Abstract
Introduction
Arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction (ASCR) using fascia lata autograft is a new surgical technique developed to overcome irreparable rotator cuff tears. There is little information about graft tear after ASCR and its impact on clinical outcome. This study is to investigate the graft tear rate, pattern of failure, and its correlation with clinical outcomes after arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction (ASCR).
Materials and methods
From June 2013 to June 2016, 31 shoulders in 31 consecutive patients (mean 65.3 years) underwent ASCR using fascia lata autograft for irreparable large-to-massive tears. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed before surgery and at mean 12.8 months (12–24 months) after surgery to assess fatty infiltration progression and graft integrity. Graft tear was defined as the loss of graft continuity and was categorized as medial and lateral rows according to the failure location. Acromiohumeral distance (AHD) was pre- and postoperatively measured with the standard radiograph. Pain visual analog scale (VAS) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score, constant score, and physical examination were used to assess clinical outcomes. Average follow-up was 15 months (range 12–24 months) after surgery.
Results
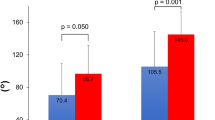
Mean active forward elevation increased from 133° to 146° (P = 0.011). Mean VAS score, ASES score, and constant score significantly improved: from 6 to 2.5, 54.4 to 73.7, and 51.7 to 63.7, respectively (P < 0.001). There was no remarkable progression of fatty infiltration after surgery. AHD increased from 5.3 mm preoperatively to 6.4 mm postoperatively (P < 0.016). Nine patients (29%) showed graft tear on follow-up MRI: 7 and 2 at the medial and lateral rows, respectively. Although the intact graft group showed better outcomes than the graft tear group (pain VAS score 2.3 vs. 3.0; ASES score 74.1 vs. 69.8; constant score 63.4 vs. 57.9), the results were not statistically significant.
Conclusions
Graft tear rate after ASCR assessed by MRI was 29%, and failures mostly occurred at the medial row. The graft tear group showed clinical improvement despite the recurred superior capsule defect.
Level of evidence
IV, case series, treatment study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badhe SP, Lawrence TM, Smith FD, Lunn PG (2008) An assessment of porcine dermal xenograft as an augmentation graft in the treatment of extensive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17:35S–39S
Boileau P, Watkinson DJ, Hatzidakis AM, Balg F (2005) Grammont reverse prosthesis: design, rationale, and biomechanics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14:147S–161S
Bond JL, Dopirak RM, Higgins J, Burns J, Snyder SJ (2008) Arthroscopic replacement of massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears using a GraftJacket allograft: technique and preliminary results. Arthroscopy 24:403–409 e401
Burkhart SS (1993) Arthroscopic debridement and decompression for selected rotator cuff tears. Clinical results, pathomechanics, and patient selection based on biomechanical parameters. Orthop Clin North Am 24:111–123
Burkhart SS, Nottage WM, Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Kohn HS, Pachelli A (1994) Partial repair of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 10:363–370
Cerciello S, Monk AP, Visona E, Carbone S, Edwards TB, Maffulli N et al (2017) The influence of critical shoulder angle on secondary rotator cuff insufficiency following shoulder arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137:913–918
Cho NS, Yi JW, Lee BG, Rhee YG (2010) Retear patterns after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: single-row versus suture bridge technique. Am J Sports Med 38:664–671
Cuff D, Pupello D, Virani N, Levy J, Frankle M (2008) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuff deficiency. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90:1244–1251
Duralde XA, Bair B (2005) Massive rotator cuff tears: the result of partial rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14:121–127
Ek ET, Neukom L, Catanzaro S, Gerber C (2013) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears in patients younger than 65 years old: results after five to fifteen years. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22:1199–1208
Fenlin JM Jr, Chase JM, Rushton SA, Frieman BG (2002) Tuberoplasty: creation of an acromiohumeral articulation-a treatment option for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 11:136–142
Frankle M, Siegal S, Pupello D, Saleem A, Mighell M, Vasey M (2005) The Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency. A minimum two-year follow-up study of sixty patients. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:1697–1705
Fuchs B, Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Gerber C (1999) Fatty degeneration of the muscles of the rotator cuff: assessment by computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 8:599–605
Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K (2004) The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Jt Surg Am 86-A:219–224
Gerber C (1992) Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of irreparable tears of the rotator cuff. Clin Orthop Relat Res 275:152–160
Gerber C, Rahm SA, Catanzaro S, Farshad M, Moor BK (2013) Latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for treatment of irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tears: long-term results at a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Jt Surg Am 95:1920–1926
Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC (1994) Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Relat Res 304:78–83
Grammont PM, Baulot E (1993) Delta shoulder prosthesis for rotator cuff rupture. Orthopedics 16:65–68
Gruber G, Bernhardt GA, Clar H, Zacherl M, Glehr M, Wurnig C (2010) Measurement of the acromiohumeral interval on standardized anteroposterior radiographs: a prospective study of observer variability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 19:10–13
Gupta AK, Hug K, Berkoff DJ, Boggess BR, Gavigan M, Malley PC et al (2012) Dermal tissue allograft for the repair of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med 40:141–147
Hamada K, Fukuda H, Mikasa M, Kobayashi Y (1990) Roentgenographic findings in massive rotator cuff tears. A long-term observation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 254:92–96
