Abstract
Background
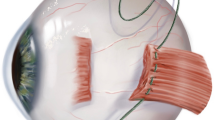
The Y-splitting procedure has been used both to treat up-shoots and down-shoots in Duane syndrome, and as a substitute for posterior fixation suture. The Y-split is often performed in conjunction with a hang-back recession when a large amount of recession or an adjustable suture is necessary. Herein, we evaluated the stability of Y-splitting hang-back recession in the rectus muscle.
Methods
Under general anesthesia, a 5-mm hang-back recession of the superior rectus muscle (SR) with Y-splitting was performed in ten eyes from ten rabbits (hang-back group). A conventional recession was performed in the SR of the fellow eye (control group). Six weeks after the procedure, the distance between the original insertion and the recessed SR (recession amount) and the width between the nasal and temporal halves of the SR were measured. These values were compared to the measurements taken at the time of surgery.
Results
The hang-back group had a significantly larger forward displacement than the control group (P < 0.001 for both the nasal and temporal halves). The width change between the nasal and temporal halves was also significantly larger in the hang-back group (4.94 ± 1.32 mm) than in the control group (1.14 ± 0.60 mm, P < 0.001). Additionally, the Y-configuration appeared to be more collapsed in the hang-back group than in the control group.
Conclusion
Y-splitting of the rectus muscle may be unstable when it is combined with a hang-back recession. Surgeons should consider this possibility when performing Y-splitting procedures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Von Noorden GK, Campos EC (2002) Binocular vision and ocular motility: theory and management of strabismus. Mosby, St. Louis
Rao VB, Helveston EM, Sahare P (2003) Treatment of upshoot and downshoot in Duane syndrome by recession and Y-splitting of the lateral rectus muscle. J AAPOS 7:389–395
Velez FG, Velez G, Hendler K, Pineles SL (2012) Isolated Y-splitting and recession of the lateral rectus muscle in patients with exo-Duane syndrome. Strabismus 20:109–114
Wang KM, Liu LJ, Zhang FH (2007) Treatment of Duane’s retraction syndrome by recession of medial and lateral rectus muscles combined with Y-splitting procedure. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 43:972–976
Rogers GL, Bremer DL (1984) Surgical treatment of the upshoot and downshoot in Duanes’ retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology 91:1380–1383
Hoerantner R, Priglinger S, Haslwanter T (2004) Reduction of ocular muscle torque by splitting of the rectus muscle II: technique and results. Br J Ophthalmol 88:1409–1413
Haslwanter T, Hoerantner R, Priglinger S (2004) Reduction of ocular muscle power by splitting of the rectus muscle I: biomechanics. Br J Ophthalmol 88:1403–1408
Repka MX, Guyton DL (1988) Comparison of hang-back medial rectus recession with conventional recession. Ophthalmology 95:782–787
Rodrigues AC, Nelson LB (2006) Long-term results of hang-back lateral rectus recession. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 43:161–164
Orlin A, Mills M, Ying GS, Liu C (2007) A comparison of hang-back with conventional recession surgery for exotropia. J AAPOS 11:597–600
Rajavi Z, Ghadim HM, Nikkhoo M, Dehsarvi B (2001) Comparison of hang-back and conventional recession surgery for horizontal strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 38:273–277
Chung AK, Rehman SU, Bradbury JA (2005) Comparison of modified anchored “hang-back technique (HBT)” with conventional HBT in bimedial rectus recession. J AAPOS 9:234–239
Liebermann L, Hatt SR, Leske DA, Holmes JM (2013) Adjustment versus no adjustment when using adjustable sutures in strabismus surgery. J AAPOS 17:38–42
Climenhaga HW, Pearce WG (1984) Adjustable sutures: experimental assessment of final muscle position. Can J Ophthalmol 19:234–236
Wysenbeek Y, Wygnanski-Jaffe T, Rosner M, Spierer A (2004) Evaluation of superior rectus muscle attachment following hang-back recession in rabbit eyes. Eur J Ophthalmol 14:464–466
Ohtsuki H, Oshima K, Hasebe S, Kobashi R, Okano M, Furuse T (1994) Extraocular muscle surgery in a rabbit model: site of reattachment following hang-back and conventional recession. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232:689–694
Davis FA (1929) The anatomy and histology of the eye and orbit of the rabbit. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 27(400):402–441
Kim JM, Kim EJ, Yoo JM (2007) The distribution of the extraocular pulley smooth muscle in the rabbit. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 48:142–149
Suh YW, Park JH, Cho YA (2011) The effect of botulinum toxin injection on the hang-back recession of rectus muscles. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249:921–924
Acknowledgments
The authors have not received grant support or research funding, and do not have any proprietary interests in the materials described in the manuscript.
The authors have full control of all primary data, and we agree to allow Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review our data upon request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, SE., Han, JY., Kim, SH. et al. Stability of Y-splitting procedure combined with hang-back recession of the rectus muscle in rabbit eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252, 59–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2511-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2511-4