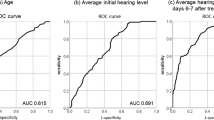
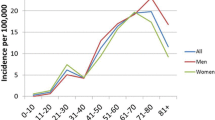
Abstract
The objective of this study is to investigate the clinical characteristics of successive bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) with an interval of more than 1 year to aid the evaluation and management of successive bilateral SSNHL (BSSNHL). 14 successive BSSNHL patients and 118 unilateral SSNHL patients with severe and profound hearing loss were reviewed retrospectively. Information about successive BSSNHL was collected included demographics, the intervals between the attacks of bilateral ears, the past medical history, inducing factors, accompanying symptoms, pure-tone tests, blood tests, b-ultrasound examinations of vertebral artery and carotid artery, and medical interventions. And the comparison of improvement rate was made between successive BSSNHL and unilateral SSNHL. SPSS 15.0 was used to analyze the data. In successive BSSNHL, there were six males and eight females; the average aged was 49.86 ± 15.45 years (20–73 years). The interval of the two attacks was 11.43 ± 12.07 years (1–50 years) on average. The onset of treatment was 18.86 ± 12.71 days. Tinnitus was seen in 100 % of the patients, followed by vertigo in 42.85 %, and ear fullness in 21.43 %. 3 of 14 patients described obvious inducing factor: tiredness. Five patients (35.71 %) had hypertension histories, three (21.43 %) had diabetes histories, two (14.29 %) had surgery histories, one (7.14 %) was with depression history, one (7.14 %) was with coronary heart disease history. 30 % (3/10) patients were with atherosclerotic plaque in carotid artery. 4 (28.57 %) patients were with high blood sugar. 8 patients (57.14 %) were with high blood lipids. Thyroid function tests were positive in 27.27 % (3/11) patients. No abnormality was found in antinuclear antibodies titer. The percentage of profound and severe hearing loss were 71.43 and 78.57 % in the recently affected ear and contralateral ear separately. The PTAs of the recently affected ear were 77.14 ± 27.12 dB before treatment and 68.84 ± 22.32 dB after treatment, the improvement rate was 28.57 %. No improvement was found in the contralateral ears. In unilateral SSNHL, the average age was 42.47 ± 14.18 years. The onset of treatment was 18.08 ± 15.84 days. The improvement rate was 57.63 %, which was much higher than that of successive BSSNHL. There was no difference in age and time of onset of treatment between successive BSSNHL and unilateral SSNHL (p > 0.05). Successive BSSNHL is rare, the hearing impairment is severe, and the outcome of treatment is poorer. It may have a completely different profile compared with the simultaneous BSSNHL and unilateral SSNHL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenman D, Arts HA (2000) Effectiveness of treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:1161–1164
Schreiber BE, Agrup C, Haskard DO, Luxon LM (2010) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 375:1203–1211
Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME (1996) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 29:393–405
Wolf M, Birger M, Ben Shoshan J, Kronenberg J (1983) Conversion deafness. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102:349–352
Mori S, Fujieda S, Yamamoto T, Takahashi N, Saito T, Saito H (2002) Psychogenic hearing loss with panic attack after the onset of acute inner ear disorder. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 64:41–44
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Barrs DM, Brown SR, Fife TD, Ford P, Ganiats TG, Hollingsworth DB, Lewandowski CA, Montano JJ, Saunders JE, Tucci DL, Valente M, Warren BE, Yaremchuk KL, Robertson PJ (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146(suppl 3):S1–S35. doi:10.1177/0194599812436449
Rauch SD (2008) Clinical practice. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. N Engl J Med 359:833–840. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0802129
Oh JH, Park K, Lee SJ, Shin YR, Choung YH (2007) Bilateral versus unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:87–91
Xenellis J, Nikolopoulos TP, Stavroulaki P, Marangoudakis P, Androulakis M, Tsangaroulakis M, Ferekidis E (2007) Simultaneous and sequential bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss: are they different from unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss? ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 69:306–310
Wang QJ, Lan L, Han B, Wang DY, Li Q, Ding HN, Li N, Zhao Y, Han DY, Yang WY (2010) A clinical and prognosis analysis for bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Chin J Otol 8(2):119–128. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2010.02.002 (Article in Chinese)
Lai W, Zhong SX, Qian Y, Hu GH, Hong SL, Wang L, Xu ZY (2014) Clinical characteristics and treatment of bilateral sudden sensornineural hearing loss: a report of 8 cases. Chin J Otology 12(4):597–602. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2014.04.023 (Article in Chinese)
Kuhn M, Heman-Ackah SE, Shaikh JA, Roehm PC (2011) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif 15:91–105. doi:10.1177/1084713811408349
Fetterman BL, Luxford WM, Saunders JE (1996) Sudden bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 106:1347–1350
Yanagita N, Murahashi K (1987) Bilateral simultaneous sudden deafness. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 244:7–10
Sara SA, Teh BM, Friedland P (2014) Bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss: review. J Laryngol Otol 128(Suppl 1):S8–S15. doi:10.1017/S002221511300306X
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N (1980) The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol 106:772–776
Mattox DE, Simmons FB (1977) Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86:463–480
Wang F, Liu XM, Zhu YH (2015) Study of the curative effect for middle and high frequency sudden sensorineural hearing loss by opisthotic dose way. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 29(4):359–360. doi:10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2015.04.017 (Article in Chinese)
Xu O, Wang JM, Liu YX, Zhang YB, Lu H (2013) Analysis of therapeutic effect of corticosteroid post auricle injection on sudden deafness after ear. J Audiol Speech Pathol 21(6):633–634
Yang XQ, Yu LS, Ma X (2007) Postaurieal injection of compound betamethasone to treat the intractable low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 42(11):814–816. doi:10.3760/j.issn:1673-0860.2007.11.004 (Article in Chinese)
Li KJ, Yu LS, Xia R, Gao FB, Luo WL, Jing YY (2012) Feasibility study of inner ear drug delivery via post-auricular injection using 7.0 Tesla MRI. Chin J Otol 10(2):144–148
Jing YY, Yu LS, Li XQ (2009) Compound Betameth pharmacokinetics in plasma of guinea pig after postaurieal injection. J Audiol Speech Pathol 14(4):354–357. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2009.04.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Ningbo Nature Science Foundation (No. 2013A610261).
Conflict of interest
Yaowen Wang, Litao Zhang, Jianhua Zhang, Xuqun Zhang, Weimin Zhang, Xing Chen, and Shixiong Tang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, J. et al. The clinical analysis of bilateral successive sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273, 3679–3684 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4028-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4028-z