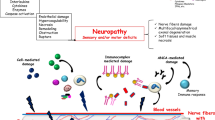
Abstract
Inflammatory neuropathies encompass groups of heterogeneous disorders characterized by pathogenic immune-mediated hematogenous leukocyte infiltration of peripheral nerves, nerve roots or both, with resultant demyelination or axonal degeneration or both. Inflammatory neuropathies may be divided into three major disease categories: Guillain–Barré syndrome (particularly the acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy variant), chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy and nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy (or peripheral nerve vasculitis). Despite major advances in molecular biology, pathology and genetics, the pathogenesis of these disorders remains elusive. There is insufficient knowledge on the mechanisms of hematogenous leukocyte trafficking into the peripheral nervous system to guide the development of specific molecular therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory neuropathies compared to disorders such as psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis. The recent isolation and characterization of human endoneurial endothelial cells that form the blood–nerve barrier provides an opportunity to elucidate leukocyte–endothelial cell interactions critical to the pathogenesis of inflammatory neuropathies at the interface between the systemic circulation and peripheral nerve endoneurium. This review discusses our current knowledge of the classic pathological features of inflammatory neuropathies, attempts at molecular classification and genetic determinants, the utilization of in vitro and in vivo animal models to determine pathogenic mechanisms at the interface between the systemic circulation and the peripheral nervous system relevant to these disorders and prospects for future potential molecular pathology biomarkers and targets for specific therapeutic intervention.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100:158–173. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000255691.76142.4a
Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res 100:174–190. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000255690.03436.ae
Andorfer B, Kieseier BC, Mathey E, Armati P, Pollard J, Oka N, Hartung HP (2001) Expression and distribution of transcription factor NF-kappaB and inhibitor IkappaB in the inflamed peripheral nervous system. J Neuroimmunol 116:226–232
Archelos JJ, Maurer M, Jung S, Miyasaka M, Tamatani T, Toyka KV, Hartung HP (1994) Inhibition of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody to the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1. Lab Invest 70:667–675
Asbury AK, Arnason BG, Adams RD (1969) The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine 48:173–215
Asbury AK, Cornblath DR (1990) Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 27(Suppl):S21–S24
Bansil S, Mithen FA, Singhal BS, Cook SD, Rohowsky-Kochan C (1992) Elevated neopterin levels in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Further evidence of immune activation. Arch Neurol 49:1277–1280
Bekircan-Kurt CE, Uceyler N, Sommer C (2014) Cutaneous activation of rage in nonsystemic vasculitic and diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 50:377–383. doi:10.1002/mus.24164
Belizna C, Duijvestijn A, Hamidou M, Tervaert JW (2006) Antiendothelial cell antibodies in vasculitis and connective tissue disease. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1545–1550. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.035295
Blum S, Csurhes P, Reddel S, Spies J, McCombe P (2014) Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and their HLA ligands in Guillain–Barre Syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 267:92–96. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.12.007
Blum S, McCombe PA (2014) Genetics of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP): current knowledge and future directions. J Peripher Nerv Syst 19:88–103. doi:10.1111/jns5.12074
Bosboom WM, Van den Berg LH, Mollee I, Sasker LD, Jansen J, Wokke JH, Logtenberg T (2001) Sural nerve T-cell receptor Vbeta gene utilization in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and vasculitic neuropathy. Neurology 56:74–81
