Abstract
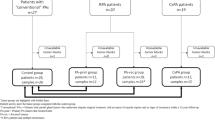
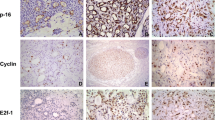
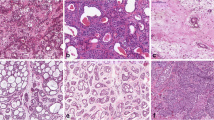
DNA repair systems play a critical role in protecting the human genome against cumulative damage. The apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a protein involved in DNA base excision repair and its expression still needs to be investigated in salivary gland tumors. The objective of this study is to analyze the immunoexpression of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 in pleomorphic adenomas and carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands. A total of 33 pleomorphic adenomas and 16 carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands underwent immunohistochemical study by the polymeric biotin-free technique. Immunopositive cells were analyzed quantitatively. For statistical analysis, Mann–Whitney test was performed and a significance level was set at p ≤ 0.05. All analyzed tumors (n = 49) were positive for apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1. However, there was a higher median expression in carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas (p < 0.001). There was no difference between this protein immunoexpression and tumors of major or minor salivary gland. Overexpression was found mainly in cases of carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.002) and invasive growth (p = 0.003), when compared to cases without metastasis and without capsular invasion (intracapsular pattern). Our findings revealed that apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is downregulated in pleomorphic adenomas and overexpressed in carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas, suggesting that this protein is possibly deregulated in pleomorphic adenoma malignant transformation. Furthermore, the increased expression of this protein is associated with a more aggressive behavior in carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenomas, which suggests that this protein may represent a prognostic biomarker in the studied salivary gland tumors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mariano FV, Noronha ALF, Gondak RO, Altemani AM, De Almeida OP, Kowalski LP (2013) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma in a Brazilian population: clinico-pathological analysis of 38 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:685–692. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2013.02.012
Hellquist HB, Skalova A (2014) Histopathology of the salivary glands. Springer, Heidelberg
Kim JW, Kwon GY, Roh JL, Choi SH, Nam SY, Kim SY et al (2011) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary glands: distinct clinicopathologic features and immunoprofiles between subgroups according to cellular differentiation. J Korean Med Sci 26:1277–1285. doi:10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1277
Bittar RF, Ferraro HP, Moraes Gonçalves FT, Couto da Cunha MG, Biamino ER (2015) Neoplasms of the salivary glands: analysis of 727 histopathological reports in a single institution. Otolaryngol Pol 69:29–34. doi:10.5604/00306657.1163578
Antony J, Gopalan V, Smith RA, Lam AKY (2012) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a comprehensive review of clinical, pathological and molecular data. Head Neck Pathol 6:1–9. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0281-z
Tell G, Damante G, Caldwell D, Kelley MR (2005) The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:804–813. doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1903
Tell G, Quadrifoglio F, Tiribelli C, Kelley MR (2009) The many functions of APE1/Ref-1: not only a DNA repair enzyme. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:601–619. doi:10.1089/ars.2008.2194
Hsia KT, Liu CJ, Mar K, Lin LH, Lin CS, Cheng MF et al (2016) The impact of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1) on treatment response and survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 38:550–559. doi:10.1002/hed.23927
Li Q, Wang JM, Peng Y, Zhang SH, Ren T, Luo H et al (2013) Association of DNA base-excision repair XRCC1, OGG1 and APE1 gene polymorphisms with nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility in a Chinese population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:5145–5151. doi:10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.9.5145
Di Maso V, Avellini C, Crocè LS, Rosso N, Quadrifoglio F, Cesaratto L et al (2006) Subcellular localization of APE1/Ref-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma: possible prognostic significance. Mol Med 13:30–39. doi:10.2119/2006
Woo J, Park H, Sung SH, Moon BI, Suh H, Lim W (2014) Prognostic value of human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) expression in breast cancer. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099528
Li Z, Qing Y, Guan W, Li M, Peng Y, Zhang S et al (2014) Predictive value of APE1, BRCA1, ERCC1 and TUBB3 expression in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving first-line platinum-paclitaxel chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74:777–786. doi:10.1007/s00280-014-2562-1
Mahjabeen I, Ali K, Zhou X, Kayani MA (2014) Deregulation of base excision repair gene expression and enhanced proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol 35:5971–5983. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-1792-5
