Neurosci Res 83:974–984
Persellin RH, Ziff M (1966) The effect of gold salt on lysosomal enzymes of the peritoneal macrophage. Arthritis Rheum 9:57–65
Potashkin JA, Meredith GE (2006) The role of oxidative stress in the dysregulation of gene expression and protein metabolism in neurodegenerative disease. Antoxid Redox Signal 8:144–151
Roach P, Eglin D, Rohde K, Perry CC (2007) Modern biomaterials: a review—bulk properties and implications of surface modifications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18:1263–1277
Santos E, Monzon-Mayor M, Romero-Alemán MM, Yanes C (2008) Distribution of Neurotrophin-3 during the ontogeny and regeneration of the lizard (gallotia gallot) visual system. Dev Neurobiol 68:31–44
Seifert G, Schilling K, Steinhauser C (2006) Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:194–206
Sennerby L, Thomsen P, Ericson LE (1993) Early tissue response to titanium implants inserted in rabbit cortical bone. J Mater Sci Mater Med 4:494–502
Sharma RP, McQueen EG (1981) Effects of gold sodium thiomalate on cytosolic copper and zinc in the rat kidney and liver tissues. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 8:591–599
Simard AR, Rivest S (2004) Role of inflammation in the neurobiology of stem cells. NeuroReport 15:2305–2310
Sofroniew MV (2005) Reaktive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 11:400–407
Tozman EC, Gottlieb NL (1987) Adverse reactions with oral and parenteral gold preparations. Med Toxicol 2:177–189
Turrin NP, Rivest S (2006) Molecular and cellular immune models of neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol 34:221–242
Vaccarino FM, Fagel DM, Ganat Y, Maragnoli ME, Ment LR, Ohkubu Y, Schwartz ML, Silbereis J, Smith KM (2007) Astroglial cells in development regeneration and repair. Neuroscientist 13:173–185
Van Raay TJ, Wang YK, Stark MR, Rasmussen JT, Francke U, Vetter ML, Rao MS (2001) frizzled-9 is expressed in neural precursor cells in the developing neural tube. Dev Genes Evol 211:453–457
Walton NM, Sutter BM, Laywell ED, Levkoff LH, Kearns SM, Marshall GP 2nd, Scheffler B, Steindler DA (2006) Microglia instruct subventricular zone neurogenesis. Glia 54:815–825
Yanni G, Nabil M, Farahat MR, Poston RN, Panayi GS (1994) Intramuscular gold decreases cytokine expression and macrophage numbers in the rheumatoid synovial membrane. Ann Rheum Dis 53:315–322
Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Chopp M (2005) Neurogenesis in the adult ischemic brain: generation, migration, survival, and restorative therapy. Neuroscientist 11:408–416
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the skillful technical assistance of Magdalena Maria Kus, Dorete Jensen, Albert Meier, Majken Sand and Karin Wiedemann. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the following foundations: IMK Almene Fond, Aase and Ejnar Danielsens Fond, Hede Nielsen Fonden, Fonden til Lægevidenskabens Fremme, Eva & Henry Frænkels Mindefond, Dir. Leo Nielsens Legat, Kathrine og Vigo Skovgaards Fond, Th. Maigaard’s Eftf. Fru Lily Benthine Lunds Fond af 1/6 1978, and the Aarhus University Research Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
Professor Danscher owns a small company, Berlock ApS, supported by government money that have patented the use of heavy metals as a dispenser of metal ions: European Patent: EP 1 395 268 (issued on January 19, 2005)based on the article “In vivo liberation of gold ions from gold implants. Histochem Cell Biol (2002) 117:447–452. The present study has been carried out at the two university laboratories (University of Aarhus and University of Copenhagen, Denmark) named in the article and the company has not been involved in the work in any way.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G. Danscher, M. Penkowa and M. Stoltenberg have contributed equally to the content of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, A., Kolind, K., Pedersen, D.S. et al. Gold ions bio-released from metallic gold particles reduce inflammation and apoptosis and increase the regenerative responses in focal brain injury. Histochem Cell Biol 130, 681–692 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0448-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0448-1