Abstract
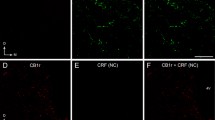
Ample evidence implicates corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-producing neurons of the central amygdaloid nucleus (CeA) in vegetative, endocrine, and behavioral responses to stress and anxiety in laboratory rats. Monoaminergic systems are involved in modulating these responses. In the present paper, interrelations between CRF-immunoreactive (ir) neurons, and noradrenergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic afferents were studied using single and double immunolabeling for light and electron microscopy in the rat CeA. Dopaminergic axons formed dense plexus in the CeA overlapping with the localization of CRF-ir neurons, and their terminals formed frequent associations with CRF-ir somata. Contacts of serotonergic axons on CRF-ir neurons were few, and contacts of noradrenergic axons were the exception. Ultrastructurally, symmetric synapses of dopaminergic terminals on CRF-ir somata and dendrites were found. More than 83% of CRF-ir somata were contacted in single ultrathin sections. About half of these possessed two or more contacts. Of non-ir somata, 37% were contacted by dopaminergic terminals, and only 13% of these had two or more contacts. Correlative in situ hybridization indicated that CeA CRF-ir neurons may express receptor subtype dopamine receptor subtype 2. In conclusion, dopaminergic afferents appear to specifically target CeA CRF neurons. They are thus in a position to exert significant influence on the rat amygdaloid CRF stress system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisman H, Zacharko RM (1992) Depression as a consequence of inadequate neurochemical adaptation in response to stressors. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 15:36–43
Asan E (1993) Comparative single and double immunolabeling with antisera against catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes: criteria for the identification of dopaminergic, noradrenergic and adrenergic structures in selected rat brain areas. Histochemistry 99:427–442
Asan E (1997a) Interrelations between tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive dopaminergic afferents and somatostatinergic neurons in the rat central amygdaloid nucleus. Histochem Cell Biol 107:65–79
Asan E (1997b) Ultrastructural features of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive afferents and their targets in the rat amygdala. Cell Tissue Res 288:449–469
Asan E (1998) The catecholaminergic innervation of the rat amygdala. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 142:1-118
Asan E, Kugler P (1995) Qualitative and quantitative detection of alkaline phosphatase coupled to an oligonucleotide probe for somatostatin mRNA after in situ hybridization using unfixed rat brain tissue. Histochemistry 103:463–471
Bakshi VP, Smith-Roe S, Newman SM, Grigoriadis DE, Kalin NH (2002) Reduction of stress-induced behavior by antagonism of corticotropin-releasing hormone 2 (CRH2) receptors in lateral septum or CRH1 receptors in amygdala. J Neurosci 22:2926–2935
Basso AM, Spina M, Rivier J, Vale W, Koob GF (1999) Corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist attenuates the "anxiogenic-like" effect in the defensive burying paradigm but not in the elevated plus-maze following chronic cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 145:21–30
Berod A, Hartman BK, Pujol JF (1981) Importance of fixation in immunohistochemistry: use of formaldehyde solutions at variable pH for the localization of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Histochem Cytochem 29:844–850
Borowski TB, Kokkinidis L (1996) Contribution of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to expression of conditional fear: effects of electrical stimulation, exitotoxin lesions, and quinpirole infusion on potentiated startle in rats. Behav Neurosci 110:1349–1364
Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1996) Stress, depression and the mesolimbic dopamine system. Psychopharmacology 128:331–342
Cassell MD, Gray TS (1989) Morphology of peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala. J Comp Neurol 281:320–333
Cassell MD, Gray TS, Kiss JZ (1986) Neuronal architecture in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala: a cytological, hodological, and immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 246:478–499
Coco ML, Kuhn CM, Ely TD, Kilts CD (1992) Selective activation of mesoamygdaloid dopamine neurons by stress: attenuation by diazepam. Brain Res 590:39–47
Commons KG, Connolley KR, Valentino RJ (2003) A neurochemically distinct dorsal raphe-limbic circuit with a potential role in affective disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:206–215
