Abstract
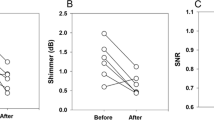
Type I thyroplasty—also called medialization thyroplasty (MT)—is considered as an effective treatment for glottic incompetence in general and for abductor vocal fold palsy in particular. In the past there have been some concerns about the experience a laryngeal framework surgeon should have in order achieve an acceptable voice outcome. To assess the learning curve of MT performed using the Montgomery® hard silicone implant. A retrospective study involving 36 patients divided into three consecutive groups (1, 2, 3) of 12 MT patients or six consecutive groups (1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b) of six MT patients. Outcome measures: acoustic and aerodynamic outcome improvements (δ) compared to the duration of intervention [operative times (OT)]. Data were analysed by Anova, Kuskal Wallis and χ 2 statistical tests, according to data distributions. OT decreased significantly between groups 1, 2 and 3 with a mean OT of 90.5′, 71.5′ and 56′ (p < 0.001), respectively. Objective δ such as maximum phonation time (MPT) (p 0.376), Estimated Sub-Glottic Pressure (ESPG) (p: 0.675) Shimmer (p: 0.543) and Jitter (p: 0.709) did not show significant improvement. Only the voice handicap index (VHI) δ of group 2 showed significant improvement (p 0.005) compared with the two other groups 1 and 3. Surgeon experience decreases the OT significantly. On the other hand, our study did not show a correlation between surgeon experience and voice outcome measures improvemnts (MPT, ESGP, Shimmer, Jitter).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montgomery WW, Blaugrund SM, Varvares MA (1993) Thyroplasty: a new approach. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102(8 Pt 1):571–579
Montgomery WW, Montgomery SK (1997) Montgomery thyroplasty implant system. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 170:1–16
Dejonckere PH, Bradley P, Clemente P, Cornut G, Crevier-Buchman L, Friedrich G, Van De Heyning P, Remacle M, Woisard V, Committee on Phoniatrics of the European Laryngological Society (ELS) (2001) A basic protocol for functional assessment of voice pathology, especially for investigating the efficacy of (phonosurgical) treatments and evaluating new assessment techniques. Guideline elaborated by the Committee on Phoniatrics of the European Laryngological Society (ELS). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258(2):77–82
Shen T, Damrose EJ, Morzaria S (2013) A meta-analysis of voice outcome comparing calcium hydroxylapatite injection laryngoplasty to silicone thyroplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148(2):197–208
Ryu IS, Nam SY, Han MW, Choi SH, Kim SY, Roh JL (2012) Long-term voice outcomes after thyroplasty for unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138(4):347–351
Sridhara SR, Ashok KG, Raghunathan M, Mann SB (2003) To study voice quality before and after thyroplasty type 1 in patients with symptomatic unilateral vocal cord paralysis. Am J Otolaryngol 24(6):361–365
Matar N, Remacle M, Bachy V, Lawson G, Giovanni A, Lejoly-Devuyst V, Legou T (2012) Objective measurement of real time subglottic pressure during medicalization thyroplasty: a feasibility study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(4):1171–1175
Storck C, Fischer C, Cecon M, Schmid S, Gambazzi F, Wolfensberger M, Brockmann M (2010) Hydroxyapatite versus titanium implant: Comparison of the functional outcome after vocal fold medialization in unilateral recurrent nerve paralysis. Head Neck 32(12):1605–1612
Laccourreye O, Benkhatar H, Ménard M (2012) Lack of adverse events after medialization laryngoplasty with the Montgomery thyroplasty implant in patients with unilateral laryngeal nerve paralysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 121(11):701–707
Laccourreye O, El Sharkawy L, Holsinger FC, Hans S, Ménard M, Brasnu D (2005) Thyroplasty type I with Montgomery implant among native French language speakers with unilateral laryngeal nerve paralysis. Laryngoscope 115(8):1411–1417
Devos M, Schultz P, Guilleré F, Debry C (2010) Thyroplasty for unilateral vocal fold paralysis using an adjustable implant in porous titanium. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 127(6):204–212
van Ardenne N, Vanderwegen J, Van Nuffelen G, De Bodt M, Van de Heyning P (2011) Medialization thyroplasty: vocal outcome of silicone and titanium implant. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268(1):101–107. doi:10.1007/s00405-010-1327-7
Rosen CA (1998) Complications of phonosurgery: results of a national survey. Laryngoscope 108(11 Pt 1):1697–1703
Young VN, Zullo TG, Rosen CA (2010) Analysis of laryngeal framework surgery: 10-year follow-up to a national survey. Laryngoscope 120(8):1602–1608
Conflict of interest
Authors deny any conflict of interest or financial interest with mentioned organization or company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desuter, G., Henrard, S., Boucquey, D. et al. Learning curve of medialization thyroplasty using a Montgomery™ implant. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 385–390 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3292-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3292-z