Abstract
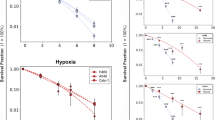
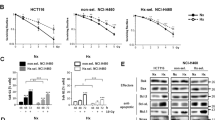
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a critical transcriptional factor for the response of cells to hypoxic microenvironment and its expression induces resistance of hypoxic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells to radiotherapy. This study investigated how the activation of HIF-1α/B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) signaling under normoxic conditions impacted radiosensitivity of NSCLC cells. The recombinant pcDNA3.0-EGFP plasmids with wild-type or mutant HIF-1α complementary DNA (cDNA) were transfected into H1299 cells, an NSCLC cell line, establishing two H1299 sublines with high expression of HIF-1α. Compared with the levels of HIF-1α and BCL-2 proteins in non-transfected cells, increased levels of both proteins were found in transfected cells. Moreover, the expression of HIF-1α in non-transfected cells induced by chloride cobalt (CoCl2), a commonly used mimetic hypoxia reagent, was concomitant with the enhancement of BCL-2 expression. Conversely, reduction of HIF-1α expression by an inhibitor decreased the levels of BCL-2 proteins. The results revealed that the stabilization and expression of HIF-1α promoted the accumulation of BCL-2 proteins in H1299 cells. Subsequent experiments showed that intracellular HIF-1α/BCL-2 signaling was triggered in a normoxic environment after H1299 cells were exposed to irradiation, causing an elevated radioresistance. In contrast, blockage of HIF-1α/BCL-2 signaling leads to an elevated radiosensitivity. Proliferation of cells assay showed that, under normoxic conditions, population doubling times (PDTs) of irradiated cells were prolonged by suppression of HIF-1α/BCL-2 signaling. It is, therefore, indicated that HIF-1α/BCL-2 signaling activated by ionizing radiation reduces the radiosensitivity of H1299 cells independent of the hypoxic environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks KR, To K, Joshi MB, Conlon DH, Herndon JE 2nd, D’Amico TA, Harpole DH Jr (2003) Measurement of chemoresistance markers in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer: a novel approach for patient selection. Ann Thorac Surg 76:187–193
Choi SM, Choi KO, Park YK, Cho H, Yang EG, Park H (2006) Clioquinol, a Cu(II)/Zn(II) chelator, inhibits both ubiquitination and asparagine hydroxylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, leading to expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin in normoxic cells. J Biol Chem 281:34056–34063
Daniel JC, Smythe WR (2004) The role of Bcl-2 family members in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 16:19–27
Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M (2005) The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer 104:1129–1137
Diensthuber M, Potinius M, Rodt T, Stan AC, Welkoborsky HJ, Samii M, Schreyögg J, Lenarz T, Stöver T (2008) Expression of bcl-2 is associated with microvessel density in olfactory neuroblastoma. J Neurooncol 89:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9602-9
Duan Y, He Q, Yue K, Si H, Wang J, Zhou X, Wang X (2017) Hypoxia induced Bcl-2/Twist1 complex promotes tumor cell invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:7729–7739. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13890
Gong C, Gu R, Jin H, Sun Y, Li Z, Chen J, Wu G (2016) Lysyl oxidase mediates hypoxia-induced radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 241:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370215609694
Gu Q, He Y, Ji J, Yao Y, Shen W, Luo J, Zhu W, Cao H, Geng Y, Xu J, Zhang S, Cao J, Ding WQ (2015) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediates radiation-induced invasiveness through the SDF-1α/CXCR8 pathway in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 6:10893–11907
Ikezawa Y, Sakakibara-Konishi J, Mizugaki H, Oizumi S, Nishimura M (2017) Inhibition of Notch and HIF enhances the antitumor effect of radiation in Notch expressing lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 22:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-016-1031-8
Jin W, Wang J, Xu S, Xiao L, Chen G, Zhang W, Li J (2013) Radioprotective effect on HepG2 cells of low concentrations of cobalt chloride: induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and clearance of reactive oxygen species. J Radiat Res 54:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrs086
