Abstract
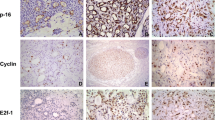
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a malignant tumor of salivary gland origin. It tends to grow slowly, but shows frequent recurrence and metastasis. Cyclin D1, a cell-cycle regulation protein, has been reported to be overexpressed in various types of cancer and to correlate with poor survival of the patients. However, the prognostic significance of cyclin D1 expression in ACC of the salivary glands has not yet been determined. To evaluate the role of cyclin D1 in the biological regulation of ACC, we constitutively expressed an antisense cyclin D1 complementary DNA (cDNA) in an established ACC cell line that exhibits high endogenous expression of cyclin D1. The effect of cyclin D1 expression on in vitro cell growth and cell cycle were examined. In addition, we also examined the immunohistochemical expression of cyclin D1 protein in 31 cases of ACC of the salivary gland and correlated its expression with proliferative activity or prognosis. There were no significant differences of the in vitro growth and in the percentage of the total cell population in the G1 phase and S phase between antisense cyclin D1 clones and control clones. Thirty-two percent of tumors derived from surgical specimens examined were immunohistochemically positive for cyclin D1 protein. No association was found between cyclin D1 expression and cell proliferation or the clinical outcome of the patients. It is concluded that cyclin D1 overexpression alone does not induce a marked increase in the proliferative activity of ACC cells and that expression of this protein is not linked to poor prognosis in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batsakis JG, Luna MA, el-Naggar A (1990) Histopathologic grading of salivary gland neoplasms: III. Adenoid cystic carcinomas. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 99:1007–1009
Bennett M, Wilson G, Dische S, Saunders M, Martindale C, Robinson B, O’Halloran A, Leslie M, Laing J (1992) Tumour proliferation assessed by combined histological and flow cytometrical analysis: implications for therapy in squamous cell carcinoma in head and neck. Br J Cancer 65:870–878
Callender T, el-Naggar AK, Lee MS, Frankenthaler R, Luna MA, Batsakis JG (1994) PRAD-1(CCND1)/cyclin D1 oncogene amplification in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 74:152–158
Chromotte G, Auriol M, Tranbaloc P, Vaillant JM (1982) Adenoid cystic carcinoma of minor salivary glands. Analysis of 86 cases. Virchow Arch 395:289–293
Corvo R, Giaretti W, Sanguineti G, Geido E, Orecchia R, Guenzi M, Margarino G, Bacigalupo A, Garaventa G, Barbieri M, Vitale V (1995) In vivo cell kinetics in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas predicts local control and helps guide radiotherapy regimen. J Clin Oncol 13:1843–1850
El-Naggar AK, Steck K, Batsakis JG (1995) Heterogeneity of the proliferative fraction and cyclin D1/CCND1 gene amplification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cytometry 21:47–51
Foster G, Cooke T, Cooke L, Stanton P, Bowie G, Stell P (1992) Tumour growth rates in squamous carcinoma of head and neck measured by in vivo bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and flow cytometry. Br J Cancer 65:698–702
Gillett C, Smith P, Gregory W, Richards M, Millis R, Peters G, Barnes D (1996) Cyclin D1 and prognosis in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 69:92–99
Hamper K, Lazar F, Dietel M, Caselitz J, Berger J, Arps H, Falkmer U, Auer G, Seifert G (1990) Prognostic factors for adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck: A retrospective evaluation of 96 cases. J Oral Pathol Med 19:101–107
Itami A, Shimada Y, Watanabe G, Imamura M (1999) Prognostic value of p27(Kip1) and cyclinD1 expression in esophageal cancer. Oncology 57:311–317
Jiang W, Kahn SM, Zhou P, Zhang YJ, Cacace AM, Infante AS, Doi S, Santella RM, Weinstein IB (1993) Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene 8:3447–3457
Kotelnikov VM, Coon J, Haleem A, Taylor S, Huchinson J, Panje W, Cardarelli D, Preisler HD (1993) Cell kinetics of head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res 1:527–537
Motokura T, Arnold A (1993) Cyclins and oncogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1155:63–78
Nakashima T, Clayman GL (2000) Antisense inhibition of cyclin D1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:957–961
Pardee AB (1989) G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science 246:603–608
Perzin KH, Gullane P, Clarmont AC (1978) Adenoid cystic carcinoma arising in salivary glands: a correlation of histologic feature and clinical course. Cancer 42:265–282
Reed SI (1997) Control of the G1/S transition. Cancer Surv 29:7–23
Resnitzky D, Gossen M, Bujard H, Reed SI (1994) Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclin D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol 14:1669–1679
Scotlandi K, Serra M, Manara MC, Maurici D, Benini S, Nini G, Campanacci M, Baldini N (1995) Clinical relevance of Ki-67 expression in bone tumors. Cancer 75:806–814
Sherr CJ (1993) Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell 73:1059–1065
Sherr CJ (1994) G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 79:551–555
Spiro RH (1986) Salivary neoplasms: overview of a 35-year experience with 2807 patients. Head Neck Surg 8:177–184
Spiro RH, Huvos AG (1992) Stage means more than grade in adenoid cystic carcinoma. Am J Surg 164:623–628
Spiro SH, Huvos AG, Strong EW (1979) Adenoid cystic carcinoma: factors influencing survival. Am J Clin Pathol 138:579–583
Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Strong EW (1979) Adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary origin. A clinicopathologic study of 242 cases. Am J Surg 128:512–520
Szanto PA, Luna MA, Tortoledo E, White RA (1984) Histologic grading of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands. Cancer 54:1062–1069
Tomasino RM, Daniele E, Bazan V, Morello V, Tralongo V, Naura R, Nagar C, Salvato M, Ingria F, Restivo S, Dardanoni G, Vecchione A, Russo A (1995) Prognostic significance of cell kinetics in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: clinicopathological associations. Cancer Res 55:6130–6108
Yang WI, Chung KY, ShinDH, Kim YB (1996) Cyclin D1 protein expression in lung cancer. Yonsei Med J 37:142–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasumatsu, R., Kuratomi, Y., Nakashima, T. et al. Cyclin D1 expression does not effect cell proliferation in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 261, 526–530 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-003-0724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-003-0724-6