Abstract
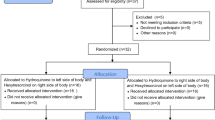
Little is known about the anti-pigmenting effects of whitening agents on solar lentigos (SLs), which comprise ~ 60% of hyperpigmented facial lesions of Asian subjects. Lotions with or without 6% l-ascorbate-2-phosphate trisodium salt (APS) [test lotion (TL) and placebo lotion (PL), respectively] were applied twice daily for 24 weeks in a double-blind half-face study of 27 Japanese females with SLs on both sides of their faces. Pigmentation scores were evaluated using a photo-scale and the skin colors were assessed using a color difference meter and a mexameter for SLs and the non-lesional surrounding skin (NLS). Although the pigmentation scores were not significantly different between the TL and PL-treated SLs after 24 weeks, the L values of TL-treated SLs and NLS increased significantly with a significantly higher △L value in SLs than in NLS. In contrast, the L values of PL-treated SLs and NLS remained unchanged after the treatment. The number of subjects with > 2.0 △L was 7 of 27 (TL) and 0 of 27 (PL) in SLs and 3 of 27 (TL) and 0 of 27 (PS) in NLS. In contrast, the melanin index in TL-treated SLs and NLS significantly decreased with a significantly higher △melanin index in SLs than in NLS. Similarly, the melanin index of PL-treated SLs and NLS were significantly decreased with a significantly higher △melanin index in SLs than in NLS. These findings strongly indicate that APS has a weak but significant anti-pigmenting effect on SLs and a significant whitening effect even on normally pigmented healthy skin.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLs:
-
Solar lentigos
- APS:
-
l-Ascorbate-2-phosphate trisodium salt
- AMP:
-
l-Ascorbate-2-phosphate Mg
- EDN:
-
Endothelin
- SCF:
-
Stem cell factor
- NLS:
-
Non-lesional surrounding skin
References
Elmore AR (2005) Final report of the safety assessment of l-ascorbic acid, calcium ascorbate, magnesium ascorbate, magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, sodium ascorbate, and sodium ascorbyl phosphate as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol 24(Suppl 2):51–111
Foco A, Gasperlin M, Kristl J (2005) Investigation of liposomes as carriers of sodium ascorbyl phosphate for cutaneous photoprotection. Int J Pharm 291(1–2):21–29
Hattori H, Kawashima M, Ichikawa Y, Imokawa G (2004) The epidermal stem cell factor is over-expressed in lentigo senilis: Implication for the mechanism of hyperpigmentation. J Invest Dermatol 122:1256–1265
Ikeno H, Apel M, Zouboulis C, Luger TA, Böhm M (2015) l-Ascorbyl-2-phosphate attenuates NF-κB signaling in SZ95 sebocytes without affecting IL-6 and IL-8 secretion. Arch Dermatol Res 307(7):595–605
Imokawa G, Yada Y, Miyagishi M (1992) Endothelins secreted from human keratinocytes are intrinsic mitogens for human melanocytes. J Biol Chem 267(34):24675–24680
Imokawa G, Yada Y, Kimura M (1996) Signaling mechanisms of endothelin-induced mitogenesis and melanogenesis in human melanocytes. Biochem J 314(Pt1):305–312
Imokawa G, Kobayashi T, Miyagishi M, Higashi K, Yada Y (1997) The role of endothelin-1 in epidermal hyperpigmentation and signaling mechanisms of mitogenesis and melanogenesis. Pigment Cell Res 10(4):218–228
Imokawa G, Kobayashi T, Miyagishi M (2000) Intracellular signaling mechanisms leading to synergistic effects of endothelin-1 and stem cell factor on proliferation of cultured human melanocytes: cross-talk via trans-activation of the tyrosine kinase c-kit receptor. J Biol Chem 275(43):33321–33328
Kadono S, Manaka I, Kawashima M, Kobayashi T, Imokawa G (2001) The role of the epidermal endothelin cascade in the hyperpigmentation mechanism of lentigo senilis. J Invest Dermatol 116(4):571–577
Kameyama K, Sakai C, Kondoh S, Yonemoto K, Nishiyama S, Tagawa M, Murata T, Ohnuma T, Quigley J, Dorsky A, Bucks D, Blanock K (1996) Inhibitory effect of magnesium l-ascorbyl-2-phosphate (VC-PMG) on melanogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Am Acad Dermatol 34(1):29–33
Khan H, Akhtar N, Ali A, Khan HMS, Sohail M, Naeem M, Nawaz Z (2016) Physical and chemical stability analysis of cosmetic multiple emulsions loaded with ascorbyl palmitate and sodium ascorbyl phosphate salts. Acta Pol Pharm 73(5):1339–1349
Khan H, Akhtar N, Ali A (2017) Assessment of combined ascorbyl palmitate (AP) and sodium ascorbyl phosphate (SAP) on facial skin sebum control in female healthy volunteers. Drug Res (Stuttg) 67(1):52–58