Bouchard C, Lacroix C, Plante V, Adams D, Chedru F, Guglielmi JM, Said G (1999) Clinicopathologic findings and prognosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 52:498–503
Brechenmacher C, Vital C, Deminiere C, Laurentjoye L, Castaing Y, Gbikpi-Benissan G, Cardinaud JP, Favarel-Garrigues JP (1987) Guillain–Barre syndrome: an ultrastructural study of peripheral nerve in 65 patients. Clin Neuropathol 6:19–24
Broglio L, Erne B, Tolnay M, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Fuhr P, Steck AJ, Renaud S (2008) Allograft inflammatory factor-1: a pathogenetic factor for vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 38:1272–1279. doi:10.1002/mus.21033
Brown MJ, Rosen JL, Lisak RP (1987) Demyelination in vivo by Guillain–Barre syndrome and other human serum. Muscle Nerve 10:263–271. doi:10.1002/mus.880100310
Brun S, Beaino W, Kremer L, Taleb O, Mensah-Nyagan AG, Lam CD, Greer JM, de Seze J, Trifilieff E (2015) Characterization of a new rat model for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. J Neuroimmunol 278:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.11.022
Brunn A, Utermohlen O, Mihelcic M, Sanchez-Ruiz M, Carstov M, Blau T, Ustinova I, Penfold M, Montesinos-Rongen M, Deckert M (2013) Differential effects of CXCR4–CXCL12- and CXCR7–CXCL12-mediated immune reactions on murine P0106-125-induced experimental autoimmune neuritis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:772–787. doi:10.1111/nan.12039
Chang KH, Lyu RK, Tseng MY, Ro LS, Wu YR, Chang HS, Hsu WC, Kuo HC, Huang CC, Chu CC, Hsieh SY, Chen CM (2007) Elevated haptoglobin level of cerebrospinal fluid in Guillain–Barre syndrome revealed by proteomics analysis. Proteomics Clin Appl 1:467–475. doi:10.1002/prca.200600949
Chavada G, Willison HJ (2012) Autoantibodies in immune-mediated neuropathies. Curr Opin Neurol 25:550–555. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328357a77f
Chia L, Fernandez A, Lacroix C, Adams D, Plante V, Said G (1996) Contribution of nerve biopsy findings to the diagnosis of disabling neuropathy in the elderly. A retrospective review of 100 consecutive patients. Brain 119 (Pt 4):1091–1098
Chiang S, Ubogu EE (2013) The role of chemokines in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Muscle Nerve 48:320–330. doi:10.1002/mus.23829
Collins MP, Arnold WD, Kissel JT (2013) The neuropathies of vasculitis. Neurol Clin 31:557–595. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2013.01.007
Collins MP, Dyck PJ, Gronseth GS, Guillevin L, Hadden RD, Heuss D, Leger JM, Notermans NC, Pollard JD, Said G, Sobue G, Vrancken AF, Kissel JT, Peripheral Nerve S (2010) Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the classification, diagnosis, investigation, and immunosuppressive therapy of non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: executive summary. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:176–184. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2010.00281.x
Collins MP, Periquet-Collins I, Sahenk Z, Kissel JT (2010) Direct immunofluoresence in vasculitic neuropathy: specificity of vascular immune deposits. Muscle Nerve 42:62–69. doi:10.1002/mus.21639
Dalakas MC (2015) Pathogenesis of immune-mediated neuropathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:658–666. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.06.013
Dalakas MC, Medscape (2011) Advances in the diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment of CIDP. Nat Rev Neurol 7:507–517. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2011.121
Deng H, Yang X, Jin T, Wu J, Hu LS, Chang M, Sun XJ, Adem A, Winblad B, Zhu J (2008) The role of IL-12 and TNF-alpha in AIDP and AMAN. Eur J Neurol 15:1100–1105. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02261.x
Devaux JJ, Odaka M, Yuki N (2012) Nodal proteins are target antigens in Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst 17:62–71. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2012.00372.x
Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ (2013) Guillain–barre syndrome. Curr Treat Options Neurol 15:338–349. doi:10.1007/s11940-013-0231-z
Duan RS, Chen Z, Bao L, Quezada HC, Nennesmo I, Winblad B, Zhu J (2004) CCR5 deficiency does not prevent P0 peptide 180-199 immunized mice from experimental autoimmune neuritis. Neurobiol Dis 16:630–637. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.04.007