Kang MH, Reynolds CP (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:1126–1132. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0144
Kim WY, Oh SH, Woo JK, Hong WK, Lee HY (2009) Targeting heat shock protein 90 overrides the resistance of lung cancer cells by blocking radiation-induced stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Cancer Res 69:1624–1632. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472
Kim YH, Yoo KC, Cui YH, Uddin N, Lim EJ, Kim MJ, Nam SY, Kim IG, Suh Y, Lee SJ (2014) Radiation promotes malignant progression of glioma cells through HIF-1alpha stabilization. Cancer Lett 354:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.048
Kuo YC, Wu HT, Hung JJ, Chou TY, Teng SC, Wu KJ (2015) Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1 (NBS1) modulates hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) stability and promotes in vitro migration and invasion under ionizing radiation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 64:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2015.04.015
Li J, Ke Y, Huang M, Huang S, Liang Y (2015) Inhibitory effects of B-cell lymphoma 2 on the vasculogenic mimicry of hypoxic human glioma cells. Exp Ther Med 9:977–981
Liu L, Ning X, Sun L, Zhang H, Shi Y, Guo C, Han S, Liu J, Sun S, Han Z, Wu K, Fan D (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha contributes to hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 99:121–128
Liu K, Sun B, Zhao X, Wang X, Li Y, Qiu Z, Gu Q, Dong X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhao N (2015) Hypoxia induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and vasculogenic mimicry formation by promoting Bcl-2/Twist1 cooperation. Exp Mol Pathol 99:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.08.009
Loriot Y, Mordant P, Brown BD, Bourhis J, Soria JC, Deutsch E (2010) Inhibition of BCL-2 in small cell lung cancer cell lines with oblimersen, an antisense BCL-2 oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN): in vitro and in vivo enhancement of radiation response. Anticancer Res 30:3869–3878
Manickam DS, Hirata A, Putt DA, Lash LH, Hirata F, Oupický D (2008) Overexpression of Bcl-2 as a proxy redox stimulus to enhance activity of non-viral redox-responsive delivery vectors. Biomaterials 29:2680–2688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.03.009
Milani M, Venturini S, Bonardi S, Allevi G, Strina C, Cappelletti MR, Corona SP, Aguggini S, Bottini A, Berruti A, Jubb A, Campo L, Harris AL, Gatter K, Fox SB, Generali D, Roviello G (2017) Hypoxia-related biological markers as predictors of epirubicin-based treatment responsiveness and resistance in locally advanced breast cancer. Oncotarget 8:78870–78881. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20239
Miyasaka A, Oda K, Ikeda Y, Sone K, Fukuda T, Inaba K, Makii C, Enomoto A, Hosoya N, Tanikawa M, Uehara Y, Arimoto T, Kuramoto H, Wada-Hiraike O, Miyagawa K, Yano T, Kawana K, Osuga Y, Fujii T (2015) PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibition overcomes radioresistance via suppression of the HIF1-α/VEGF pathway in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 138:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.04.015
Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2012) Nrf2 protein up-regulates antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem 287:9873–9886. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.312694
Provencio M, Sánchez A (2014) Therapeutic integration of new molecule-targeted therapies with radiotherapy in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 3:89–94. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751
Radwan SM, Hamdy NM, Hegab HM, El-Mesallamy HO (2016) Beclin-1 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α genes expression: potential biomarkers in acute leukemia patients. Cancer Biomark 16:619–626. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160603
Rajendran JG, Mankoff DA, O’Sullivan F, Peterson LM, Schwartz DL, Conrad EU, Spence AM, Muzi M, Farwell DG, Krohn KA (2004) Hypoxia and glucose metabolism in malignant tumors: evaluation by [18F]fluoromisonidazole and [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging. Clin Cancer Res 10:2245–2252. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0688-3
