Abstract
Introduction
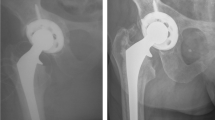
We report the results of a titanium acetabular reinforcement ring with a hook (ARRH) in primary total hip arthroplasty (THA), which was introduced in 1987 and continues to be used routinely in our center. The favorable results of this device in arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia and difficult revisions motivated its use in primary THA. With this implant only minimal acetabular reaming is necessary, anatomic positioning is achieved by placing the hook around the teardrop and a homogenous base for cementing the polyethylene cup is provided.
Materials and methods
Between April 1987 and December 1991, 241 THAs with insertion of an ARRH were performed in 178 unselected, consecutive patients (average age 58 years; range 30–84 years) with a secondary osteoarthrosis in 41% of the cases.
Results
At the time of the latest follow-up, 33 patients (39 hips) had died and 17 cases had been lost to follow-up. The median follow-up was 122 months with a minimum of 10 years. Eight hips had been revised, leaving 177 hips in 120 living patients without revision. Six cups were revised because of aseptic loosening. Two hips were revised for sepsis. The mean Merle d’Aubigné score for the remaining hips was 16 (range 7–18) at the latest follow-up. For aseptic loosening, the probability of survival of the cup was 0.97 (95% confidence interval, 0.94–0.99). However, analysis of radiographs implied loosening in seven other cups without clinical symptoms.
Conclusions
The results of primary THA using an acetabular reinforcement ring parallel the excellent results of these implants often observed in difficult primary and revision arthroplasty at a minimum of 10 years. Survivorship is comparable to modern cementless implants. Medial migration that occurs with loosening of the acetabular component seems to be prevented with this implant. Radiographic loosening signs can exist without clinical symptoms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- THA:
-
Total hip arthroplasty
- ARRH:
-
Acetabular reinforcement ring with hook
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
References
Aebi M, Richner L, Ganz R (1989) Long term results of primary hip total prosthesis with acetabulum reinforcement ring. Orthopäde 18:504–510 (In German)
Aldinger PR, Thomsen M, Lukoschek M, Mau H, Ewerbeck V, Breusch SJ (2004) Long-term fate of uncemented, threaded acetabular components with smooth surface treatment: minimum 10-year follow-up of two different designs. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:469–475
Archibeck MJ, Berger RA, Jacobs JJ, Quigley LR, Gitelis S, Rosenberg A, Galante JO (2001) Second-generation cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1666–1673
Bauer R, Kerschbaumer F, Poisel S, Oberthaler W (1979) The transgluteal approach to the hip joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 95:47–49
Blacha J (2004) High osteolysis and revision rate with the hydroxyapatite-coated ABG hip prostheses: 65 hips in 56 young patients followed for 5–9 years. Acta Orthop Scand 75:276–282
Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH (1973) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55:1629–1632
Castoldi F, Rossi R, La Russa M, Sibelli P, Rossi P, Ranawat AS (2007) Ten-year survivorship of the Anatomique Benoist Girard I total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22:363–368
Clohisy JC, Harris WH (1999) The Harris–Galante uncemented femoral component in primary total hip replacement at 10 years. J Arthroplasty 14:915–917
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life-tables (with discussion). J Roy Statist Soc Ser B Method 34:187–220
Garcia-Rey E, Garcia-Cimbrelo E (2007) Long-term results of uncemented acetabular cups with an ACS polyethylene liner. A 14–16-year follow-up study. Int Orthop 31:205–210
Gerber A, Pisan M, Zurakowski D, Isler B (2003) Ganz reinforcement ring for reconstruction of acetabular defects in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85:2358–2364
Goodman SB, Adler SJ, Fyhrie DP, Schurman DJ (1988) The acetabular teardrop and its relevance to acetabular migration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 236:199–204
Grübl A, Chiari C, Gruber M, Kaider A, Gottsauner-Wolf F (2002) Cementless total hip arthroplasty with a tapered, rectangular titanium stem and a threaded cup: a minimum 10-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:425–431
Gurtner P, Aebi M, Ganz R (1993) The acetabular roof cup in revision arthroplasty of the hip. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 131:594–600 (In German)
Haentjens P, de Boeck H, Handelberg F, Casteleyn PP, Opdecam P (1993) Cemented acetabular reconstruction with the Müller support ring. A minimum 5-year clinical and roentgenographic follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:225–235
Hendrich C, Mehling I, Sauer U, Kirschner S, Martell JM (2006) Cementless acetabular reconstruction and structural bone-grafting in dysplastic hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:387–394
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (1999) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York, pp 40–52
Johnston RC, Fitzgerald RH, Harris WH, Müller ME, Sledge CB (1990), Clinical and radiographic evaluation of total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:161–168
