Abstract
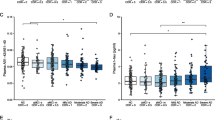
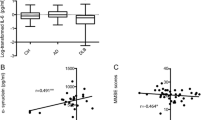
Previously, chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) protein level was increased in various inflammatory conditions and cancers. This study was aimed to evaluate the plasma CHI3L1 level as a potential prognostic biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Forty-nine patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), 61 patients with mild to severe AD, and 35 healthy elderly controls were recruited for this study. They were given a comprehensive neuropsychological test battery including a mini-mental status examination (MMSE), clinical dementia rating (CDR), and neuropsychiatric inventory (NPI). The CHI3L1 levels were measured using a specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). A significant increase in the mean plasma level of CHI3L1 was found in early AD patients compared to control subjects and MCI patients. No significant difference was found between MCI patients and controls. There was a significant positive correlation between CHI3L1 levels and neuropsychological test scores such as CDR and NPI in MCI and early AD patients. Our results demonstrate that CHI3L1 plasma levels are elevated in early AD compared to control or MCI patients. Thus, CHI3L1 plasma levels may be useful as a biomarker, reflecting disease severity in AD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Apelt J, Schliebs R (2001) Beta-amyloid-induced glial expression of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex of aged transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer plaque pathology. Brain Res 894:21–30
Bonneh-Barkay D, Wang G, Starkey A, Hamilton RL, Wiley CA (2010) In vivo CHI3L1 (YKL-40) expression in astrocytes in acute and chronic neurological diseases. J Neuroinflamm 7:34
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40:373–383
Choi J, Lee HW, Suk K (2011) Increased plasma levels of lipocalin 2 in mild cognitive impairment. J Neurol Sci 305(1–2):28–33
Coffman FD (2008) Chitinase 3-Like-1 (CHI3L1): a putative disease marker at the interface of proteomics and glycomics. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 45:531–562
Craig-Schapiro R, Perrin RJ, Roe CM, Xiong C, Carter D, Cairns NJ, Mintun MA, Peskind ER, Li G, Galasko DR, Clark CM, Quinn JF, D’Angelo G, Malone JP, Townsend RR, Morris JC, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM (2010) YKL-40: a novel prognostic fluid biomarker for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 68:903–912
Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R, Myers RH, Pericak-Vance MA, Risch N, van Duijn CM (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278:1349–1356
Johansen JS (2006) Studies on serum YKL-40 as a biomarker in diseases with inflammation, tissue remodelling, fibroses and cancer. Dan Med Bull 53:172–209
Junker N, Johansen JS, Hansen LT, Lund EL, Kristjansen PE (2005) Regulation of YKL-40 expression during genotoxic or microenvironmental stress in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Sci 96:183–190
Lafon-Cazal M, Adjali O, Galeotti N, Poncet J, Jouin P, Homburger V, Bockaert J, Marin P (2003) Proteomic analysis of astrocytic secretion in the mouse. Comparison with the cerebrospinal fluid proteome. J Biol Chem 278:24438–24448
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
McShane R, Keene J, Fairburn C, Jacoby R, Hope T (1998) Psychiatric symptoms in patients with dementia predict the later development of behavioural abnormalities. Psychol Med 28:1119–1127
Meenagh A, Williams F, Ross OA, Patterson C, Gorodezky C, Hammond M, Leheny WA, Middleton D (2002) Frequency of cytokine polymorphisms in populations from western Europe, Africa, Asia, the Middle East and South America. Hum Immunol 63:1055–1061
Morris JC (1997) Clinical dementia rating: a reliable and valid diagnostic and staging measure for dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int Psychogeriatr 9(Suppl 1):173–176 discussion 177-178
Ostergaard C, Johansen JS, Benfield T, Price PA, Lundgren JD (2002) YKL-40 is elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with purulent meningitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 9:598–604
Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 256:183–194
Rejman JJ, Hurley WL (1988) Isolation and characterization of a novel 39 kilodalton whey protein from bovine mammary secretions collected during the nonlactating period. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 150:329–334
Rubin EH, Kinscherf DA (1989) Psychopathology of very mild dementia of the Alzheimer type. Am J Psychiatry 146:1017–1021
Shimabukuro J, Awata S, Matsuoka H (2005) Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia characteristic of mild Alzheimer patients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 59:274–279
Thouvenot E, Lafon-Cazal M, Demettre E, Jouin P, Bockaert J, Marin P (2006) The proteomic analysis of mouse choroid plexus secretome reveals a high protein secretion capacity of choroidal epithelial cells. Proteomics 6:5941–5952
Tombaugh TN (2005) Test-retest reliable coefficients and 5-year change scores for the MMSE and 3MS. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 20:485–503
Tsuji T, Matsuyama Y, Natsume N, Hasegawa Y, Kondo S, Kawakami H, Yoshihara H, Iwata H (2002) Analysis of chondrex (YKL-40, HC gp-39) in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with spine disease. Spine 27:732–735
Weiner MF, Koss E, Wild KV, Folks DG, Tariot P, Luszczynska H, Whitehouse P (1996) Measures of psychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer patients: a review. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 10:20–30
Wener MH, Daum PR, McQuillan GM (2000) The influence of age, sex, and race on the upper reference limit of serum C-reactive protein concentration. J Rheumatol 27:2351–2359
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Mid-career Researcher Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) (No. 2009-0078941), and the Basic Science Research Program through the NRF funded by the MEST (No. 2010-0029460).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Lee, HW. & Suk, K. Plasma level of chitinase 3-like 1 protein increases in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol 258, 2181–2185 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6087-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6087-9