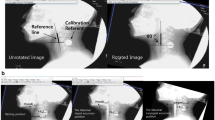
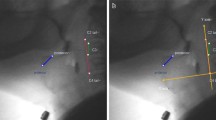
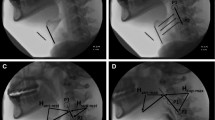
Abstract
Reduced hyoid displacement is thought to contribute to aspiration and pharyngeal residues in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients with dysphagia. To further study hyoid elevation and anterior excursion in HNC patients, this study reports on temporal/kinematic measures of hyoid displacement, with the additional goal to investigate correlations with clinical swallowing impairment. A single-blind analysis of data collected as part of a larger prospective study was performed at three time points before and after chemoradiotherapy. Twenty-five patients had undergone clinical swallowing assessments at baseline, 10-weeks, and 1-year post-treatment. Analysis of videofluoroscopic studies was done on different swallowing consistencies of varying amounts. The studies were independently reviewed frame-by-frame by two clinicians to assess temporal (onset and duration) and kinematic (anterior/superior movement) measures of hyoid displacement (ImageJ), laryngeal penetration/aspiration, and presence of vallecula/pyriform sinus residues. Patient-reported oral intake and swallowing function were also evaluated. Mean maximum hyoid displacement ranged from 9.4 mm (23 % of C2–4 distance) to 12.6 mm (27 %) anteriorly, and from 18.9 mm (41 %) to 24.9 mm (54 %) superiorly, depending on bolus volume and consistency. Patients with reduced superior hyoid displacement perceived significantly more swallowing impairment. No correlation between delayed or reduced hyoid excursion and aspiration or residue scores could be demonstrated. Hyoid displacement is subject to variability from a number of sources. Based on the results, this parameter seems not very valuable for clinical use in HNC patients with dysphagia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perlman AL, VanDaele DJ, Otterbacher MS (1995) Quantitative assessment of hyoid bone displacement from video images during swallowing. J Speech Hear Res 38(3):579–585
Bingjie L, Tong Z, Xinting S, Jianmin X, Guijun J (2010) Quantitative videofluoroscopic analysis of penetration-aspiration in post-stroke patients. Neurol India 58(1):42–47
Wang TG, Chang YC, Chen WS, Lin PH, Hsiao TY (2010) Reduction in hyoid bone forward movement in irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 91(6):926–931
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Chau T, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M, Waito AA, Zoratto DC (2011) The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin Otolaryngol 36(1):30–36
Pearson WG Jr, Hindson DF, Langmore SE, Zumwalt AC (2013) Evaluating swallowing muscles essential for hyolaryngeal elevation by using muscle functional magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(3):735–740
Zu Y, Yang Z, Perlman AL (2011) Hyoid displacement in post-treatment cancer patients: preliminary findings. J Speech Lang Hear Res 54(3):813–820
Hutcheson KA, Lewin JS, Barringer DA, Lisec A, Gunn GB, Moore MW, Holsinger FC (2012) Late dysphagia after radiotherapy-based treatment of head and neck cancer. Cancer 118(23):5793–5799
Kim Y, McCullough GH (2010) Maximal hyoid excursion in poststroke patients. Dysphagia 25(1):20–25
Molfenter SM, Steele CM (2014) Kinematic and temporal factors associated with penetration-aspiration in swallowing liquids. Dysphagia 29(2):269–276
Steele CM, Cichero JA (2014) Physiological factors related to aspiration risk: a systematic review. Dysphagia 29(3):295–304
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH (2000) Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res 43(5):1264–1274
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ (2001) Hyoid movement during swallowing in older patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surgery 127(10):1224–1229
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ (2002) Oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older women: videofluoroscopic analysis. J Speech Lang Hear Research 45(3):434–445
Kim Y, McCullough GH (2008) Maximum hyoid displacement in normal swallowing. Dysphagia 23(3):274–279
Paik NJ, Kim SJ, Lee HJ, Jeon JY, Lim JY, Han TR (2008) Movement of the hyoid bone and the epiglottis during swallowing in patients with dysphagia from different etiologies. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18(2):329–335
