Abstract
Introduction
The rate of periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty is rising and the estimated current lifetime incidence is 0.4–2.1%. While most authors recommend revision arthroplasty in patients with loose femoral shaft components, treatment options for patients with stable stem are not fully elucidated.
Method
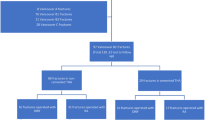
Against this background we performed a retrospective chart analysis with clinical follow-up examination of 32 cases that sustained a Vancouver type B1 or C periprosthetic fracture (stable stem).
Patients
Overall 16 cases were treated by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) by plate osteosynthesis and 16 cases by revision arthroplasty (RA). Both groups were comparable regarding age, gender, follow-up time interval, time interval from primary hip arthroplasty to fracture and rate of cemented femoral components, but more type C fractures were treated by ORIF.
Results
Functional outcome expressed by the median timed “Up and Go” test did not differ significantly (30 s ORIF vs. 24 s RA, P = 0.19). However, by comparable systemic complications surgery-related complications were significantly more frequent in plate osteosynthesis (ORIF n = 10 vs. RA n = 3, P = 0.03). Based on our results, further studies, preferable via a multicenter approach, should focus on identifying patients that benefit from ORIF in periprosthetic fractures. A misinterpretation of type B2 fractures with loose implant as type B1 fractures may cause implant failure in case of ORIF.
Conclusion
The use of angular stable implants, additional cable wires or bone enhancing means is recommended.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2000) The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplast 15(1):59–62
Buttaro MA, Farfalli G, Paredes Nunez M, Comba F, Piccaluga F (2007) Locking compression plate fixation of Vancouver type-B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(9):1964–1969
Chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J (2007) Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver Type B1 and Type C periprosthetic fractures of femur: a report on 12 patients. Injury 38(6):725–733
Duncan CP, Masri BA (1995) Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect 44:293–304
Erhardt JB, Grob K, Roderer G, Hoffmann A, Forster TN, Kuster MS (2008) Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with the non-contact bridging plate: a new angular stable implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(4):409–416
Haidar SG, Goodwin MI (2005) Dynamic compression plate fixation for post-operative fractures around the tip of a hip prosthesis. Injury 36(3):417–423
Kaab MJ, Stockle U, Schutz M, Stefansky J, Perka C, Haas NP (2006) Stabilisation of periprosthetic fractures with angular stable internal fixation: a report of 13 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126(2):105–110
Lindahl H (2007) Epidemiology of periprosthetic femur fracture around a total hip arthroplasty. Injury 38(6):651–654
Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regner H, Herberts P, Malchau H (2006) Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(6):1215–1222
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplast 20(7):857–865
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Oden A, Garellick G (2006) Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(1):26–30
Masri BA, Meek RM, Duncan CP (2004) Periprosthetic fractures evaluation and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:80–95
Muller M, Kaab M, Tohtz S, Haas NP, Perka C (2009) Periprosthetic femoral fractures: outcome after treatment with LISS internal fixation or stem replacement in 36 patients. Acta Orthop Belg 75(6):776–783
Ninan TM, Costa ML, Krikler SJ (2007) Classification of femoral periprosthetic fractures. Injury 38(6):661–668
Parvizi J, Rapuri VR, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF, Rothman RH, Hozack WJ (2004) Treatment protocol for proximal femoral periprosthetic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(Suppl 2):8–16
Podsiadlo D, Richardson S (1991) The timed “Up & Go”: a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 39(2):142–148
Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR, Loftus T, Cox C, Mitchell S, Borrelli J Jr (2005) Indirect reduction and plate fixation, without grafting, for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures about a stable intramedullary implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(10):2240–2245
Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE (2004) Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12(1):12–20
Wutzler S, Laurer HL, Lehnert M, Maier B, Marzi I (2006) Versorgungsstrategien bei periprothetischen Frakturen nach Hüftgelenkersatz. In: Effenberger H, Zichner L, Richolt J (eds) Hüftschäfte. MCU-Vertrieb, Grieskirchen, pp 292–296
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurer, H.L., Wutzler, S., Possner, S. et al. Outcome after operative treatment of Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fractures: open reduction and internal fixation versus revision arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 983–989 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1272-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1272-y