Iannotti JP, Codsi MJ, Kwon YW, Derwin K, Ciccone J, Brems JJ (2006) Porcine small intestine submucosa augmentation of surgical repair of chronic two-tendon rotator cuff tears. A randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88:1238–1244
Jeon YS, Kim RG, Shin SJ (2018) A novel remaining tendon preserving repair technique leads to improved outcomes in special rotator cuff tear patterns. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2956-3
Jost B, Puskas GJ, Lustenberger A, Gerber C (2003) Outcome of pectoralis major transfer for the treatment of irreparable subscapularis tears. J Bone Jt Surg Am 85-A:1944–1951
Kim SJ, Lee IS, Kim SH, Lee WY, Chun YM (2012) Arthroscopic partial repair of irreparable large to massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 28:761–768
Lafosse L, Jost B, Reiland Y, Audebert S, Toussaint B, Gobezie R (2007) Structural integrity and clinical outcomes after arthroscopic repair of isolated subscapularis tears. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89:1184–1193
Lee BG, Cho NS, Rhee YG (2011) Results of arthroscopic decompression and tuberoplasty for irreparable massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 27:1341–1350
McElvany MD, McGoldrick E, Gee AO, Neradilek MB, Matsen FA (2015) Rotator cuff repair: published evidence on factors associated with repair integrity and clinical outcome. Am J Sports Med 43:491–500
Mihata T, Lee TQ, Watanabe C, Fukunishi K, Ohue M, Tsujimura T et al (2013) Clinical results of arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 29:459–470
Mihata T, McGarry MH, Kahn T, Goldberg I, Neo M, Lee TQ (2016) Biomechanical effects of acromioplasty on superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable supraspinatus tendon tears. Am J Sports Med 44:191–197
Mihata T, McGarry MH, Pirolo JM, Kinoshita M, Lee TQ (2012) Superior capsule reconstruction to restore superior stability in irreparable rotator cuff tears: a biomechanical cadaveric study. Am J Sports Med 40:2248–2255
Millett PJ, Espinoza C, Horan MP, Ho CP, Warth RJ, Dornan GJ et al (2017) Predictors of outcomes after arthroscopic transosseous equivalent rotator cuff repair in 155 cases: a propensity score weighted analysis of knotted and knotless self-reinforcing repair techniques at a minimum of 2 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137:1399–1408
Muh SJ, Streit JJ, Wanner JP, Lenarz CJ, Shishani Y, Rowland DY et al (2013) Early follow-up of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in patients sixty years of age or younger. J Bone Jt Surg Am 95:1877–1883
Mulieri P, Dunning P, Klein S, Pupello D, Frankle M (2010) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tear without glenohumeral arthritis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 92:2544–2556
Nove-Josserand L, Edwards TB, O’Connor DP, Walch G (2005) The acromiohumeral and coracohumeral intervals are abnormal in rotator cuff tears with muscular fatty degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:90–96
Pogorzelski J, Horan MP, Godin JA, Hussain ZB, Fritz EM, Millett PJ (2018) Achilles tendon allograft-augmented latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for the treatment of massive irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2943-8
Rockwood CA Jr, Williams GR Jr, Burkhead WZ Jr (1995) Debridement of degenerative, irreparable lesions of the rotator cuff. J Bone Jt Surg Am 77:857–866
Russell RD, Knight JR, Mulligan E, Khazzam MS (2014) Structural integrity after rotator cuff repair does not correlate with patient function and pain: a meta-analysis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 96:265–271
Saupe N, Pfirrmann CW, Schmid MR, Jost B, Werner CM, Zanetti M (2006) Association between rotator cuff abnormalities and reduced acromiohumeral distance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:376–382
Sclamberg SG, Tibone JE, Itamura JM, Kasraeian S (2004) Six-month magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of large and massive rotator cuff repairs reinforced with porcine small intestinal submucosa. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 13:538–541
Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J (2007) Repair integrity and functional outcome after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. A prospective outcome study. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89:953–960
Tashjian RZ, Hollins AM, Kim HM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Steger-May K et al (2010) Factors affecting healing rates after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med 38:2435–2442
Toussaint B, Schnaser E, Bosley J, Lefebvre Y, Gobezie R (2011) Early structural and functional outcomes for arthroscopic double-row transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med 39:1217–1225
Walch G, Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Nove-Josserand L, Neyton L, Szabo I (2005) Arthroscopic tenotomy of the long head of the biceps in the treatment of rotator cuff tears: clinical and radiographic results of 307 cases. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14:238–246
Walton JR, Bowman NK, Khatib Y, Linklater J, Murrell GA (2007) Restore orthobiologic implant: not recommended for augmentation of rotator cuff repairs. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89:786–791
Werner CM, Steinmann PA, Gilbart M, Gerber C (2005) Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:1476–1486
Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C (2008) The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90:2423–2431
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jeong Hee Park, CNS (Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea) for providing assistance during data collection.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
IRB/ethical committee approval
AMC IRB 2017-0487.
Additional information
The authors or their immediate families have not received any financial payment or benefits from any commercial company related to this study. The keynote of this paper was presented at AANA17—the 36th Annual Meeting of the Arthroscopy Association of North America, Denver, Colorado, May 18–20, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, S., AlRamadhan, H., Kwak, JM. et al. Graft tears after arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction (ASCR): pattern of failure and its correlation with clinical outcome. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139, 231–239 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3025-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3025-7