Kaplan E, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Kawamura H, Dunbar MJ, Murray P, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH (2001) The porous coated anatomic total hip replacement: a ten to fourteen-year follow-up study of a cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1333–1338
Koch PP, Tannast M, Fujita H, Siebenrock KA and Ganz R (2008) Minimum ten year results of total hip arthroplasty with the acetabular reinforcement ring in avascular osteonecrosis. Int Orthop, in press
Livermore J, Ilstrup D, Morrey B (1990) Effect of femoral head size on wear of the polyethylene acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:518–528
Madey SM, Callaghan JJ, Olejniczak JP, Goetz DD, Johnston RC (1997) Charnley total hip arthroplasty with use of improved techniques of cementing. The results after a minimum of fifteen years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:53–64
McAuley JP, Moore KD, Culpepper WJ, Engh CA (1998) Total hip Arthroplasty with porous-coated prostheses fixed without cement in patients who are sixty-five years of age or older. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80:1648–1655
Merle d’Aubigné R, Postel M (1954) Functional results of hip arthroplasty with acrylic prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 36:451–475
Mulroy RD, Harris WH (1990) Failure of acetabular autogenous grafts in total hip arthroplasty. Increasing incidence: a follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:1536–1540
Older J (1986) Low-friction arthroplasty of the hip. A 10–12-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 211:36–42
Oosterbos CJ, Rahmy AI, Tonino AJ, Witpeerd W (2004) High survival rate of hydroxyapatite-coated hip prostheses: 100 consecutive hips followed for 10 years. Acta Orthop Scand 75:127–133
Pagnano MW, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, Shaughnessy WJ (1996) The effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. Long-term results in patients who have Crowe type-II congenital dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:1004–1014
Raut VV, Siney PD, Wroblewski BM (1996) Revision of the acetabular component of a total hip arthroplasty with cement in young patients without rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:1853–1856
Reikeras O, Gunderson RB (2006) Long-term results of HA coated threaded versus HA coated hemispheric press fit cups: 287 hips followed for 11 to 16 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126:503–508
Rosson J, Schatzker J (1992) The use of reinforcement rings to reconstruct deficient acetabula. J Bone Joint Surg Br 74:716–720
Shetty AA, Slack R, Tindall A, James KD, Rand C (2005) Results of a hydroxyapatite-coated (Furlong) total hip replacement: a 13- to 15-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:1050–1054
Siebenrock KA, Tannast M, Kim S, Morgenstern W, Ganz R (2005) Acetabular reconstruction using a roof reinforcement ring with hook for total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip-osteoarthritis minimum 10-year follow-up results. J Arthroplasty 20:492–498
Siebenrock KA, Trochsler M, Sadri H, Ganz R (2001) Hooked roof cup in revision of difficult loose hip prosthesis cups. Results after a minimum of 10 years. Orthopäde 30:273–279 (In German)
Smith SE, Harris WH (1997) Total hip arthroplasty performed with insertion of the femoral component with cement and the acetabular component without cement. Ten to thirteen-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:1827–1833
Stockl B, Beerkotte J, Krismer M, Fischer M, Bauer R (1997) Results of the Müller acetabular reinforcement ring in revision arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116:55–59
Surdam JW, Archibeck MJ, Schultz SC, Junick DW, White RE (2007), A second-generation cementless total hip arthroplasty mean 9-year results. J Arthroplasty 22:204–209
Tannast M, Langlotz U, Siebenrock KA, Wiese M, Bernsmann K, Langlotz F (2005) Anatomic referencing of cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 436:144–150
Thomas BJ, Saa J, Lane JM (1996) Total hip arthroplasty. Curr Opin Rheumatol 8:148–153
Wroblewski BM, Fleming PA, Siney PD (1999) Charnley low-frictional torque arthroplasty of the hip: 20- to 30-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:427–430
Wroblewski BM, Siney PD (1993) Charnley low-friction arthroplasty of the hip. Long-term results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 292:191–201
Xenos JS, Callaghan JJ, Heekin RD, Hopkinson WJ, Savory CG, Moore MS (1999) The porous-coated anatomic total hip prosthesis, inserted without cement. A prospective study with a minimum ten years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:74–82
Zehntner MK, Ganz R (1994) Midterm results (5.5–10 years) of acetabular allograft reconstruction with the acetabular reinforcement ring during total hip revision. J Arthroplasty 9:469–479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadri, H., Pfander, G., Siebenrock, KA. et al. Acetabular reinforcement ring in primary total hip arthroplasty: a minimum 10-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128, 869–877 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0612-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0612-z