Seiwert TY, Wang X, Heitmann J, Villegas-Bergazzi V, Sprott K et al (2014) DNA repair biomarkers XPF and phospho-MAPKAP kinase 2 correlate with clinical outcome in advanced head and neck cancer. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102112
Shin JH, Choi S, Lee YR, Park MS, Na YG, Irani K et al (2015) APE1/ref-1 as a serological biomarker for the detection of bladder cancer. Cancer Res Treat 47:823–833. doi:10.4143/crt.2014.074
Alaizari NA, Tarakji B, Al-Maweri SA, Al-Shamiri HM, Darwish S, Baba F (2015) p53 expression in pleomorphic adenoma of salivary glands: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Oral Biol 60:1437–1441. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.06.019
Skalova A, Altemani A, Di Palma S, Simpson RH, Hosticka L, Andrle P et al (2012) Pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary glands with intravascular tumor deposits: a diagnostic pitfall. Am J Surg Pathol 36:1674–1682. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182690afe
Soares A, Altemani A, De Araújo VC (2011) Study of histopathological, morphological and immunohistochemical features of recurrent pleomorphic. J Oral Pathol Med 40:352–358. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00956.x
Di Palma S (2013) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, with particular emphasis on early lesions. Head Neck Pathol 7:68–76. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0454-z
Obtulowicz T, Swoboda M, Speina E, Gackowski D, Rozalski R, Siomek A et al (2010) Oxidative stress and 8-oxoguanine repair are enhanced in colon adenoma and carcinoma patients. Mutagenesis 25:463–471. doi:10.1093/mutage/geq028
Qing Y, Li Q, Ren T, Xia W, Peng Y, Liu GL et al (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 and APE1 is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:901–909. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S75152
Altemani A, Martins MT, Freitas L, Soares F, Araújo NS, Araújo VC (2005) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA): immunoprofile of the cells involved in carcinomatous progression. Histopathology 46:635–641. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02157.x
Nagoya H, Futagami S, Shimpuku M, Tatsuguchi A, Wakabayashi T, Yamawaki H et al (2014) Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1 is associated with angiogenesis and VEGF production via upregulation of COX-2 expression in esophageal cancer tissues. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 306:G183–G190. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00057.2013
Puglisi F, Barbone F, Tell G, Aprile G, Pertoldi B, Raiti C et al (2002) Prognostic role of Ape/Ref-1 subcellular expression in stage I–III breast PubMed commons. Oncol Rep 9:11–17
Wang D, Luo M, Kelley MR (2004) Human apurinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) expression and prognostic significance in osteosarcoma: enhanced sensitivity of osteosarcoma to DNA damaging agents using silencing RNA APE1 expression inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther 3:679–686 (pii:3/6/679)
Moore DH, Michael H, Tritt R, Parsons SH, Kelley MR (2000) Alterations in the expression of the DNA repair/redox enzyme APE/ref-1 in epithelial ovarian cancers 1. Clin Cancer Res 6:602–609
Kakolyris S, Kaklamanis L, Engels K, Fox SB, Taylor M, Hickson ID et al (1998) Human AP endonuclease 1 (HAP1) protein expression in breast cancer correlates with lymph node status and angiogenesis. Br J Cancer 77:1169–1173
Sheng Q, Zhang Y, Wang R, Zhang J, Chen B, Wang J et al (2012) Prognostic significance of APE1 cytoplasmic localization in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Med Oncol 29:1265–1271. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9931-y
Al-Attar A, Gossage L, Fareed KR, Shehata M, Mohammed M, Zaitoun AM et al (2010) Human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE1) is a prognostic factor in ovarian, gastro-oesophageal and pancreatico-biliary cancers. Br J Cancer 102:704–709. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605541
Santana T, Sá MC, Santos EM, Galvão HC, Coletta RD, Freitas RF (2017) DNA base excision repair proteins APE-1 and XRCC-1 are overexpressed in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Path Med. doi:10.1111/jop.12529
Ang MK, Patel MR, Yin XY, Sundaram S, Fritchie K, Zhao N, Liu Y et al (2011) High XRCC1 protein expression is associated with poorer survival in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17(20):6542–6552. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1604
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving the patient were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The approval of the local ethics committee is present in the methods section in this article.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patients in this study.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, L.P., Santana, T., Sedassari, B.T. et al. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) is overexpressed in malignant transformation of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3203–3209 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4605-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4605-9