Abstract
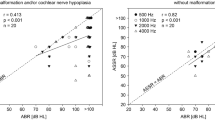
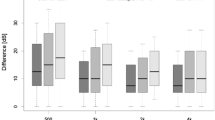
The aim of the study was to predict hearing level thresholds with click-evoked ABR and to study the residual hearing when ABR was absent. In 85 hearing-impaired children, the conclusive pure-tone hearing level thresholds are reported. The exclusion criterion used was deteriorating hearing loss. The Jewett V-wave was identified in 48.2% of the subjects and was bilaterally absent in 51.8%. The correlation between ABR and PTA (2–4 kHz) thresholds was significant ( P <0.01). Audiometrically, 65.9% of the children with no response on ABR had hearing, and in 34.5% of these, the hearing loss was sloping. The median PTA (2–4 kHz) was 102 dB and the range from 65 to 120 dB. The accuracy of ABR is reasonably ineffective, because it overestimates the hearing loss in moderate and severe impairments. The absence of ABR indicates a significant hearing loss, but PTAs (2–4 kHz) as good as 65 dB were still found. Thus, a lack of response to click stimuli does not directly suggest none-viable residual hearing.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookhouser PE, Gorga MP, Kelly WJ (1990) Auditory brainstem response results as predictors of behavioral auditory thresholds in severe and profound hearing impairment. Laryngoscope 100:803–810
Cone-Wesson B, Dowell RC, Tomlin D, Rance G, Ming WJ (2002) The auditory steady-state response: comparisons with the auditory response. J Am Acad Audiol 13:173–187
Drift JFC van der, Brocaar MP, van Zanten GA (1987) The relation between the pure-tone audiogram and the click auditory brainstem response thresholds in cochlear hearing loss. Audiology 26:1–10
Fria TJ, Doyle WJ (1984) Maturation of the auditory brain stem response (ABR): additional perspectives. Ear Hear 5:361–365
Gorga MP, Kaminski JR, Beauchaine KL, Bergman BM (1993) A comparison of auditory brain stem response thresholds and latencies elicited by air-and bone-conducted stimuli. Ear Hear 14:85–94
Hyde ML, Malizia K, Riko K, Alberti PW (1991) Audiometric estimation error with the ABR in high-risk infants. Acta Otolaryngol 111:212–219
Jauhiainen T, Karikoski JO, Marttila TI (1998) The predominant mode of communication—oral or sign—as an outcome measure of rehabilitation in hearing impaired children. In: Ruben RJ, Karma P (eds) Advances in pediatric otorhinolaryngology. Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology June 7–10, Helsinki, Finland. Elsevier, CD-ROM
Jerger J, Mauldin L (1978) Prediction of sensorineural hearing loss from the brainstem evoked response. Arch Otolaryngol l04:456–461
Kiukaanniemi HJ, Mattila P (1980) Long-term speech spectra. A computerized method of measurement and a comparative study of Finnish and English data. Scand Audiol 9:67–72
Palva A (1965) Filtered speech audiometry. Basic studies with Finnish speech towards the creation of a method for the diagnosis of central hearing disorders. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl 210]:86
Parving A, Christensen B (1992) Children younger than 4 years of age, referred to an audiological department. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 23:161–170
Picton TW, Durieux-Smith A, Moran LM (1994) Recording auditory brainstem responses from infants. Int Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 28:93–110
Purdy SC, Houghton JM, Keith WJ, Greville KA (1989) Frequency-specific auditory brainstem responses. Effective masking levels and relationship to behavioral thresholds in normal hearing adults. Audiology 28:82–91
Rance G, Dowell RC, Rickards FW, Beer DE, Clark GM (1998) Steady-state evoked potential and behavioral hearing thresholds in a group of children with absent click-evoked auditory brainstem response. Ear Hear 19:48–61
Sasama R (1990) Hearing threshold investigations in infants and children. Audiology 29:76–84
Schoonhoven R, Lamore PJ, de Laat JA, Grote JJ (2000) Long-term audiometric follow-up of click-evoked auditory brainstem response in hearing-impaired infants. Audiology 39:135–145
Sininger YS, Abdala C (1996) Hearing threshold as measured by auditory brainstem response in human neonates. Ear Hear 17:395–401
Sininger YS, Abdala C, Cone-Wesson B (1997) Auditory thresholds sensitivity of the human neonate as measured by the auditory brainstem response. Hear Res 104:27–38
Stapells DR, Picton TW, Durieux-Smith A (1994) Electrophysiologic measures of frequency-specific auditory function. In: Jacobson JT (ed) Principles and applications in auditory evoked potentials. Allyn and Baron, Needham Hill, MA, pp 251–283
Stapells DR, Gravel JS, Martin BA (1995) Thresholds for auditory brainstem responses to tones in notched noise from infants and young children with normal hearing or sensorineural hearing loss. Ear Hear 16:361–371
Stueve MO, O’Rourke C (2003) Estimation of hearing loss in children: comparison of auditory steady-state response, auditory brainstem response, and behavioural test methods. Am J Audiol 12:125–136
The British Society of Audiology (1988) Descriptors for pure tone audiograms. Br J Audiol 22:123
World Health Organization (1991) Grades of hearing impairment. Network News no 1, September
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marttila, T.I., Karikoski, J.O. Comparison between audiometric and ABR thresholds in children. Contradictory findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263, 399–403 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-1019-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-1019-x