Abstract
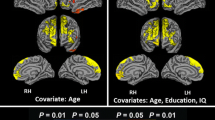
Subcortical vascular cognitive impairment (SVCI) refers to cognitive impairment associated with small vessel disease. Motor intentional disorders (MID) have been reported in patients with SVCI. However, there are no studies exploring the neuroanatomical regions related to MID in SVCI patients. The aim of this study, therefore, was to investigate the neural correlates of MID in SVCI patients. Thirty-one patients with SVCI as well as 10 healthy match control participants were included. A “Pinch-Grip” apparatus was used to quantify the force control capabilities of the index finger in four different movement phases including initiation, development, maintenance, and termination. All participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Topographical cortical areas and white matter tracts correlated with the performances of the four different movement phases were assessed by the surface-based morphometry and tract-based spatial statistics analyses. Poorer performance in the maintenance task was related to cortical thinning in bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal, orbitofrontal and parietal cortices, while poorer performance in the termination task was associated with the disruption of fronto-parietal cortical areas as well as the white matter tracts including splenium and association fibers such as superior longitudinal fasciculus. Our study demonstrates that cortical areas and underlying white matter tracts associated with fronto-parietal attentional system play an important role in motor impersistence and perseveration in SVCI patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SH, Park JS, Ahn HJ, Seo SW, Lee JM, Kim ST, Han SH, Na DL (2011) Voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment: correlates with cognitive and motor deficits. J Neuroimaging 21:317–324
Kim CH, Seo SW, Kim GH, Shin JS, Cho H, Noh Y, Kim SH, Kim MJ, Jeon S, Yoon U, Lee JM, Oh SJ, Kim JS, Kim ST, Lee JH, Na DL (2012) Cortical thinning in subcortical vascular dementia with negative 11C-PiB PET. J Alzheimers Dis 31:315–323
Seo SW, Ahn J, Yoon U, Im K, Lee JM, Tae Kim S, Ahn HJ, Chin J, Jeong Y, Na DL (2010) Cortical thinning in vascular mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia of subcortical type. J Neuroimag 20:37–45
Heilman KM (2004) Intentional neglect. Front Biosci 9:694–705
Seo SW, Jung K, You H, Lee BH, Kim GM, Chung CS, Lee KH, Na DL (2009) Motor-intentional disorders in right hemisphere stroke. Cogn Behav Neurol 22:242–248
Yoon DS, Jung K, Kim GH, Kim SH, Lee BH, Seo SW, You H, Na DL (2014) Motor intentional disorders in vascular mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia of subcortical type. Neurocase 20:53–60
Chamorro A, Marshall RS, Valls-Sole J, Tolosa E, Mohr JP (1997) Motor behavior in stroke patients with isolated medial frontal ischemic infarction. Stroke 28:1755–1760
Kertesz A, Nicholson I, Cancelliere A, Kassa K, Black SE (1985) Motor impersistence: a right-hemisphere syndrome. Neurology 35:662–666
Inzitari D, Erkinjuntti T, Wallin A, Del Ser T, Romanelli M, Pantoni L (2000) Subcortical vascular dementia as a specific target for clinical trials. Ann N Y Acad Sci 903:510–521
Gandola M, Toraldo A, Invernizzi P, Corrado L, Sberna M, Santilli I, Bottini G, Paulesu E (2013) How many forms of perseveration? Evidence from cancellation tasks in right hemisphere patients. Neuropsychologia 51:2960–2975
Gmitrowicz A, Kucharska A (1994) Developmental disorders in the fourth edition of the American classification: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM IV—optional book). Psychiatr Pol 28:509–521
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, Schmidt R, Kleinert G, Payer F, Radner H, Lechner H (1993) Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology 43:1683–1689
Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 256:183–194
Seo SW, Im K, Lee JM, Kim YH, Kim ST, Kim SY, Yang DW, Kim SI, Cho YS, Na DL (2007) Cortical thickness in single- versus multiple-domain amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 36:289–297
Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, Na DL (2010) Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci 25:1071–1076
Kang Y, Na DL (2003) Seoul neuropsychological screening battery. Human Brain Research & Consulting Co, Incheon
Kim SH, Seo SW, Go SM, Chin J, Lee BH, Lee JH, Han SH, Na DL (2011) Pyramidal and extrapyramidal scale (PEPS): a new scale for the assessment of motor impairment in vascular cognitive impairment associated with small vessel disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:181–187
