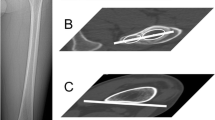
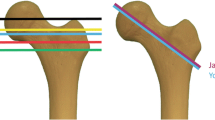
Abstract
Introduction
Computed tomography (CT) is considered the method of choice for detecting rotational malalignment of the femur. However, it is unclear how reliable the method is, and what the causes are of potential inaccuracies.
Materials and methods
To address these issues three observers measured the CT images of the femur of 76 patients on two separate occasions. The images were made during follow-up of a unilateral femoral shaft fractures. Rotational malalignment was determined by comparing the torsion angle of the injured to the noninjured leg.
Results
The pooled intraobserver variance was 3.9° and interobserver variance 4.1°. Of the two measurements of one observer 95% were up to 10.8° different, and between observers 95% of the measurements were up to 15.6° different.
Conclusions
CT measurements of rotational malalignment of the femur are not accurate. This is due principally to the difficulty in defining a line through the axis of the femoral neck. The accuracy can be improved by taking the average of two measurements.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bland JM, Altman DG (1996) Measurement error. BMJ 312:1654
Bråten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I (1992) Femoral anteversion in normal adults: ultrasound measurements in 50 men and 50 women. Acta Orthop Scand 63:29–32
Bråten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I (1993) Torsional deformity after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:799–803
Dunlap K, Shands AR Jr, Hollister LC Jr, Gaul JS Jr, Streit HA (1953) A new method for determination of torsion of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 35:289–311
Dunn DM (1952) Anteversion of the neck of the femur: a method of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br181–186
Ehrenstein T, Rikli DA, Peine R, Gutberlet M, Mittlmeier T, Banzer D, Mäurer J, Felix R (1999) A new ultrasound-based method for the assessment of torsional differences following closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. Skeletal Radiol 28:336–341
Jaarsma RL, Pakvis DFM, Verdonschot N, Biert J, van Kampen A (2004) Rotational malalignment after intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma (in press)
Jeanmart L, Baert AL, Wackenheim A (1983) Computer tomography of neck, chest, spine and limbs. Atlas of pathologic computer tomography, vol 3. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–177
Kuo TY, Skedros JG, Bloebaum RD (2003) Measurement of femoral anteversion by biplane radiography and computed tomography imaging: comparison with anatomic reference. Invest Radiol 38:221–229
Sennerich T, Sutter P, Ritter G, Zapf S (1992) Computertomographische Kontrolle des Antetorsionwinkels nach Oberschenkelschaftfrakturen des Erwachsenen. Unfallchirurg 95:301–305
Starker M, Hanusek S, Rittmeister M, Thoma W (1998) Validation of computerized tomography antetorsion angle measurement of the femur. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 136:420–427
Strecker W, Franzreb M, Pfeiffer T, Pokar S, Wikström M, Kinzl L (1994) Computerized tomography measurement of torsion angle of the lower extremities. Unfallchirurg 97:609–613
Svenningsen S, Apalset K, Terjesen T, Anda S (1989) Regression of femoral anteversion: a prospective study of intoeing children. Acta Orthop Scand 60:170–173
Terjesen T, Anda S, Svenningsen S (1990) Femoral anteversion in adolescents and adults measured by ultrasound. Clin Orthop 256:274–279
Wissing H et al. (1986) Determination of rotational defects of the femur by computer tomographic determination of antetorsion angle of the femoral neck. Unfallchirurg 12:1–11
Wissing H, Buddenbrock B (1993) Determining rotational errors of the femur by axial computerized tomography in comparison with clinical and conventional radiologic determination. Unfallchirurg 19:145–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaarsma, R.L., Bruggeman, A.W.A., Pakvis, D.F.M. et al. Computed tomography determined femoral torsion is not accurate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124, 552–554 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0729-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0729-7