Curtis AL, Bello NT, Connolley KR, Valentino RJ (2002) Corticotropin-releasing factor neurones of the central nucleus of the amygdala mediate locus coeruleus activation by cardiovascular stress. J Neuroendocrinol 14:667–682
Dagerlind A, Friberg K, Bean AJ, Hokfelt T (1992) Sensitive mRNA detection using unfixed tissue: combined radioactive and non-radioactive in situ hybridization histochemistry. Histochemistry 98:39–49
Day HEW, Curran EJ, Watson SJ Jr, Akil H (1999) Distinct neurochemical populations in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: evidence for their selective activation by interleukin-1β. J Comp Neurol 413:113–128
Day HEW, Vittoz NM, Oates MM, Badiani A, Watson SJ Jr, Robinson TE, Akil H (2002) A 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the mesostriatal dopamine system decreases the expression of corticotropin releasing hormone and neurotensin mRNAs in the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Brain Res 945:151–159
Derouiche A, Asan E (1999) The dopamine D2 receptor subfamily in rat retina: ultrastructural immunogold and non-radioactive in situ hybridization studies. Eur J Neurosci 11:1391–1402
Dunn AJ (1988) Stress-related activation of cerebral dopaminergic systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 537:188–205
Eaton MJ, Cheung S, Moore KE, Lookingland KJ (1996) Dopamine receptor-mediated regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res 738:60–66
Erb S, Salmaso N, Rodaros D, Stewart J (2001) A role for the CRF-containing pathway from central nucleus of the amygdala to bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 158:360–365
Fallon JH, Ciofi P (1992) Distribution of monoamines within the amygdala. In: Aggleton JP (ed) The amygdala. Neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory and mental dysfunction. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 97–114
Fendt M, Fanselow MS (1999) The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:743–760
Fibiger HC (1991) The dopamine hypotheses of schizophrenia and mood disorders: contradictions and speculations. In: Willner P, Scheel-Krüger J (eds) The mesolimbic dopamine system: from motivation to action. Wiley, Chichester, pp 615–637
Gerdeman GL, Partridge JG, Lupica CR, Lovinger DM (2003) It could be habit forming: drugs of abuse and striatal synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 26:184–192
Gifkins A, Greba Q, Kokkinidis L (2002) Ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons mediate the shock sensitization of acoustic startle: a potential site of action for benzodiazepine anxiolytics. Behav Neurosci 116:785–794
Graeff FG (1994) Neuroanatomy and neurotransmitter regulation of defensive behaviors and related emotions in mammals. Braz J Med Biol Res 27:811–829
Graeff FG, Guimaraes FS, de Andrade TG, Deakin JF (1996) Role of 5-HT in stress, anxiety, and depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:129–141
Gray TS, Bingaman EW (1996) The amygdala: corticotropin-releasing factor, steroids, and stress. Crit Rev Neurobiol 10:155–168
Greba Q, Munro LJ, Kokkinidis L (2000) The involvement of ventral tegmental area cholinergic muscarinic receptors in classically conditioned fear expression as measured with fear-potentiated startle. Brain Res 870:135–141
Greba Q, Gifkins A, Kokkinidis L (2001) Inhibition of amygdaloid D2 receptors impairs emotional learning measured with fear-potentiated startle. Brain Res 899:218–226
Groenink L, Joordens RJ, Hijzen TH, Dirks A, Olivier B (2000) Infusion of flesinoxan into the amygdala blocks the fear-potentiated startle. Neuroreport 11:2285–2288
Guaracci FA, Kapp BS (1999) An electrophysiological characterization of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons during differential Pavlovian fear conditioning in the awake rabbit. Behav Brain Res 99:169–179
Guaracci FA, Frohardt RJ, Young SL, Kapp BS (1999) A functional role for dopamine transmission in the amygdala during conditioned fear. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:732–736
Guaracci FA, Frohardt RJ, Falls WA, Kapp BS (2000) The effects of intra-amygdaloid infusions of a D2 dopamine receptor antagonist on Pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 114:647–651
Hariri AR, Mattay VS, Tessitore A, Kolachana B, Fera F, Goldman D, Egan MF, Weinberger DR (2002) Serotonin transporter genetic variation and the response of the human amygdala. Science 297:400–403
Heinrichs SC, Menzaghi F, Merlo Pich E, Britton KT, Koob GF (1995) The role of CRF in behavioral aspects of stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci 771:92–104
Heinrichs SC, Lapsansky J, Lovenberg TW, De Souza EB, Chalmers DT (1997) Corticotropin-releasing-factor CRF1, but not CRF2, receptors mediate anxiogenic-like behavior. Regul Pept 71:15–21