Zijdenbos AP, Forghani R, Evans AC (2002) Automatic “pipeline” analysis of 3-D MRI data for clinical trials: application to multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imagin 21:1280–1291
Kabani N, Le Goualher G, MacDonald D, Evans AC (2001) Measurement of cortical thickness using an automated 3-D algorithm: a validation study. Neuroimage 13:375–380
Lerch JP, Pruessner JC, Zijdenbos A, Hampel H, Teipel SJ, Evans AC (2005) Focal decline of cortical thickness in Alzheimer’s disease identified by computational neuroanatomy. Cereb Cortex 15:995–1001
Lee JK, Lee JM, Kim JS, Kim IY, Evans AC, Kim SI (2006) A novel quantitative cross-validation of different cortical surface reconstruction algorithms using MRI phantom. Neuroimage 31:572–584
Singh V, Chertkow H, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dorr AE, Kabani NJ (2006) Spatial patterns of cortical thinning in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 129:2885–2893
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peters TM, Evans AC (1994) Automatic 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:192–205
Zijdenbos A, Evans A, Riahi F, Sled J, Chui J, Kollokian V (1996) Automatic quantification of multiple sclerosis lesion volume using stereotaxic space. Vis Biomed Comput 1131:439–448
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998) A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imagin 17:87–97
MacDonald D, Kabani N, Avis D, Evans AC (2000) Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 12:340–356
Kim JS, Singh V, Lee JK, Lerch J, Ad-Dab’bagh Y, MacDonald D, Lee JM, Kim SI, Evans AC (2005) Automated 3-D extraction and evaluation of the inner and outer cortical surfaces using a Laplacian map and partial volume effect classification. Neuroimage 27:210–221
Lerch JP, Evans AC (2005) Cortical thickness analysis examined through power analysis and a population simulation. Neuroimage 24:163–173
Robbins S, Evans AC, Collins DL, Whitesides S (2004) Tuning and comparing spatial normalization methods. Med Image Anal 8:311–323
Lyttelton O, Boucher M, Robbins S, Evans A (2007) An unbiased iterative group registration template for cortical surface analysis. Neuroimage 34:1535–1544
Smith SM, Zhang Y, Jenkinson M, Chen J, Matthews PM, Federico A, De Stefano N (2002) Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. Neuroimage 17:479–489
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36:893–906
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66:259–267
Genovese CR, Lazar NA, Nichols T (2002) Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. Neuroimage 15:870–878
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 44:83–98
Hua K, Zhang J, Wakana S, Jiang H, Li X, Reich DS, Calabresi PA, Pekar JJ, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2008) Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. Neuroimage 39:336–347
Wakana S, Caprihan A, Panzenboeck MM, Fallon JH, Perry M, Gollub RL, Hua K, Zhang J, Jiang H, Dubey P, Blitz A, van Zijl P, Mori S (2007) Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. Neuroimage 36:630–644
Corbetta M, Shulman GL (2002) Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:201–215
Fan J, McCandliss BD, Fossella J, Flombaum JI, Posner MI (2005) The activation of attentional networks. Neuroimage 26:471–479
Lopez OL, Becker JT, Boller F (1991) Motor impersistence in Alzheimer’s disease. Cortex 27:93–99
Passingham RE (1996) Attention to action. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351:1473–1479
Cummings JL (1993) Frontal-subcortical circuits and human behavior. Arch Neurol 50:873–880
Rolls ET, Grabenhorst F (2008) The orbitofrontal cortex and beyond: from affect to decision-making. Prog Neurobiol 86:216–244
Gusnard DA, Ollinger JM, Shulman GL, Cloninger CR, Price JL, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2003) Persistence and brain circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:3479–3484
Frank MJ, Claus ED (2006) Anatomy of a decision: striato-orbitofrontal interactions in reinforcement learning, decision making, and reversal. Psychol Rev 113:300–326
Jung YC, Ku J, Namkoong K, Lee W, Kim SI, Kim JJ (2010) Human orbitofrontal-striatum functional connectivity modulates behavioral persistence. NeuroReport 21:502–506
Rushworth MF, Johansen-Berg H, Gobel SM, Devlin JT (2003) The left parietal and premotor cortices: motor attention and selection. Neuroimage 20(Suppl 1):S89–S100
