Abstract.
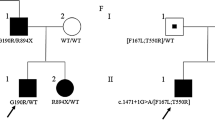
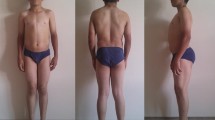
We have performed genetic screening on the skeletal muscle chloride channel gene (CLCN1) in Taiwanese population. A total of four patients with myotonia congenita (MC) together with 106 normal individuals were examined. All 23 exons of the CLCN1 gene were analysed by direct sequencing of PCR products to detect the nucleotide changes. Five mutations and three polymorphisms were identified in this study. Among these, three missense mutations (S471F, P575S, D644G) and one polymorphism (T736I) are novel and could be unique to the Taiwanese. In addition, a previously documented recessive G482R mutation was identified in a heterozygous patient and his nonsymptomatic father, indicating that this mutation might indeed function recessively or dominantly with incomplete penetrance. In conclusion, this is the first report of MC in Taiwan with proven CLCN1 gene mutations and showing high molecular heterogeneity in Taiwanese MC patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jou, SB., Chang, LI., Pan, H. et al. Novel CLCN1 mutations in Taiwanese patients with myotonia congenita. J Neurol 251, 666–670 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0383-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0383-6