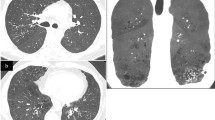
Abstract
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare multisystemic disease of women of child-bearing age and affects mainly the lungs, promoting cystic destruction of lung parenchyma or leading to abdominal tumor formation (e.g., angiomyolipomas, lymphangioleiomyomas). LAM can arise sporadically or in association with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), an autosomal inherited syndrome characterized by hamartoma-like tumor growth and pathologic features that are distinct from manifestations of pulmonary LAM. A substantial body of evidence has now been gathered suggesting that the two diseases share a common genetic origin. TSC is caused by mutations in two genes, TSC1 on chromosome 9q34 and TSC2 on 16p13. Both of these genes are tumor suppressor genes encoding hamartin (TSC1) and tuberin (TSC2). Sporadic LAM is correlated with a mutation in the TSC2 gene and tuberin appears to play a central role in the pathogenesis of the disease. A TSC2 loss or mutation leads to disruption of the tuberin-hamartin heteromer and dysregulation of S6K1 activation leading to aberrant cell proliferation seen in LAM disease. The extremely diverse clinical and radiologic features of the disease and the complex therapeutic approach are reviewed in detail. Although new therapeutic agents have been tested, to date no effective treatment has been proposed and the prognosis of patients with LAM remains poor. As long as newer therapeutic agents do not change this picture, lung transplantation remains the last hope for patients with respiratory failure at the advanced stage of the disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LAM:
-
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- TSC:
-
Tuberous sclerosis complex
- LOH:
-
Loss of heterozygosity
- PFTs:
-
Pulmonary function tests
- AMLs:
-
Renal angiomyolipomas
- LCC:
-
Lymphatic endothelial cells
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
References
Steagall WK, Taveira-DaSilva AM, Moss J (2005) Clinical and molecular insights into lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 22(Suppl 1):S49–S66
Johnson SR (2006) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Eur Respir J 27:1056–1065
Ryu JH, Moss J, Beck GJ, Lee JC, Brown KK, Chapman JT, Finlay GA, Olson EJ, Ruoss SJ, Maurer JR, Raffin TA, Peavy HH, McCarthy K, Taveira-DaSilva A, McCormack FX, Avila NA, Decastro RM, Jacobs SS, Stylianou M, Fanburg BL, NHLBI LAM Registry Group (2006) The NHLBI lymphangioleiomyomatosis registry: charactreristics of 230 patients at enrollment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:105–111
Cohen MM, Pollock-BarZiv S, Johnson SR (2005) Emerging clinical picture of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Thorax 60:875–879
Johnson SR, Tattersfield AE (2000) Clinical experience of lymphangioleiomyomatosis in the UK. Thorax 55:1052–1057
Khalife WI, Mahmoud F, Larson E, Hardie R (2005) Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis in a postmenopausal woman: case report with review of literature. S D J Med 58(4):139–143
Johnson SR, Tattersfield AE (2002) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 23(2):85–92
Yano S (2002) Exacerbation of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis by exogenous oestrogen used for infertility treatment. Thorax 57:1085–1086
Urban TJ, Lazor R, Lacronique J, Murris M, Labrune S, Valeyre D, Cordier JF (1999) Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a study of 69 patients. Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies “Orphelines” Pulmonaires (GERM”O”P). Medicine (Baltimore) 78:321–337
Wahedna I, Cooper S, Williams J, Paterson IC, Britton JR, Tattersfield AE (1994) Relation of pulmonary lymphangio-leiomyomatosis to use of the oral contraceptive pill and fertility in the UK: a national case control study. Thorax 49(9):910–914
Torres VE, Bjornsson J, King BF, Kumar R, Zincke H, Edell ES, Wilson TO, Hattery RR, Gomez MR (1995) Extrapulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis and lymphangiomatous cysts in tuberous sclerosis complex. Mayo Clin Proc 70:641–648
McCormack FX (2008) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a clinical update. Chest 133:507–516
Smolarek TA, Wessner LL, McCormack FX, Mylet JC, Menon AG, Henske EP (1998) Evidence that lymphangiomyomatosis is caused by TSC2 mutations: chromosome 16p13 loss of heterozygosity in angiomyolipomas and lymph nodes from women with lymphangiomyomatosis. Am J Hum Genet 62:810–815
Hancok E, Tomkins S, Sampson J, Osborne J (2002) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis and tuberous sclerosis. Respir Med 96(1):7–13
Moss J, Avila NA, Barnes PM, Litzenberger RA, Bechtle J, Brooks PG, Hedin CJ, Hunsberger S, Kristof AS (2001) Prevalence and clinical characteristics of lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:669–671
Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP (2006) The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med 355:1345–1356
Finlay G (2004) The LAM cell: what is it, where does it come from, and why does it grow? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L690–L693
McCormack F, Brody A, Meyer C, Leonard J, Chuck G, Dabora S, Sethuraman G, Colby TV, Kwiatkowski DJ, Franz DN (2002) Pulmonary cysts consistet with lymphangioleiomyomatosis are common in women with tuberous sclerosis: genetics and radiographic analysis. Chest 121(3 Suppl):61S
Sullivan EJ (1998) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a review. Chest 114:1689–1703
Logginidou H, Ao X, Russo I, Henske EP (2000) Frequent estrogen and progesterone receptor immunoreactivity in renal angiomyolipomas from women with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Chest 117:25–30
Johnson S (1999) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: clinical features, management and basic mechanisms Thorax 54:254–264
Carsillo T, Astrinidis A, Henske EP (2000) Mutations in the tuberous sclerosis complex gene TSC2 are a cause of sporadic pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6085–6090
Astrinidis A, Khare L, Carsillo T, Smolarek T, Au KS, Northrup H, Henske EP (2000) Mutational analysis of the tuberous sclerosis gene TSC2 in patients with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. J Med Genet 37:55–57
Yu J, Astrinidis A, Henske EP (2001) Chromosome 16 loss of heterozygosity in tuberous sclerosis and sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1537–1540
McManus EJ, Alessi DR (2002) TSC1-TSC2: a complex tale of PKB-mediated S6K regulation. Nat Cell Biol 4:E214–E216
Goncharova EA, Goncharov DA, Eszterhas A, Hunter DS, Glassberg MK, Yeung RS, Walker CL, Noonan D, Kwiatkowski DJ, Chou MM, Panettieri RA Jr, Krymskaya VP (2002) Tuberin regulates p70 S6 kinase activation and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylationA role for the TSC2 tumor suppressor gene in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). J Biol Chem 277:30958–30967
Nellist M, van Slegtenhorst MA, Goedbloed M, van den Ouweland AM, Halley DJ, van der Sluijs P (1999) Characterization of the cytosolic tuberin-hamartin complex: tuberin is a cytosolic chaperone for hamartin. J Biol Chem 274:35647–35652
Goncharova EA, Krymskaya VP (2008) Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): progress and current challenges. J Cell Biochem 103:369–382
Wienecke R, Konig A, DeClue JE (1995) Identification of tuberin, the tuberous sclerosis-2 product: tuberin possesses specific Rap1GAP activity. J Biol Chem 270:16409–16414
Krymskaya VP (2008) Smooth muscle-like cells in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:119–126
Goncharova EA, Goncharov DA, Spaits M, Noonan DJ, Talovskaya EV, Eszterhas A, Krymskaya VP (2006) Abnormal smooth muscle cell growth in lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): role for tumor suppressor TSC2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 34(5):561–572
Astrinidis A, Henske EP (2005) Tuberous sclerosis complex: linking growth and energy signalling pathways with human disease. Oncogene 24(50):7475–7481
Vignola AM, Paganin F, Capieu L, Scichilone N, Bellia M, Maakel L, Bellia V, Godard P, Bousquet J, Chanez P (2004) Airway remodelling assessed by sputum and high resolution computed tomography in asthma and COPD. Eur Respir J 24(6):910–917
Matsui K, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Travis WD, Moss J, Ferrans VJ (2000) Role for activation of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124:267–275
Hayashi T, Fleming MV, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Fishback N, Koss MN, Liotta LA, Ferrans VJ, Travis WD (1997) Immunohistochemical study of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). Hum Pathol 28:1071–1078
Zhe X, Yang Y, Jakkaraju S, Schuger L (2003) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 downregulation in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: potential consequence of abnormal serum response factor expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28:504–511
Hill C S, Wynne J, Treisman R (1995) The Rho family of GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell 81:1159–1170
Krymskaya VP, Shipley JM (2003) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a complex tale of serum response factor-mediated tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28(5):546–550
Almoosa KF, McCormack FX, Sahn SA (2006) Pleural disease in LAM. Clin Chest Med 27(2):355–368