Engelhardt A, Lorler H, Neundorfer B (1993) Immunohistochemical findings in vasculitic neuropathies. Acta Neurol Scand 87:318–321
Fekih-Mrissa N, Mrad M, Riahi A, Sayeh A, Zaouali J, Gritli N, Mrissa R (2014) Association of HLA-DR/DQ polymorphisms with Guillain-Barre syndrome in Tunisian patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 121:19–22. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.03.014
Fokke C, van den Berg B, Drenthen J, Walgaard C, van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC (2014) Diagnosis of Guillain–Barre syndrome and validation of Brighton criteria. Brain 137:33–43. doi:10.1093/brain/awt285
Geleijns K, Brouwer BA, Jacobs BC, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, van Duijn CM, van Doorn PA (2004) The occurrence of Guillain–Barre syndrome within families. Neurology 63:1747–1750
Griffin JW, Stoll G, Li CY, Tyor W, Cornblath DR (1990) Macrophage responses in inflammatory demyelinating neuropathies. Ann Neurol 27(Suppl):S64–S68
Gwathmey KG, Burns TM, Collins MP, Dyck PJ (2014) Vasculitic neuropathies. Lancet Neurol 13:67–82. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70236-9
Hadden RD, Gregson NA, Gold R, Smith KJ, Hughes RA (2002) Accumulation of immunoglobulin across the ‘blood–nerve barrier’ in spinal roots in adoptive transfer experimental autoimmune neuritis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28:489–497
Hadden RD, Gregson NA, Gold R, Willison HJ, Hughes RA (2001) Guillain-Barre syndrome serum and anti-Campylobacter antibody do not exacerbate experimental autoimmune neuritis. J Neuroimmunol 119:306–316
Hafer-Macko CE, Sheikh KA, Li CY, Ho TW, Cornblath DR, McKhann GM, Asbury AK, Griffin JW (1996) Immune attack on the Schwann cell surface in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 39:625–635. doi:10.1002/ana.410390512
Hall SM, Hughes RA, Atkinson PF, McColl I, Gale A (1992) Motor nerve biopsy in severe Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 31:441–444. doi:10.1002/ana.410310416
Han RK, Cheng YF, Zhou SS, Guo H, He RD, Chi LJ, Zhang LM (2014) Increased circulating Th17 cell populations and elevated CSF osteopontin and IL-17 concentrations in patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Clin Immunol 34:94–103. doi:10.1007/s10875-013-9965-3
Harrison BM, Hansen LA, Pollard JD, McLeod JG (1984) Demyelination induced by serum from patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 15:163–170. doi:10.1002/ana.410150209
Hartung HP, Reiners K, Schmidt B, Stoll G, Toyka KV (1991) Serum interleukin-2 concentrations in Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic idiopathic demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison with other neurological diseases of presumed immunopathogenesis. Ann Neurol 30:48–53. doi:10.1002/ana.410300110
Haslbeck KM, Bierhaus A, Erwin S, Kirchner A, Nawroth P, Schlotzer U, Neundorfer B, Heuss D (2004) Receptor for advanced glycation endproduct (RAGE)-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation in vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 29:853–860. doi:10.1002/mus.20039
Heuss D, Probst-Cousin S, Kayser C, Neundorfer B (2000) Cell death in vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 23:999–1004
Honavar M, Tharakan JK, Hughes RA, Leibowitz S, Winer JB (1991) A clinicopathological study of the Guillain-Barre syndrome. Nine cases and literature review. Brain 114(Pt 3):1245–1269
Hu W, Dehmel T, Pirhonen J, Hartung HP, Kieseier BC (2006) Interleukin 23 in acute inflammatory demyelination of the peripheral nerve. Arch Neurol 63:858–864. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.6.858
Hu W, Janke A, Ortler S, Hartung HP, Leder C, Kieseier BC, Wiendl H (2007) Expression of CD28-related costimulatory molecule and its ligand in inflammatory neuropathies. Neurology 68:277–282. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000250240.99311.9d
Huang YC, Lyu RK, Tseng MY, Chang HS, Hsu WC, Kuo HC, Chu CC, Wu YR, Ro LS, Huang CC, Chen CM (2009) Decreased intrathecal synthesis of prostaglandin D2 synthase in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 206:100–105. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.10.011