Dodds WJ, Man KM, Cook IJ, Kahrilas PJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK (1988) Influence of bolus volume on swallow-induced hyoid movement in normal subjects. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150(6):1307–1309
Nagy A, Molfenter SM, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Stokely S, Steele CM (2014) The effect of bolus volume on hyoid kinematics in healthy swallowing. BioMed Res Int 2014:738971
Sia I, Carvajal P, Carnaby-Mann GD, Crary MA (2012) Measurement of hyoid and laryngeal displacement in video fluoroscopic swallowing studies: variability, reliability, and measurement error. Dysphagia 27(2):192–197
Baijens L, Barikroo A, Pilz W (2013) Intrarater and interrater reliability for measurements in videofluoroscopy of swallowing. Eur J Radiol 82(10):1683–1695
Molfenter SM, Steele CM (2011) Physiological variability in the deglutition literature: hyoid and laryngeal kinematics. Dysphagia 26(1):67–74
Lal PT, Verma A, Maria Das KP, Baijal SS, Bajpai R, Kumar P, Srivastava A, Kumar S (2009) Role of videofluorography in assessing functional abnormalities in patients of head and neck cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Asia Pacific J Clin Oncol 5(5):264–269
van der Molen L, Heemsbergen WD, de Jong R, van Rossum MA, Smeele LE, Rasch CR, Hilgers FJ (2013) Dysphagia and trismus after concomitant chemo-Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (chemo-IMRT) in advanced head and neck cancer; dose-effect relationships for swallowing and mastication structures. Radiother Oncol 106(3):364–369
van der Molen L, van Rossum MA, Burkhead LM, Smeele LE, Rasch CR, Hilgers FJ (2011) A randomized preventive rehabilitation trial in advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy: feasibility, compliance, and short-term effects. Dysphagia 26(2):155–170
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL (1996) A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11(2):93–98
Logemann JA (1997) Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders, 2nd edn. Pro-ed, ISBN-10:0890797285, ISBN-13:978-0890797280, p 406
Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Logemann JA, Stein D, Beery Q, Newman L, Hanchett C, Tusant S, MacCracken E (2000) Pretreatment swallowing function in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 22(5):474–482
Kendall KA, McKenzie S, Leonard RJ, Goncalves MI, Walker A (2000) Timing of events in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia 15(2):74–83
Leonard RJ, Kendall KA, McKenzie S, Goncalves MI, Walker A (2000) Structural displacements in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia 15(3):146–152
Leonard R, Kendall C (1997) Dysphagia assessment and treatment planning: a team approach, 1st edn. Singular, ISBN-10:156593749X, ISBN-13:978-1565937499, p 320
van der Molen L, van Rossum MA, Ackerstaff AH, Smeele LE, Rasch CR, Hilgers FJ (2009) Pretreatment organ function in patients with advanced head and neck cancer: clinical outcome measures and patients’ views. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 9:10
van der Kruis JG, Baijens LW, Speyer R, Zwijnenberg I (2011) Biomechanical analysis of hyoid bone displacement in videofluoroscopy: a systematic review of intervention effects. Dysphagia 26(2):171–182
Kraaijenga SA, van der Molen L, Jacobi I, Hamming-Vrieze O, Hilgers FJ, van den Brekel MW (2015) Prospective clinical study on long-term swallowing function and voice quality in advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy and preventive swallowing exercises. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(11):3521–3531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was made possible by Grants provided by Atos Medical (Sweden), the Verwelius Foundation (The Netherlands), and “Stichting de Hoop” (The Netherlands).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Appendix I: Selection of the translated Dutch study-specific questionnaire
Appendix I: Selection of the translated Dutch study-specific questionnaire

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kraaijenga, S.A.C., van der Molen, L., Heemsbergen, W.D. et al. Hyoid bone displacement as parameter for swallowing impairment in patients treated for advanced head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 597–606 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4029-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4029-y