Taveira-DaSilva AM, Hedin C, Stylianou MP, Travis WD, Matsui K, Ferrans VJ, Moss J (2001) Reversible airflow obstruction, proliferation of abnormal smooth muscle cells and impairment of gas exchange as predictors of outcome in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1072–1076
Yamakado K, Tanaka N, Nakagawa T, Kobayashi S, Yanagawa M, Takeda K (2002) Renal angiomyolipoma: relationships between tumor size, aneurysm formation, and rupture. Radiology 225:78–82
L’Hostis H, Deminiere C, Ferriere JM, Coindre JM (1999) Renal angiomyolipoma: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and follow-up study of 46 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 23:1011–1020
Matsui K, Tatsuguchi A, Valencia J, Yu Z, Bechtle J, Beasley MB, Avila N, Travis WD, Moss J, Ferrans VJ (2000) Extrapulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): clinicopathologic features in 22 cases. Hum Pathol 31:1242–1248
Avila NA, Chen CC, Chu SC, Wu M, Jones EC, Neumann RD, Moss J (2000) Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: correlation of ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy, chest radiography, and CT with pulmonary function tests. Radiology 214:441–446
Harari S, Paciocco G (2005) An integrated clinical approach to diffuse cystic lung diseases. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 22(Suppl 1):S31–S39
Paciocco G, Uslenghi E, Bianchi A, Mazzarella G, Roviaro GC, Vecchi G, Harari S (2004) Diffuse cystic lung diseases: correlation between radiologic and functional status. Chest 125:135–142
Taveira-DaSilva AM, Stylianou MP, Hedin CJ, Kristof AS, Avila NA, Rabel A, Travis WD, Moss J (2003) Maximal oxygen uptake and severity of disease in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:1427–1431
Gyatt GH, Pugsley SO, Sullivan MJ, Thompson PJ, Berman L, Jones NL, Fallen EL, Taylor DW (1984) Effect of encouragement on walking test performance. Thorax 39(11):818–822
Bonetti F, Chiodera PL, Pea M, Martignoni G, Bosi F, Zamboni G, Mariuzzi GM (1993) Transbronchial biopsy in lymphangiomyomatosis of the lung: HMB45 for diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol 17:1092–1102
Oberstein EM, Fleming LE, Gomez-Marin O, Glassberg MK (2003) Pulmonary lymphangio-leiomyomatosis (LAM): examining oral contraceptive pills and onset of disease. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 12:81–85
Taveira-DaSilva AM, Stylianou MP, Hedin CJ, Hathaway O, Moss J (2005) Bone mineral density in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:61–67
Yu J, Astrinidis A, Howard S, Henske EP (2004) Estradiol and tamoxifen stimulate LAM-associated angiomyolipoma cell growth and activate both genomic and nongenomic signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L694–L700
Finlay GA, Hunter DS, Walker CL, Paulson KE, Fanburg BL (2003) Regulation of PDGF production and ERK activation by estrogen is associated with TSC2 gene expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C409–C418
Eliasson AH, Phillips YY, tenholder MF (1989) Treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a meta-analysis. Chest 96:1352–1355
Denoo X, Hermans G, Degives R, Foidart JM (1999) Successful treatment of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis with progestins. Chest 115:276–279
Matsui K, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Valencia J, Travis WD, Moss J, Ferrans VJ (2000) Downregulation of estrogen and progesterone receptors in the abnormal smooth muscle cells in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis following therapy: an immunochemical study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(3 Pt 1):1002–1009
Civic D, Scholes D, Ichikawa L, LaCroix AZ, Yoshida CK, Ott SM, Barlow WE (2000) Depressive symptoms in users and non-users of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate. Contraception 61:385–890
Ohori NP, Yousem SA, Sonmez-Alpan E, Colby TV (1991) Estrogen and progesterone receptors in lymphangioleiomyomatosis, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, and sclerosing hemangioma of the lung. Am J Clin Pathol 96(4):529–535
Johnson SR, Tattersfield AE (1999) Decline in lung function in patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis: effect of menopause and progesterone treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:628–633
Taveira-DaSilva AM, Stylianou MP, Hedin CJ, Hathaway O, Moss J (2004) Decline in lung function in patients with Lymphangioleiomyomatosis treated with or without progesterone. Chest 126:1867–1874
Desurmont S, Bauters C, Copin MC, Dewailly D, Tonnel AB, Wallaert B (1996) [Treatment of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis using a GnRH agonist]. Rev Mal Respir 13:300–304 [in French]
Rossi GA, Balbi B, Oddera S, Lantero S, Ravazzoni C (1991) Response to treatment with an analog of the luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone in a patient with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 143(1):174–176