Hughes R, Atkinson P, Coates P, Hall S, Leibowitz S (1992) Sural nerve biopsies in Guillain–Barre syndrome: axonal degeneration and macrophage-associated demyelination and absence of cytomegalovirus genome. Muscle Nerve 15:568–575. doi:10.1002/mus.880150506
Inglis HR, Csurhes PA, McCombe PA (2007) Antibody responses to peptides of peripheral nerve myelin proteins P0 and P2 in patients with inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:419–422. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.106617
Jander S, Stoll G (2001) Interleukin-18 is induced in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 114:253–258
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Kallenberg CG, Lamprecht P, Langford CA, Luqmani RA, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Ozen S, Pusey CD, Rasmussen N, Rees AJ, Scott DG, Specks U, Stone JH, Takahashi K, Watts RA (2013) 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11. doi:10.1002/art.37715
Jin T, Hu LS, Chang M, Wu J, Winblad B, Zhu J (2007) Proteomic identification of potential protein markers in cerebrospinal fluid of GBS patients. Eur J Neurol 14:563–568. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01761.x
Joint Task Force of the E, the PNS (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—First Revision. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2010.00245.x
Jung S, Gaupp S, Korn T, Kollner G, Hartung HP, Toyka KV (2004) Biphasic form of experimental autoimmune neuritis in dark Agouti rats and its oral therapy by antigen-specific tolerization. J Neurosci Res 75:524–535. doi:10.1002/jnr.10879
Kaida K, Ariga T, Yu RK (2009) Antiganglioside antibodies and their pathophysiological effects on Guillain–Barre syndrome and related disorders—a review. Glycobiology 19:676–692. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwp027
Kanda T, Numata Y, Mizusawa H (2004) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: decreased claudin-5 and relocated ZO-1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:765–769
Kanda T, Yamawaki M, Mizusawa H (2003) Sera from Guillain–Barre patients enhance leakage in blood–nerve barrier model. Neurology 60:301–306
Kaslow RA, Sullivan-Bolyai JZ, Hafkin B, Schonberger LB, Kraus L, Moore MJ, Yunis E, Williams RM (1984) HLA antigens in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Neurology 34:240–242
Khalili-Shirazi A, Gregson NA, Londei M, Summers L, Hughes RA (1998) The distribution of CD1 molecules in inflammatory neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 158:154–163
Kiefer R, Dangond F, Mueller M, Toyka KV, Hafler DA, Hartung HP (2000) Enhanced B7 costimulatory molecule expression in inflammatory human sural nerve biopsies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69:362–368
Kiefer R, Kieseier BC, Bruck W, Hartung HP, Toyka KV (1998) Macrophage differentiation antigens in acute and chronic autoimmune polyneuropathies. Brain 121(Pt 3):469–479
Kieseier BC, Kiefer R, Gold R, Hemmer B, Willison HJ, Hartung HP (2004) Advances in understanding and treatment of immune-mediated disorders of the peripheral nervous system. Muscle Nerve 30:131–156. doi:10.1002/mus.20076
Kieseier BC, Tani M, Mahad D, Oka N, Ho T, Woodroofe N, Griffin JW, Toyka KV, Ransohoff RM, Hartung HP (2002) Chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammatory demyelinating neuropathies: a central role for IP-10. Brain 125:823–834
Kim HJ, Jung CG, Jensen MA, Dukala D, Soliven B (2008) Targeting of myelin protein zero in a spontaneous autoimmune polyneuropathy. J Immunol 181:8753–8760
Koski CL, Chou DK, Jungalwala FB (1989) Anti-peripheral nerve myelin antibodies in Guillain–Barre syndrome bind a neutral glycolipid of peripheral myelin and cross-react with Forssman antigen. J Clin Investig 84:280–287. doi:10.1172/JCI114152
Krendel DA, Parks HP, Anthony DC, St Clair MB, Graham DG (1989) Sural nerve biopsy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 12:257–264. doi:10.1002/mus.880120402
Kusunoki S, Kaida K (2011) Antibodies against ganglioside complexes in Guillain–Barre syndrome and related disorders. J Neurochem 116:828–832. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07029.x
Leppert D, Hughes P, Huber S, Erne B, Grygar C, Said G, Miller KM, Steck AJ, Probst A, Fuhr P (1999) Matrix metalloproteinase upregulation in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy. Neurology 53:62–70
