Abstract
Introduction
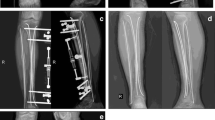
Tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop may lead to significant complications. The optimal management of these injuries remains controversial. Recently, locking plate used as a definitive external fixator is attractive because it not only minimizes trauma to the soft tissues, but also overcomes the shortcomings of standard external fixators. The objective of this study was to evaluate the outcome of using locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop.
Patients and methods
A prospective series of 12 consecutive tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop were treated using locking plate as a definitive external fixator. Of these patients, six were Gustilo and Anderson type IIIA, three were type II and three were closed fractures (AO/ASIF soft tissue injury classification IC4: 2, IC5: 1). Time to union, nonunion, malunion, leg shortening, range of motion and function for the knee and ankle, deep infection, pin tract infections were evaluated.
Results
The mean bone healing time was 37.8 weeks (range 20–56 weeks). Eventually, all of the fractures united. Most of the fractures healed in acceptable positions. There were no cases of deep infection. Pin tract infection was seen in 1 (8.3 %) patient, no loosening or failure of the external fixator was seen. At the most recent follow-up, the mean range of motion at the knee was extension 0° to flexion 135°, and the mean ankle range of motion was dorsi flexion 12° to plantar flexion 32°. All patients had excellent or good functional results and were fully weight bearing with a well-healed tibia at the final follow-up.
Conclusion
The locking plate used as a definitive external fixator provided a high rate of union. The patients experienced a comfortable clinical course, excellent knee and ankle joint motion, satisfactory functional results and an acceptable complication rate. However, the stiffness of external locked plating is not clear, therefore, clinical recommendation on its practical use to reduce the risk of implant failure still need to be determined.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFerran MA, Smith SW, Boulas HJ, Schwartz HS (1992) Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 6(2):195–200
Tejwani NC, Hak DJ, Finkemeier CG, Wolinsky PR (2006) High-energy proximal tibial fractures: treatment options and decision making. Instr Course Lect 55:367–379
Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr (1999) A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(2):78–84
Tejwani NC, Achan P (2004) Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 62(1–2):62–66
Marsh JL, Smith ST, Do TT (1995) External fixation and limited internal fixation for complex fractures of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(5):661–673
Watson JT, Moed BR, Karges DE, Cramer KE (2000) Pilon fractures. Treatment protocol based on severity of soft tissue injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res 375:78–90
Ma CH, Wu CH, Yu SW, Yen CY, Tu YK (2010) Staged external and internal less-invasive stabilisation system plating for open proximal tibial fractures. Injury 41(2):190–196. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2009.08.022
Ma CH, Yu SW, Tu YK, Yen CY, Yeh JJ, Wu CH (2010) Staged external and internal locked plating for open distal tibial fractures. Acta Orthop 81(3):382–386. doi:10.3109/17453674.2010.487244
Ma CH, Tu YK, Yeh JH, Yang SC, Wu CH (2011) Using external and internal locking plates in a two-stage protocol for treatment of segmental tibial fractures. J Trauma 71(3):614–619. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3182041175
Kloen P (2009) Supercutaneous plating: use of a locking compression plate as an external fixator. J Orthop Trauma 23(1):72–75. doi:10.1097/BOT.0b013e31818f8de4
Tulner SA, Strackee SD, Kloen P (2012) Metaphyseal locking compression plate as an external fixator for the distal tibia. Int Orthop 36(9):1923–1927. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1585-7
Ma CH, Wu CH, Tu YK, Lin TS (2013) Metaphyseal locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating open tibial fractures–clinical outcome and a finite element study. Injury 44(8):1097–1101. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2013.04.023
Giannoudis PV, Hinsche AF, Cohen A, Macdonald DA, Matthews SJ, Smith RM (2003) Segmental tibial fractures: an assessment of procedures in 27 cases. Injury 34(10):756–762 S0020138302003935 [pii]
Teraa M, Blokhuis TJ, Tang L, Leenen LP (2013) Segmental tibial fractures: an infrequent but demanding injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(9):2790–2796. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2739-z
Apivatthakakul T, Sananpanich K (2007) The locking compression plate as an external fixator for bone transport in the treatment of a large distal tibial defect: a case report. Injury 38(11):1318–1325. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2007.05.005
Woon CY, Wong MK, Howe TS (2010) LCP external fixation–external application of an internal fixator: two cases and a review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res 5:19. doi:10.1186/1749-799X-5-19
Koulouvaris P, Stafylas K, Mitsionis G, Vekris M, Mavrodontidis A, Xenakis T (2007) Long-term results of various therapy concepts in severe pilon fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(5):313–320. doi:10.1007/s00402-007-0306-y
Papadokostakis G, Kontakis G, Giannoudis P, Hadjipavlou A (2008) External fixation devices in the treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond: a systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(1):1–6. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.90B1.19858
Phieffer LS, Goulet JA (2006) Delayed unions of the tibia. Instr Course Lect 55:389–401
Edwards CC, Jaworski MF (1979) Hoffman external fixation in open tibial fractures with tissue loss. Orthop Trans 3(1):261–262
Velazco A, Whitesides TE Jr, Fleming LL (1983) Open fractures of the tibia treated with the lottes nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65(7):879–885
Fang X, Jiang L, Wang Y, Zhao L (2012) Treatment of Gustilo grade III tibial fractures with unreamed intramedullary nailing versus external fixator: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit 18(4):49–56 882610 [pii]
Dillin L, Slabaugh P (1986) Delayed wound healing, infection, and nonunion following open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. J Trauma 26(12):1116–1119
Acknowledgments
This study has received financial support from the Peak Talents Foundation in Jiangsu Province (#2012-WS-092), Key Project of Department of Health, Nanjing, China (JQX12005), and the Key Program of Science and Technique Development Foundation in Jiangsu Province (BE20116004). We acknowledge Dr. Hong-fei Shi, Dr. Jun Jiang, Dr. Xiao-xiao Xie, and Dr. Chang-jun Wang for their assistance during the data collection. The authors would also like to thank Ms. Xiao-xia Zhong for her help in patient follow-up.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Xs., Yuan, H., Zheng, X. et al. Locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 383–388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1916-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1916-1