Rushworth MF, Krams M, Passingham RE (2001) The attentional role of the left parietal cortex: the distinct lateralization and localization of motor attention in the human brain. J Cogn Neurosci 13:698–710
Rushworth MF, Nixon PD, Renowden S, Wade DT, Passingham RE (1997) The left parietal cortex and motor attention. Neuropsychologia 35:1261–1273
Pekkala S, Albert ML, Spiro A 3rd, Erkinjuntti T (2008) Perseveration in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 25:109–114
Possin KL, Filoteo JV, Roesch SC, Zizak V, Rilling LM, Davis JD (2005) Is a perseveration a perseveration? An evaluation of cognitive error types in patients with subcortical pathology. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 27:953–966
Paulesu E, Goldacre B, Scifo P, Cappa SF, Gilardi MC, Castiglioni I, Perani D, Fazio F (1997) Functional heterogeneity of left inferior frontal cortex as revealed by fMRI. NeuroReport 8:2011–2017
Smith EE, Jonides J (1999) Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science 283:1657–1661
Luria AR (1965) Two kinds of motor perseveration in massive injury of the frontal lobes. Brain 88:1–10
Sandson J, Albert ML (1984) Varieties of perseveration. Neuropsychologia 22:715–732
Sandson J, Albert ML (1987) Perseveration in behavioral neurology. Neurology 37:1736–1741
Aron AR, Fletcher PC, Bullmore ET, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2003) Stop-signal inhibition disrupted by damage to right inferior frontal gyrus in humans. Nat Neurosci 6:115–116
Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA (2004) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci 8:170–177
Gusnard DA, Akbudak E, Shulman GL, Raichle ME (2001) Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: relation to a default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:4259–4264
Cassaday HJ, Nelson AJ, Pezze MA (2014) From attention to memory along the dorsal-ventral axis of the medial prefrontal cortex: some methodological considerations. Front Syst Neurosci 8:160
Ragozzino ME (2007) The contribution of the medial prefrontal cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and dorsomedial striatum to behavioral flexibility. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1121:355–375
Smith E, Salat D, Jeng J, McCreary C, Fischl B, Schmahmann J, Dickerson B, Viswanathan A, Albert M, Blacker D (2011) Correlations between MRI white matter lesion location and executive function and episodic memory. Neurology 76:1492–1499
Román GC, Kalaria RN (2006) Vascular determinants of cholinergic deficits in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Neurobiol Aging 27:1769–1785
Jensen AR, Rohwer WD Jr (1966) The stroop color-word test: a review. Acta Psychol (Amst) 25:36–93
Polk TA, Drake RM, Jonides JJ, Smith MR, Smith EE (2008) Attention enhances the neural processing of relevant features and suppresses the processing of irrelevant features in humans: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study of the stroop task. J Neurosci 28:13786–13792
Wood AG, Saling MM, Abbott DF, Jackson GD (2001) A neurocognitive account of frontal lobe involvement in orthographic lexical retrieval: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 14:162–169
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TE (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A090632), a grant of the Original Technology Research Program for Brain Science through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. 2014M3C7A1064752), by the Korean Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) NRL program grant funded by the Korean government (MEST; 2011-0028333 & 2010-0014026), by Samsung Biomedical Research Institute grants (C-B0-217-3), and by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health &Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI14C3484).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
Informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center.
Conflicts of interest
G. H. Kim, K. Jung, O. Kwon, H. Kwon, B. H. Lee, D. S. Yoon and J. W. Hwang report no disclosures. S. W. Seo, MD, J. H. Kim, J. H. Roh, M. J. Kim, J. H. Jeong, J. M. Lee, H. You and K. Heilman report no disclosures. D. L. Na reports no disclosures.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G.H., Seo, S.W., Jung, K. et al. The neural correlates of motor intentional disorders in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment. J Neurol 263, 89–99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7946-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7946-6