Abstract
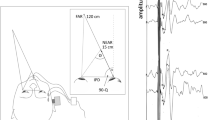
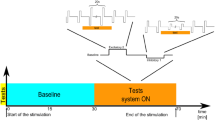
Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (oVEMPs) represent extraocular muscle activity in response to vestibular stimulation. oVEMP amplitudes are known to increase with increasing upward gaze angle, while the patient fixates a visual target. We investigated two different methods of presenting a visual target during oVEMP recordings. 57 healthy subjects were enrolled in this study. oVEMPs were elicited by 500 Hz air-conducted tone bursts while the subjects were looking upward at a marking which was either fixed on the wall or originated from a head-mounted laser attached to a headband, in either case corresponding to a 35° upward gaze angle. oVEMP amplitudes and latencies did not differ between the subjects looking at the fixed marking and the ones looking at the laser marking. The intra-individual standard deviation of amplitudes obtained by two separate measurements for each subject, however, as a measure of test–retest reliability, was significantly smaller for the laser headband group (0.60) in comparison to the group looking at the fixed marking (0.96; p = 0.007). The intraclass correlation coefficient revealed better test–retest reliability for oVEMP amplitudes when using the laser headband (0.957) than using the fixed marking (0.908). Hence, the use of a visual target originating from a headband enhances the reproducibility of oVEMPs. This might be due to the fact that the laser headband ensures a constant gaze angle and rules out the influence of small involuntary head movements on the gaze angle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kantner C, Gürkov R (2012) Characteristics and clinical applications of ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Hear Res 294:55–63
Rosengren SM, McAngus Todd NP, Colebatch JG (2005) Vestibular-evoked extraocular potentials produced by stimulation with bone-conducted sound. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1938–1948
Govender S, Rosengren SM, Colebatch JG (2009) The effect of gaze direction on the ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential produced by air-conducted sound. Clin Neurophysiol 120:1386–1391
Kantner C, Gürkov R (2013) The effects of commonly used upward gaze angles on ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Otol Neurotol 35:289–293
Iwasaki S, Smulders YE, Burgess AM et al (2008) Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials to bone conducted vibration of the midline forehead at Fz in healthy subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2135–2147
Rosengren SM, Colebatch JG, Straumann D, Weber KP (2013) Why do oVEMPs become larger when you look up? Explaining the effect of gaze elevation on the ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential. Clin Neurophysiol 124:785–791
Welgampola MS, Migliaccio AA, Myrie OA, Minor LB, Carey JP (2009) The human sound-evoked vestibulo-ocular reflex and its electromyographic correlate. Clin Neurophysiol 120:158–166
Acknowledgments
The Eclipse VEMP recording system was provided by Interacoustics AS, Assens, Denmark. This study was supported by the Federal German Ministry of Education and Research (Grant No. 01EO0901).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jerin, C., Bartl, K., Schneider, E. et al. Enhancing the reproducibility of ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials by use of a visual target originating from a head-mounted laser. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2737–2740 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3271-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3271-4