Heinrichs SC, Klaassen A, Koob GF, Schulteis G, Ahmed S, De Souza EB (1998) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor blockade enhances conditioned aversive properties of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 136:247–255
Hitchcott PK, Phillips GD (1998) Double dissociation of the behavioural effects of R(+) 7-OH-DPAT infusions in the central and basolateral amygdala nuclei upon Pavlovian and instrumental conditioned appetitive behaviours. Psychopharmacology 140:458–469
Hornby PJ, Piekut DT (1989) Opiocortin and catecholamine input to CRF-immunoreactive neurons in rat forebrain. Peptides 10:1139–1146
Hsu DT, Chen FL, Takahashi LK, Kalin NH (1998) Rapid stress-induced elevations in corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in rat central amygdala nucleus and hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: an in situ hybridization analysis. Brain Res 788:305–310
Imperato A, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1993) Repeated stressful experiences differently affect the time-dependent responses of the mesolimbic dopamine system to the stressor. Brain Res 601:333–336
Inglis FM, Moghaddam B (1999) Dopaminergic innervation of the amygdala is highly responsive to stress. J Neurochem 72:1088–1094
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Koyama T (1994) Regional changes in dopamine and serotonin activation with various intensity of physical and psychological stress in the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:911–920
Isovich E, Mijnster MJ, Flugge G, Fuchs E (2000) Chronic psychosocial stress reduces the density of dopamine transporters. Eur J Neurosci 12:1071–1078
Jingami H, Mizuno N, Takahashi H, Shibahara S, Furutani Y, Imura H, Numa S (1985) Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for rat corticotropin-releasing factor precursor. FEBS Lett 191:63–66
Khoshbouei H, Cecchi M, Dove S, Javors M, Morilak D (2002) Behavioral reactivity to stress: amplification of stress-induced noradrenergic activation elicits a galanin-mediated anxiolytic effect in central amygdala. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:407–417
Killcross S, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1997) Different types of fear-conditioned behaviour mediated by separate nuclei within amygdala. Nature 388:377–380
Klimek V, Schenck JE, Han H, Stockmeier CA, Ordway GA (2002) Dopaminergic abnormalities in amygdaloid nuclei in major depression: a postmortem study. Biol Psychiatry 52:740–748
Koob GF (1999a) Corticotropin-releasing factor, norepinephrine, and stress. Biol Psychiatry 46:1167–1180
Koob GF (1999b) Stress, corticotropin-releasing factor, and drug addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 897:27–45
Koob GF (2000) Neurobiology of addiction. Toward the development of new therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 909:170–185
Koob GF, Heinrichs SC (1999) A role for corticotropin releasing factor and urocortin in behavioral responses to stressors. Brain Res 848:141–152
Liposits Z, Phelix C, Paull WK (1986) A combined light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical method for the simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens. Histochemistry 85:95–106
Makino S, Shibasaki T, Yamauchi N, Nishioka T, Mimoto T, Wakabayashi I, Gold PW, Hashimoto K (1999) Psychological stress increases corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA and content in the central nucleus of the amygdala but not in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the rat. Brain Res 850:136–143
McBride WJ (2002) Central nucleus of the amygdala and the effects of alcohol and alcohol-drinking behavior in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:509–515
McDonald AJ (1982) Cytoarchitecture of the central amygdaloid nucleus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 208:401–418
Meador-Woodruff JH, Damask SP, Watson SJ Jr (1994) Differential expression of autoreceptors in the ascending dopamine systems of the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:8297–8301
Merali Z, McIntosh J, Kent P, Michaud D, Anisman H (1998) Aversive and appetitive events evoke the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone and bombesin-like peptides at the central nucleus of the amygdala. J Neurosci 18:4758–4766
Merali U, Kent P, Michaud D, McIntyre D, Anisman H (2001) Differential impact of predator or immobilization stressors on central corticotropin-releasing hormone and bombesin-like peptides in fast and slow seizing rat. Brain Res 906:60–73
Merchant KM, Bush LG, Gibb JW, Hanson (1989) Dopamine D2 receptors exert tonic regulation over discrete neurotensin systems of the rat brain. Brain Res 500:21–29
Merlo Pich E, Lorang M, Yeganeh M, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Raber J, Koob GF, Weiss F (1995) Increase of extracellular corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity levels in the amygdala of awake rats during restraint stress and ethanol withdrawal as measured by microdialysis. J Neurosci 15:5439–5447