Li C, Zhao P, Sun X, Che Y, Jiang Y (2013) Elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma interleukin-37 in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2013:639712. doi:10.1155/2013/639712
Li S, Yu M, Li H, Zhang H, Jiang Y (2012) IL-17 and IL-22 in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma are elevated in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2012:260473. doi:10.1155/2012/260473
Lindenlaub T, Sommer C (2003) Cytokines in sural nerve biopsies from inflammatory and non-inflammatory neuropathies. Acta Neuropathol 105:593–602. doi:10.1007/s00401-003-0689-y
Madia F, Frisullo G, Nociti V, Conte A, Luigetti M, Del Grande A, Patanella AK, Iorio R, Tonali PA, Batocchi AP, Sabatelli M (2009) pSTAT1, pSTAT3, and T-bet as markers of disease activity in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 14:107–117. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2009.00220.x
Maimone D, Annunziata P, Simone IL, Livrea P, Guazzi GC (1993) Interleukin-6 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 47:55–61
Makowska A, Pritchard J, Sanvito L, Gregson N, Peakman M, Hayday A, Hughes R (2008) Immune responses to myelin proteins in Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:664–671. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.123943
Man S, Ubogu EE, Ransohoff RM (2007) Inflammatory cell migration into the central nervous system: a few new twists on an old tale. Brain Pathol 17:243–250. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00067.x
Manolov V, Petrova I, Vasilev V (2014) VEGF levels in diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy. Clin Lab 60:1573–1577
Mathey EK, Park SB, Hughes RA, Pollard JD, Armati PJ, Barnett MH, Taylor BV, Dyck PJ, Kiernan MC, Lin CS (2015) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: from pathology to phenotype. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2014-309697
Mathey EK, Pollard JD, Armati PJ (1999) TNF alpha, IFN gamma and IL-2 mRNA expression in CIDP sural nerve biopsies. J Neurol Sci 163:47–52
Matsumuro K, Izumo S, Umehara F, Osame M (1994) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: histological and immunopathological studies on biopsied sural nerves. J Neurol Sci 127:170–178
McCombe PA, van der Kreek SA, Pender MP (1992) Neuropathological findings in chronic relapsing experimental allergic neuritis induced in the Lewis rat by inoculation with intradural root myelin and treatment with low dose cyclosporin A. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18:171–187
Mei FJ, Ishizu T, Murai H, Osoegawa M, Minohara M, Zhang KN, Kira J (2005) Th1 shift in CIDP versus Th2 shift in vasculitic neuropathy in CSF. J Neurol Sci 228:75–85. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2004.10.001
Melendez-Vasquez C, Redford J, Choudhary PP, Gray IA, Maitland P, Gregson NA, Smith KJ, Hughes RA (1997) Immunological investigation of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 73:124–134
Meyer zu Horste G, Hartung HP, Kieseier BC (2007) From bench to bedside–experimental rationale for immune-specific therapies in the inflamed peripheral nerve. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:198–211. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0452
Meyer zu Horste G, Reiners J, Lehmann HC, Airas L, Kieseier BC (2009) CD73 is expressed on invading T lymphocytes in the inflamed peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve 40:287–289. doi:10.1002/mus.21325
Mitchell GW, Williams GS, Bosch EP, Hart MN (1991) Class II antigen expression in peripheral neuropathies. J Neurol Sci 102:170–176
Mitsuma N, Yamamoto M, Iijima M, Hattori N, Ito Y, Tanaka F, Sobue G (2004) Wide range of lineages of cells expressing nerve growth factor mRNA in the nerve lesions of patients with vasculitic neuropathy: an implication of endoneurial macrophage for nerve regeneration. Neuroscience 129:109–117. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.083
Monos DS, Papaioakim M, Ho TW, Li CY, McKhann GM (1997) Differential distribution of HLA alleles in two forms of Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Infect Dis 176(Suppl 2):S180–S182
Mrad M, Fekih-Mrissa N, Mansour M, Seyah A, Riahi A, Gritli N, Mrissa R (2013) Association of HLA-DR/DQ polymorphism with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) in Tunisian patients. Transfus Apher Science 49:623–626. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2013.07.024