Klock J, Ikeno H, Ohmori K, Nishikawa T, Vollhardt J, Schehlmann V (2005) Sodium ascorbyl phosphate shows in vitro and in vivo efficacy in the prevention and treatment of acne vulgaris. Int J Cosmet Sci 27(3):171–176
Kobayashi S, Takehana M, Itoh S, Ogata E (1996) Protective effect of magnesium-l-ascorbyl-2 phosphate against skin damage induced by UVB irradiation. Photochem Photobiol 64(1):224–228
Lee WJ, Kim SL, Lee KC, Sohn MY, Jang YH, Lee SJ, Kim DW (2016) Effects of magnesium ascorbyl phosphate on the expression of inflammatory biomarkers after treatment of cultured sebocytes with Propionibacterium acnes or ultraviolet B radiation. Ann Dermatol 28(1):129–132
Liao AH, Lu YJ, Hung CR, Yang MY (2016) Efficacy of transdermal magnesium ascorbyl phosphate delivery after ultrasound treatment with microbubbles in gel-type surrounding medium in mice. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 61:591–598
Murtaza F, Bangash AR, Khushdil A, Noor SM (2016) Efficacy of trichloro-acetic acid peel alone versus combined topical magnesium ascorbyl phosphate for epidermal melasma. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 26(7):557–561
Nayama S, Takehana M, Kanke M, Itoh S, Ogata E, Kobayashi S (1999) Protective effects of sodium-L-ascorbyl-2 phosphate on the development of UVB-induced damage in cultured mouse skin. Biol Pharm Bull 22(12):1301–1305
Niwano T, Terazawa S, Nakajima H, Imokawa G (2018) The stem cell factor-stimulated melanogenesis in human melanocytes can be abrogated by interrupting the phosphorylation of MSK1: evidence for involvement of the p38/MSK1/CREB/MITF axis. Arch Dermatol Res 310(3):187–196
Niwano T, Terazawa S, Sato Y, Kato T, Nakajima H, Imokawa G (2018) Glucosamine abrogates the stem cell factor + endothelin-1-induced stimulation of melanogenesis via a deficiency in MITF expression due to the proteolytic degradation of CREB in human melanocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 310(8):625–637
Parvez S, Kang M, Chung HS, Cho C, Hong MC, Shin MK, Bae H (2006) Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting and lightening agents. Phytother Res 20(11):921–934
Ruamrak C, Lourith N, Natakankitkul S (2009) Comparison of clinical efficacies of sodium ascorbyl phosphate, retinol and their combination in acne treatment. Int J Cosmet Sci 31(1):41–46
Sato-Jin K, Nishimura EK, Akasaka E, Huber W, Nakano H, Miller A, Du J, Wu M, Hanada K, Sawamura D, Fisher DE, Imokawa G (2008) Epistatic connections between MITF and endothelin signaling in Waardenburg Syndrome and other pigmentary disorders. FASEB J 22(4):1155–1168
Shaikh ZI, Mashood AA (2014) Treatment of refractory melasma with combination of topical 5% magnesium ascorbyl phosphate and fluorescent pulsed light in Asian patients. Int J Dermatol 53(1):93–99
Silva GM, Maia Campos PM (2000) Histopathological, morphometric and stereological studies of ascorbic acid and magnesium ascorbyl phosphate in a skin care formulation. Int J Cosmet Sci 22(3):169–179
Slominski AT, Tobin DJ, Shibahara S, Wortsman J (2004) Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol Rev 84(4):1155–1228
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Plonka PM, Szaflarski JP, Paus R (2018) How UV light touches the brain and endocrine system through skin, and why. Endocrinology 159(5):1992–2007
Slominski AT, Hardeland R, Zmijewski MA, Slominski RM, Reiter RJ, Paus R (2018) Melatonin: a cutaneous perspective on its production, metabolism, and functions. J Invest Dermatol 138(3):490–499
Wang PC, Huang YL, Hou SS, Chou CH, Tsai JC (2013) Lauroyl/palmitoyl glycol chitosan gels enhance skin delivery of magnesium ascorbyl phosphate. J Cosmet Sci 64(4):273–286
Woolery-Lloyd H, Baumann L, Ikeno H (2010) Sodium L-ascorbyl-2-phosphate 5% lotion for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Cosmet Dermatol 9(1):22–27
Yada Y, Higuchi K, Imokawa G (1991) Effects of endothelins on signal transduction and proliferation in human melanocytes. J Biol Chem 266(27):18352–18357
Yamamoto K, Shichiri H, Ishida T, Kaku K, Nishioka T, Kume M, Makimoto H, Nakagawa T, Hirano T, Bito T, Nishigori C, Yano I, Hirai M (2017) Effects of ascorbyl-2-phosphate magnesium on human keratinocyte toxicity and pathological changes by sorafenib. Biol Pharm Bull 40(9):1530–1536
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, Y., Niwano, T., Hirano, S. et al. Whitening effect of l-ascorbate-2-phosphate trisodium salt on solar lentigos. Arch Dermatol Res 311, 183–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01892-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01892-2