Moga MM, Gray TS (1985) Evidence for corticotropin-releasing factor, neurotensin, and somatostatin in the neural pathway from the central nucleus of the amygdala to the parabrachial nucleus. J Comp Neurol 241:275–284
Monsma FJ, McVittie LD, Gerfen CR, Mahan LC, Sibley DR (1989) Multiple D2 dopamine receptors produced by alternative RNA splicing. Nature 342:926–929
Monsma FJ, Mahan LC, McVittie LC, Gerfen CR, Sibley DR (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:6723–6727
Murer MG, Dziewczapolski G, Salin P, Vila M, Tseng KY, Ruberg M, Rubinstein M, Kelly MA, Grandy DK, Low MJ, Hirsch E, Raisman-Vozari R, Gershanik (2000) The indirect basal ganglia pathway in dopamine D(2) receptor-deficient mice. Neuroscience 99:643–650
Ninan PT (1999) The functional anatomy, neurochemistry, and pharmacology of anxiety. J Clin Psychiatry 60 (22):12–17
Panagis G, Hildebrand BE, Svensson TH, Nomikos GG (2000) Selective c-fos induction and decreased dopamine release in rats displaying a mecamylamine-precipitated nicotine withdrawal syndrome. Synapse 35:15–25
Pani L, Porcella A, Gessa GL (2000) The role of stress in the pathophysiology of the dopaminergic system. Mol Psychiatry 5:14–21
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, Sydney
Phelix CF, Liposits Z, Paull WK (1992) Serotonin-CRF interaction in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: a light microscopic double-label immunocytochemical analysis. Brain Res Bull 28:943–948
Phelix CF, Liposits Z, Paull WK (1994) Catecholamine-CRF synaptic interaction in a septal bed nucleus: afferents of neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Brain Res Bull 33:109–119
Pickel VM, Chan J (1999) Ultrastructural localization of the serotonin transporter in limbic and motor compartments of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 19:7356–7366
Pitman RK (1997) Overview of biological themes in PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 821:1–9
Post RM (1992) Transduction of psychosocial stress into the neurobiology of recurrent affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 149:999–1010
Quirarte GL, Galvez R, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL(1998) Norepinephrine release in the amygdala in response to footshock and opioid peptidergic drugs. Brain Res 808:134–140
Raber J, Koob GF, Bloom FE (1995) Interleukin-2 (IL-2) induces corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) release from the amygdala and involves a nitric oxide-mediated signaling: comparison with the hypothalamic response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:815–824
Rassnick S, Heinrichs SC, Britton KT, Koob GF (1993) Microinjection of a corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist into the central nucleus of the amygdala reverses anxiogenic-like effects of ethanol. Brain Res 605:25–32
Ressler KJ, Nemeroff CB (2000) Role of serotonergic and noradrenergic systems in the pathophysiology of depression and anxiety disorder. Depress Anxiety 12 (Suppl 1):2–19
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Rezayof A, Zarrindast M-R, Sahraei H, Haeri-Rohani A (2002) Involvement of dopamine D2 receptors of the central amygdala on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference in rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:187–197
Richter RM, Weiss F (1999) In vivo CRF release in rat amygdala is increased during cocaine withdrawal in self-administering rats. Synapse 32:254–261
Richter RM, Zorrilla EP, Basso AM, Koob GF, Weiss F (2000) Altered amygdalar CRF release and increased anxiety-like behavior in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats: a microdialysis and behavioral study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:1765–1772
Rivier J, Spiess J, Vale W (1983) Characterization of rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80:4851–4855
Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1999) Drug addiction: bad habits add up. Nature 398:567–570
Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Carrera MR, Navarro M, Koob GF, Weiss F (1997) Activation of corticotropin-releasing factor in the limbic system during cannabinoid withdrawal. Science 276:2050–2054
Sakanaka M, Shibasaki T, Lederis K (1986) Distribution and efferent projections of corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the rat amygdaloid complex. Brain Res 382:213–238
Sarnyai Z, Shaham Y, Heinrichs SC (2001) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in drug addiction. Pharmacol Rev 53:209–243
Scibilia RJ, Lachowicz JE Kilts CD (1992) Topographic nonoverlapping distribution of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the amygdaloid nuclear complex of the rat brain. Synapse 11:146–154