Schmidt LH, Görlich D, Spieker T, Rohde C, Schuler M, Mohr M, Humberg J, Sauer T, Thoenissen NH, Huge A, Voss R, Marra A, Faldum A, Müller-Tidow C, Berdel WE, Wiewrodt R (2014) Prognostic impact of Bcl-2 depends on tumor histology and expression of MALAT-1 lncRNA in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 9:1294–1304. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000243
Sermeus A, Genin M, Maincent A, Fransolet M, Notte A, Leclere L, Riquier H, Arnould T, Michiels C (2012) Hypoxia-induced modulation of apoptosis and BCL-2 family proteins in different cancer cell types. PLoS One 7:e47519. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047519
Subtil FS, Wilhelm J, Bill V, Westholt N, Rudolph S, Fischer J, Scheel S, Seay U, Fournier C, Taucher-Scholz G, Scholz M, Seeger W, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Rose F, Dahm-Daphi J, Hänze J (2014) Carbon ion radiotherapy of human lung cancer attenuates HIF-1 signaling and acts with considerably enhanced therapeutic efficiency. FASEB J 28:1412–1421. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-242230
Sun Y, Xing X, Liu Q, Wang Z, Xin Y, Zhang P, Hu C, Liu Y (2015) Hypoxia-induced autophagy reduces radiosensitivity by the HIF-1α/miR-210/Bcl-2 pathway in colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 46:750–756. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2745
Tomiyama A, Tachibana K, Suzuki K, Seino S, Sunayama J, Matsuda KI, Sato A, Matsumoto Y, Nomiya T, Nemoto K, Yamashita H, Kayama T, Ando K, Kitanaka C (2010) MEK-ERK-dependent multiple caspase activation by mitochondrial proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins is essential for heavy ion irradiation-induced glioma cell death. Cell Death Dis 1:e60. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2010.37
van der Heijden M, Zimberlin CD, Nicholson AM, Colak S, Kemp R, Meijer SL, Medema JP, Greten FR, Jansen M, Winton DJ, Vermeulen L (2016) Bcl-2 is a critical mediator of intestinal transformation. Nat Commun 7:10916. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10916
Wang JH, Wu QD, Bouchier-Hayes D, Redmond HP (2002) Hypoxia upregulates Bcl-2 expression and suppresses interferon-gamma induced antiangiogenic activity in human tumor derived endothelial cells. Cancer 94:2745–2755
Yang C, He L, He P, Liu Y, Wang W, He Y, Du Y, Gao F (2015a) Increased drug resistance in breast cancer by tumor-associated macrophages through IL-10/STAT3/bcl-2 signaling pathway. Med Oncol 32:352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0352-6
Yang L, Liu L, Xu Z, Liao W, Feng D, Dong X, Xu S, Xiao L, Lu J, Luo X, Tang M, Bode AM, Dong Z, Sun L, Cao Y (2015b) EBV-LMP1 targeted DNAzyme enhances radiosensitivity by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis via the JNKs/HIF-1 pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:5804–5817
Zhang M, Qiu Q, Li Z, Sachdeva M, Min H, Cardona DM, DeLaney TF, Han T, Ma Y, Luo L, Ilkayeva OR, Lui K, Nichols AG, Newgard CB, Kastan MB, Rathmell JC, Dewhirst MW, Irsch DG (2015) HIF-1 alpha regulates the response of primary sarcomas to radiation therapy through a cell autonomous mechanism. Radiat Res 183:594–609
Zhao Y, Butler EB, Tan M (2013) Targeting cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis 4:e532. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.60
Zhao Q, Li Y, Tan BB, Fan LQ, Yang PG, Tian Y (2015) HIF-1α induces multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by inducing MiR-27a. PLoS One 10:e0132746. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132746
Zou K, Tong E, Xu Y, Deng X, Zou L (2014) Down regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin decreases HIF-1α and survivin expression in anoxic lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell to elemene and/or irradiation. Tumour Biol 35:9735–9741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2226-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1432124 and 81673099). We appreciate the assistance by Ms. Micha Davila (Centre for Molecular Immunology and Infectious Disease, the Pennsylvania State University) for improvement of the English of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Xiao, L., Wang, F. et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α/B-cell lymphoma 2 signaling impacts radiosensitivity of H1299 non-small cell lung cancer cells in a normoxic environment. Radiat Environ Biophys 58, 439–448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-019-00802-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-019-00802-4