Harari S, Cassandro R, Chiodini J, Taveira-DaSilva AM, Moss J (2008) Effect of a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogue on lung function in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Chest 133:448–454
Almoosa KF, Ryu JH, Mendez J, Huggins JT, Young LR, Sullivan EJ, Maurer J, McCormack FX, Sahn SA (2006) Management of pneumothorax in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: effects on recurrence and lung transplantation complications. Chest 129:1274–1281
Ryu JH, Doerr CH, Fisher SD, Olson EJ, Sahn SA (2003) Chylothorax in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Chest 123:623–627
Johnson SR, Tattersfield AE (1998) Pregnancy in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:A807
Fujimoto M, Ohara N, Sasaki H, Funakoshi T, Morita H, Deguchi M, Maruo T (2005) Pregnancy complicated with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: case report. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 32(3):199–200
Boehler A, Speich R, Russi EW, Weder W (1996) Lung transplantation for lymphangioleiomyomatosis. N Engl J Med 335:1275–1280
Kpodonou J, Massad MG, Chaer RA, Caines A, Evans A, Snow NJ, Geha AS (2005) The US experience with lung transplantation for pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. J Heart Lung Transplant 24(9):1247–1253
O’Brien JD, Lium JH, Parosa JF, Deyoung BR, Wick MR, Trulock EP (1995) Lymphangiomyomatosis recurrence in the allograft after single-lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:2033–2036
Karbowniczek M, Astrinidis A, Balsara BR, Testa JR, Lium JH, Colby TV, McCormack FX, Henske EP (2003) Recurrent lymphangiomyomatosis after transplantation: genetic analyses reveal a metastatic mechanism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:976–982
Bittmann I, Dose TB, Muller C, Dienemann H, Vogelmeier C, Lohrs U (1997) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: recurrence after single lung transplantation. Hum Pathol 28:1420–1423
Bittman I, Rolf B, Amann G, Lohrs U (2003) Recurrence of lymphangioleiomyomatosis after single lung transplantation: new insights into pathogenesis. Hum Pathol 34(1):95–98
Dabbeche C, Chaker M, Chemali R, Perot V, El Hajj L, Ferriere JM, Ballanger P, Chabbert V, Cimpean A, Otal P, Huyghe E, Grenier N, Joffre F (2006) Role of embolization in renal angiomyolipomas. J Radiol 87(12 Pt 1):1859–1867
Lazor R, Valeyre D, Lacronique J, Wallaert B, Urbane T, Cordier JF, The Group d’ Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies Orphelines Pulmonaires (2004) Low initial KCO predicts rapid FEV1 decline in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Respir Med 98(6):536–541
Johnson SR, Whale CI, Hubbard RB, Lewis SA, Tattersfield AE (2004) Survival and disease progression in UK patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Thorax 59:800–803
Sawicka EH, Morris AJ (1985) A report of two long-surviving cases of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis and the response to progesterone therapy. Br J Dis Chest 79(4):400–406
Buhaescu I, Izzedine H, Covic A (2006) Sirolimus–challenging current perspectives. Ther Drug Monit 28(5):577–584
Grinyo JM, Cruzado JM (2006) Mycophenolate mofetil and sirolimus combination in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant 6(9):1991–1999
Taille C, Debray MP, Crestani B (2007) Sirolimus treatment for pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Ann Intern Med 146(9):687–688
Bissler JJ, McCormack FX, Young LR, Elwing JM, Chuck G, Leonard JM, Schmithorst VJ, Laor T, Brody AS, Bean J, Salisbury S, Franz DN (2008) Sirolimus for angiomyolipoma in tuberous sclerosis complex or lymphangioleiomyomatosis. N Engl J Med 358:140–151
Taveira-DaSilva AM, Steagall WK, Moss J (2006) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Cancer Control 13(4):276–285
Franco C, Ho B, Mulholland D, Hou G, Islam M, Donaldson K, Bendeck MP (2006) Doxycycline alters vascular smooth muscle cell adhesion, migration, and reorganization of fibrillar collagen matrices. Am J Pathol 168:1697–1709
Moses MA, Harper J, Folkman J (2006) Doxycycline treatment for lymphangioleiomyomatosis with urinary monitoring for MMPs. N Engl J Med 354:2621–2622
Valencia JC, Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Carmona AK, Xavier J, Bruneval P, Riemenschneider WK, Ikeda Y, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Moss J (2006) Tissue-specific renin-angiotensin system in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35(1):40–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chorianopoulos, D., Stratakos, G. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Lung 186, 197–207 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-008-9087-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-008-9087-5