Smialowska M, Bajkowska M, Przewlocki MM, Turchan J, Przewlocki R (1999) Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on neuropeptide Y and corticotropin-releasing factor expression in rat amygdala. Neuroscience 94:1125–1132
Somogyi P, Takagi H (1982) A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience 7:1779–1783
Stewart J (2000) Pathways to relapse: the neurobiology of drug- and stress-induced relapse to drug-taking. J Psychiatry Neurosci 25:125–136
Strome EM, Wheler GHT, Higley JD, Loriaux DL, Suomi SJ, Doudet DJ (2002) Intracerebroventricular corticotropin-releasing factor increases limbic glucose metabolism and has social context-dependent behavioral effects in nonhuman primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15749–15754
Sur C, Betz H, Schloss P (1996) Immunocytochemical detection of the serotonin transporter in rat brain. Neuroscience 73:217–231
Suzuki T, Ishigooka J, Watanabe S, Miyaoka H (2002) Enhancement of delayed release of dopamine in the amygdala induced by conditioned fear stress in methamphetamine-sensitized rats. Eur J Pharmacol 435:59–65
Swiergiel AH, Takahashi LK, Kalin NH (1993) Attenuation of stress-induced behavior by antagonism of corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in the central amygdala in the rat. Brain Res 623:229–234
Tanaka M, Yoshida M, Emoto H, Ishii H (2000) Noradrenaline systems in the hypothalamus, amygdala and locus coeruleus are involved in the provocation of anxiety: basic studies. Eur J Pharmacol 405:397–406
Van Bockstaele EJ, Colago EE, Valentino RJ (1998) Amygdaloid corticotropin-releasing factor targets locus coeruleus dendrites: substrate for the co-ordination of emotional and cognitive limbs of the stress response. J Neuroendocrinol 10:743–757
Veening JG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE (1984) The organization of projections from the central nucleus of the amygdala to brainstem sites involved in central autonomic regulation. A combined retrograde transport-immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 303:337–357
Weiss F, Maldonado-Vlaar CS, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O (2000) Control of cocaine-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats: effects on recovery of extinguished operant-responding and extracellular dopamine levels in amygdala and nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4321–4326
Weiss F, Ciccocioppo R, Parsons LH, Katner S, Liu X, Zorrilla EP, Valdez GR, Ben-Shahar O, Angeletti S, Richter RR (2001) Compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse. Neuroadaptation, stress, and conditioning factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937:1–26
Wu J-S, Ku Y-H, Li L-S, Lu Y-C, Din X, Wang Y-G (1999) Corticotropin releasing factor and substance P mediate the nucleus amygdaloideus centralis-nucleus ventromedialis-nucleus dorsomedialis pressor system. Brain Res 842:392–398
Yadid G, Overstreet DH, Zangen A (2001) Limbic dopaminergic adaptation to a stressful stimulus in a rat model of depression. Brain Res 896:43–47
Yamamoto H, Fujimiya M, Shirai Y, Nakashita M, Oyasu M, Saito N (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of serotonin transporter in normal and colchicine treated rat brain. Neurosci Res 32:305–312
Yilmazer-Hanke DM, Faber-Zuschratter H, Linke R, Schwegler H (2002) Contribution of amygdala neurons containing peptides and calcium-binding proteins to fear-potentiated startle and exploration-related anxiety in inbred Roman high- and low-avoidance rats. Eur J Neurosci 15:1206–1218
Yu B, Shinnick-Gallagher P (1998) Corticotropin-releasing factor increases dihydropyridine- and neurotoxin-resistant calcium currents in neurons of the central amygdala. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:170–179
Zaborszky L, Heimer L (1989) Combinations of tracer techniques, especially HRP and PHA-L, with transmitter identification for correlated light and electron microscopic studies. In: Heimer L, Zaborszky L (eds) Neuroanatomical tract tracing methods 2. Plenum, New York, pp 49–96
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Rita Herrmann and Sieglinde Schenk for skillful technical assistance. The investigations were supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (As 89/2–1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eliava, M., Yilmazer-Hanke, D. & Asan, E. Interrelations between monoaminergic afferents and corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons in the rat central amygdaloid nucleus: ultrastructural evidence for dopaminergic control of amygdaloid stress systems. Histochem Cell Biol 120, 183–197 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0557-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0557-9