Abstract
Purpose
To study the safety and biocompatibility of Laponite clay (LAP) within an intravitreal and suprachoroidal administration in rabbit eyes.
Methods
Thirty-two New Zealand albino rabbits were divided into two experimental groups to test intravitreal (IVT group) and suprachoroidal (SCS group) administration of a 100-μl and 50-μl Laponite suspension respectively. Following injection, the eyes were monitored by ocular tonometry, slit-lamp eye examination and indirect ophthalmoscopy, at 24 h, 1, 4, 12, and 14 weeks post administration. Histological examination was also performed to determine whether any ocular pathological change had occurred. Throughout the study, LAP presence in vitreous was estimated by complexometric titration with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), taking advantage of the Laponite high content of magnesium ions.
Results
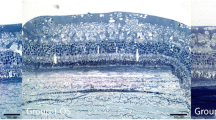
Neither significant differences in the intraocular pressure, nor relevant ocular complications were found in the two experimental groups after LAP administration. The histology of the retina remained unchanged. LAP presence in vitreous could be indirectly confirmed by complexometric titration until 14 weeks post administration in eyes of IVT group.
Conclusion
Laponite could be considered as a vehicle for potential clinical use in ocular drug administration, due to its proven ocular biocompatibility and its transparency in gel state.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal D, Kaur IP (2005) Improved pharmacodynamics of timolol maleate from a mucoadhesive niosomal ophthalmic drug delivery system. Int J Pharm 290:155–159
Lee SS, Robinson MR (2009) Novel drug delivery systems for retinal diseases. A review. Ophthalmic Res 41:124–135
Rodrigues LA, Figueiras A, Veiga F, de Freitas RM, Nunes LC, da Silva Filho EC, da Silva Leite CM (2013) The systems containing clays and clay minerals from modified drug release: a review. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 103:642–651
Da Silva GR, Ayres E, Orefice RL, Moura SA, Cara DC, Cunha Ada S Jr (2009) Controlled release of dexamethasone acetate from biodegradable and biocompatible polyurethane and polyurethane nanocomposite. J Drug Target 17:374–383
Ruzicka B, Zulian L, Ruocco G (2006) More on the phase diagram of Laponite. Langmuir 22:1106–1111
Ghadiri M, Chrzanowski W, Rohanizadeh R (2014) Antibiotic eluting clay mineral (Laponite(R)) for wound healing application: an in vitro study. J Mater Sci Mater Med 25:2513–2526
Viseras C, Aguzzi C, Cerezo P, López-Galindo A (2007) Uses of clay minerals in semisolid health care and therapeutic products. Appl Clay Sci 36:37–50
Wang C, Wang S, Li K, Ju Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Li J, Liu X, Shi X, Zhao Q (2014) Preparation of laponite bioceramics for potential bone tissue engineering applications. PLoS One 9:e99585
European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines (EDQM) (2005) European pharmacopoeia, 5th edn. Council of Europe, Strasbourg, p 1958
Vogel AI (1989) Vogel’s textbook of quantitative chemical analysis, 5th edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 328–331
Fraile JM, Garcia-Martin E, Gil C, Mayoral JA, Pablo LE, Polo V, Prieto E, Vispe E (2016) Laponite as carrier for controlled in vitro delivery of dexamethasone in vitreous humor models. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 108:83–90
Harris DC (2007) Quantitative chemical analysis, 7th edn. WH Freeman and Company, New York, p 245
Achouri D, Alhanout K, Piccerelle P, Andrieu V (2013) Recent advances in ocular drug delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 39:1599–1617
Kompella UB, Amrite AC, Pacha RR, Durazo SA (2013) Nanomedicines for back of the eye drug delivery, gene delivery, and imaging. Prog Retin Eye Res 36:172–198
Chen M, Li X, Liu J, Han Y, Cheng L (2015) Safety and pharmacodynamics of suprachoroidal injection of triamcinolone acetonide as a controlled ocular drug release model. J Control Release 203:109–117
Han HK, Lee YC, Lee MY, Patil AJ, Shin HJ (2011) Magnesium and calcium organophyllosilicates: synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity study. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:2564–2572
Goncalves M, Figueira P, Maciel D, Rodrigues J, Shi X, Tomas H, Li Y (2014) Antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin-loaded laponite/alginate hybrid hydrogels. Macromol Biosci 14:110–120
Olsen TW, Feng X, Wabner K, Conston SR, Sierra DH, Folden DV, Smith ME, Cameron JD (2006) Cannulation of the suprachoroidal space: a novel drug delivery methodology to the posterior segment. Am J Ophthalmol 142:777–787
Peng Y, Ang M, Foo S, Lee WS, Ma Z, Venkatraman SS, Wong TT (2011) Biocompatibility and biodegradation studies of subconjunctival implants in rabbit eyes. PLoS One 6:e22507
Peng YJ, Kau YC, Wen CW, Liu KS, Liu SJ (2010) Solvent-free biodegradable scleral plugs providing sustained release of vancomycin, amikacin, and dexamethasone—an in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res A 94:426–432
Lambuk L, Jafri AJ, Arfuzir NN, Iezhitsa I, Agarwal R, Rozali KN, Agarwal P, Bakar NS, Kutty MK, Yusof AP, Krasilnikova A, Spasov A, Ozerov A, Ismail NM (2017) Neuroprotective effect of magnesium acetyltaurate against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in rat retina. Neurotox Res 31:31–45
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the collaboration of the staff members of the Centro de Investigación Biomédica de Aragón (CIBA) in animal supply, care, feeding, and maintenance services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Author disclosure statement
All the listed authors agree with the submission of this manuscript, and none of them has any conflicting financial interests related to the submission, either currently or over the past 5 years.
Disclosure conflict of interest
This study has received financial support from the following institutions: Instituto de Salud Carlos III (grant PI12/02285), and Diputación General de Aragón (E11 Group co-financed by the European Regional Development Funds). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the in-house Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments of the University of Zaragoza (Spain) at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prieto, E., Vispe, E., De Martino, A. et al. Safety study of intravitreal and suprachoroidal Laponite clay in rabbit eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256, 535–546 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3893-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3893-5