Abstract
Introduction
Rotator cuff tear (RCT) is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a fraction of whole blood containing concentrated growth factors and proteins important for tissue healing. This study aimed at investigating the effects of local autologous PRP injection on repaired rotator cuff (RC) tendon repair in rats.
Methods
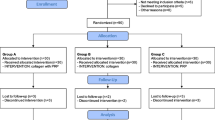
Following experimental RCT and suturing, 44 Wistar rats were randomly allocated into two groups: (1) RC repair only (controls); (2) RC repair + PRP administration-shoulders were treated with intra-articular PRP immediately after the repair. Animals were killed after 3 weeks and tendon, were tested biomechanically in tension (12 rats/group). The remaining tendons (10 rats/group) were stained using hematoxylin and eosin and Picro-sirius Red. Histological analysis evaluated the cellular aspects of the repair tissue.
Results
PRP administration following experimental RC tear and suture resulted in a significantly higher maximal load (p < 0.001) and stiffness (p < 0.005) as compared to non-treated animals. Bonar score of PRP-treated tendons was significantly better (p = 0.018) than the control group. Collagen birefringence was significantly higher in PRP shoulders (p = 0.002), indicating improved organization. Vascularity scores were similar in both groups.
Conclusion
Application of a single dose autologous PRP in adjunct to surgical repair resultes in improved tendon-to-bone healing, assessed by histological and biomechanical testing in a rat model of acute RCT, when tested at 3 weeks compared to controls. Further studies will be essential to determine the role of PRP in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chahal J, Van Thiel GS, Mall N, Heard W, Bach BR, Cole BJ, Nicholson GP, Verma NN, Whelan DB, Romeo AA (2012) The role of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a systematic review with quantitative synthesis. Arthroscopy 28(11):1718–1727. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2012.03.007S0749-8063(12)00178
Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Perren SM, Nyffeler RW (1999) Experimental rotator cuff repair. a preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81(9):1281–1290
Rodeo SA, Potter HG, Kawamura S, Turner AS, Kim HJ, Atkinson BL (2007) Biologic augmentation of rotator cuff tendon-healing with use of a mixture of osteoinductive growth factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(11):2485–2497. (89/11/248510.2106/JBJS.C.01627)
Thomopoulos S, Hattersley G, Rosen V, Mertens M, Galatz L, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ (2002) The localized expression of extracellular matrix components in healing tendon insertion sites: an in situ hybridization study. J Orthop Res 20(3):454–463. doi:10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00144-9
Arnoczky SP, Tarvin GB, Marshall JL (1982) Anterior cruciate ligament replacement using patellar tendon. an evaluation of graft revascularization in the dog. J Bone Joint Surg Am 64(2):217–224
Werner S, Grose R (2003) Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev 83(3):835–870. doi:10.1152/physrev.00031.200283/3/835
Alsousou J, Thompson M, Hulley P, Noble A, Willett K (2009) The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg British 91(8):987–996. (91-B/8/98710.1302/0301-620X.91B8.22546)
Anitua E, Andia I, Ardanza B, Nurden P, Nurden AT (2004) Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost 91(1):4–15. doi:10.1267/THRO0401000404010004
Anitua E, Sanchez M, Nurden AT, Nurden P, Orive G, Andia I (2006) New insights into and novel applications for platelet-rich fibrin therapies. Trends Biotechnol 24(5):227–234. (S0167-7799(06)00056-410.1016/j.tibtech.2006.02.010)
Baksh N, Hannon CP, Murawski CD, Smyth NA, Kennedy JG (2013) Platelet-rich plasma in tendon models: a systematic review of basic science literature. Arthroscopy 29(3):596–607. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2012.10.025S0749-8063(12)01798-7
Moraes VY, Lenza M, Tamaoki MJ, Faloppa F, Belloti JC (2013) Platelet-rich therapies for musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD010071. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010071.pub2
Marx RE (2001) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): what is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent 10(4):225–228
Maffulli N, Longo UG, Franceschi F, Rabitti C, Denaro V (2008) Movin and Bonar scores assess the same characteristics of tendon histology. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(7):1605–1611. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0261-0
Galatz LM, Sandell LJ, Rothermich SY, Das R, Mastny A, Havlioglu N, Silva MJ, Thomopoulos S (2006) Characteristics of the rat supraspinatus tendon during tendon-to-bone healing after acute injury. J Orthop Res 24(3):541–550. doi:10.1002/jor.20067
Cohen DB, Kawamura S, Ehteshami JR, Rodeo SA (2006) Indomethacin and celecoxib impair rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. Am J Sports Med 34(3):362–369. (036354650528042810.1177/0363546505280428)
International CRL (2008) Clinical laboratory parameters for Crl:Wi(Han) rats
Fernandez-Sarmiento JA, Dominguez JM, Granados MM, Morgaz J, Navarrete R, Carrillo JM, Gomez-Villamandos RJ, Munoz-Rascon P, de Martin Las Mulas J, Millan Y, Garcia-Balletbo M, Cugat R (2013) Histological study of the influence of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) on the healing of divided Achilles tendons in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95(3):246–255. doi:10.2106/JBJS.K.016591558609
Ersen A, Demirhan M, Atalar AC, Kapicioglu M, Baysal G (2013) Platelet-rich plasma for enhancing surgical rotator cuff repair: evaluation and comparison of two application methods in a rat model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1914-3
Hapa O, Cakici H, Kukner A, Aygun H, Sarkalan N, Baysal G (2012) Effect of platelet-rich plasma on tendon-to-bone healing after rotator cuff repair in rats: an in vivo experimental study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 46(4):301–307
Beck J, Evans D, Tonino PM, Yong S, Callaci JJ (2012) The biomechanical and histologic effects of platelet-rich plasma on rat rotator cuff repairs. Am J Sports Med 40(9):2037–2044. doi:10.1177/03635465124533000363546512453300
Taylor DW, Petrera M, Hendry M, Theodoropoulos JS (2011) A systematic review of the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine as a new treatment for tendon and ligament injuries. Clin J Sport Med 21(4):344–352. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e31821d0f65
Sadoghi P, Lohberger B, Aigner B, Kaltenegger H, Friesenbichler J, Wolf M, Sununu T, Leithner A, Vavken P (2013) Effect of platelet-rich plasma on the biologic activity of the human rotator-cuff fibroblasts: a controlled in vitro study. J Orthop Res 31(8):1249–1253. doi:10.1002/jor.22360
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Oleg Dolkart and Ofir Chechik contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolkart, O., Chechik, O., Zarfati, Y. et al. A single dose of platelet-rich plasma improves the organization and strength of a surgically repaired rotator cuff tendon in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 1271–1277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2026-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2026-4