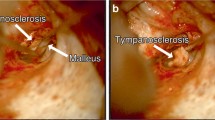
Abstract
We aimed to investigate the effect of stapes fixation on hearing results in patients who underwent mobilization surgery due to tympanosclerosis (TS). Seventy-nine patients were retrospectively analyzed and divided into two groups. Forty-four (55.7 %) patients with mobile stapes were classified as group 1, and 35 (44.3 %) patients with fixed stapes were classified as group 2. Improvement of the air-bone gap (ABG) to become less than 20 dB and the pure-tone average (PTA) by at least 10 dB postoperatively were accepted as success criteria. The PTA and ABG levels were significantly improved in both groups. The pre- and post-operative PTAs were 46.57 ± 15.55 and 25.84 ± 15.47 dB, respectively, in group 1 (p = 0.001). The pre- and post-operative PTAs were 55.64 ± 12.69 and 36.20 ± 14.47 dB, respectively, in group 2 (p = 0.001). The pre- and post-operative ABG levels were 35.36 ± 10.53 and 16.91 ± 8.54 dB, respectively, in group 1 (p = 0.001). The pre- and post-operative ABG levels were 41.68 ± 8.78 and 22.20 ± 10.03 dB, respectively, in group 2 (p = 0.001). A gain ≥10-dB in the PTA in groups 1 and 2 was found in 34 (77.2 %) and 23 (65.7 %) patients, respectively, and the difference between the groups was not significant (p = 0.684). The post-operative AGB in groups 1 and 2 was less than 20 dB in 32 (72.7 %) and 21 (60 %) patients, respectively, and the difference between the groups was not significant (p = 0.733). No significant negative effect of stapes fixation on post-operative hearing results in TS was detected. Successful results can be obtained with a mobilization procedure, even if the stapes is fixed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayazit YA, Ozer E, Kara C, Gokpinar S, Kanlikama M, Mumbuc S (2004) An analysis of the single-stage tympanoplasty with over-underlay grafting in tympanosclerosis. Otol Neurotol 25:211–214
Erdurak SC, Coskun BU, Sakalli E, Tansuker HD, Turan F, Kaya D (2014) Does the use of radiofrequency myringotomy for insertion of a ventilation tube reduce the incidence of myringosclerosis? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(3):459–462
Albu S, Babighian G, Trabalzini F (2000) Surgical treatment of tympanosclerosis. Am J Otol 2:631–635
Yetiser S, Hidir Y, Karatas E, Karapinar U (2007) Management of tympanosclerosis with ossicular fixation: review and presentation of long term results of 30 new cases. J Otolaryngol 36:303–308
Kizilkaya Z, Emir H, Ceylan K, Gocmen H, Samim E (2008) The effect of stapes mobility on hearing outcome and which procedure to choose in fixed stapes in children tympanosclerosis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolarnygol 72:849–856
Celik H, Felek SA, Islam A, Arslan N, Demirci M, Can IH (2008) The effect of mobility of ossicles and surgical approach on hearing results in patients with tympanosclerosis. Mediterr J Otol 4:184–190
American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head Neck Surgery Foundation Inc (1995) Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. Otolarnygol Head Neck Surg 113:186–187
Asiri S, Hasham A, al Anazy F et al (1999) Tympanosclerosis: review of literature and incidence among patients with middle-ear infection. J Laryngol Otol 113:1076–1080
Pal I, Sengupta A (2005) Clinicopathological and audiological study of tympanosclerosis. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 57:235–239
Tos M (2000) Surgical solutions for conductive hearing loss. Thieme, Stuttgart
Teufert KB, De La Cruz A (2002) Tympanosclerosis: long-term hearing results after ossicular reconstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:264–272
Vincent R, Oates J, Sperling NM (2002) Stapedetomy for tympanosclerotic stapes fixation: is it safe and efficient? A review of 68 cases. Otol Neurotol 23:866–872
Giddings NA, House JW (1992) Tympanosclerosis of the stapes : hearing results for various surgical treatments. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107:644–650
Tos M, Lau T, Arndal H et al (1990) Tympanosclerosis of the middle ear: late results of surgical treatment. J Laryngol Otol 104:685–689
Tsuzuki K, Yanagihara N, Hinohira Y, Sakagami M (2006) Tympanosclerosis involving the ossicular chain: mobility of the stapes in association with hearing results. Acta Otolaryngol 126:1046–1052
Smyth GDL (1982) Tympanomastoid disease. In: Smith MFW (ed) Gibb AG. Otology, London Butterworths, pp 3–18
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial obligations to disclose related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakalli, E., Celikyurt, C., Guler, B. et al. The effect of stapes fixation on hearing results in tympanosclerosis treated by mobilization. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3271–3275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3414-7