Muller M, Stenner M, Wacker K, Ringelstein EB, Hickey WF, Kiefer R (2006) Contribution of resident endoneurial macrophages to the local cellular response in experimental autoimmune neuritis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:499–507. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000229239.43866.d1
Musso AM, Zanusso GL, Bonazzi ML, Tomelleri G, Bonetti B, Moretto G, Vio M, Monaco S (1994) Increased serum levels of ICAM-1, ELAM-1 and TNF-alpha in inflammatory disorders of the peripheral nervous system. Ital J Neurol Sci 15:267–271
Nagai A, Murakawa Y, Terashima M, Shimode K, Umegae N, Takeuchi H, Kobayashi S (2000) Cystatin C and cathepsin B in CSF from patients with inflammatory neurologic diseases. Neurology 55:1828–1832
Nishino S, Kanbayashi T, Fujiki N, Uchino M, Ripley B, Watanabe M, Lammers GJ, Ishiguro H, Shoji S, Nishida Y, Overeem S, Toyoshima I, Yoshida Y, Shimizu T, Taheri S, Mignot E (2003) CSF hypocretin levels in Guillain–Barre syndrome and other inflammatory neuropathies. Neurology 61:823–825
Nyati KK, Prasad KN, Verma A, Paliwal VK (2010) Correlation of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 with proinflammatory cytokines in Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Neurosci Res 88:3540–3546. doi:10.1002/jnr.22514
Nyland H, Matre R, Mork S (1981) Immunological characterization of sural nerve biopsies from patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 9(Suppl):80–86
Oka N, Akiguchi I, Nagao M, Nishio T, Kawasaki T, Kimura J (1994) Expression of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 44:946–950
Oka N, Kawasaki T, Mizutani K, Sugiyama H, Akiguchi I (2007) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha may be a marker for vasculitic neuropathy. Neuropathology 27:509–515. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1789.2007.00817.x
Oomes PG, van der Meche FG, Markus-Silvis L, Meulstee J, Kleyweg RP (1991) In vivo effects of sera from Guillain–Barre subgroups: an electrophysiological and histological study on rat nerves. Muscle Nerve 14:1013–1020. doi:10.1002/mus.880141013
Orlikowski D, Chazaud B, Plonquet A, Poron F, Sharshar T, Maison P, Raphael JC, Gherardi RK, Creange A (2003) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and chemokine receptor CCR2 productions in Guillain-Barre syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis. J Neuroimmunol 134:118–127
Petzold A, Brettschneider J, Jin K, Keir G, Murray NM, Hirsch NP, Itoyama Y, Reilly MM, Takeda A, Tumani H (2009) CSF protein biomarkers for proximal axonal damage improve prognostic accuracy in the acute phase of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Muscle Nerve 40:42–49. doi:10.1002/mus.21239
Pollard JD, Baverstock J, McLeod JG (1987) Class II antigen expression and inflammatory cells in the Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 21:337–341. doi:10.1002/ana.410210404
Pollard JD, McCombe PA, Baverstock J, Gatenby PA, McLeod JG (1986) Class II antigen expression and T lymphocyte subsets in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 13:123–134
Press R, Nennesmo I, Kouwenhoven M, Huang YM, Link H, Pashenkov M (2005) Dendritic cells in the cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral nerves in Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 159:165–176. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2004.09.020
Press R, Pashenkov M, Jin JP, Link H (2003) Aberrated levels of cerebrospinal fluid chemokines in Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Clin Immunol 23:259–267
Previtali SC, Archelos JJ, Hartung HP (1998) Expression of integrins in experimental autoimmune neuritis and Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 44:611–621. doi:10.1002/ana.410440406
Prineas JW (1981) Pathology of the Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 9(Suppl):6–19
Probst-Cousin S, Neundorfer B, Heuss D (2010) Microvasculopathic neuromuscular diseases: lessons from hypoxia-inducible factors. Neuromuscul Disord 20:192–197. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2010.01.005
Putzu GA, Figarella-Branger D, Bouvier-Labit C, Liprandi A, Bianco N, Pellissier JF (2000) Immunohistochemical localization of cytokines, C5b-9 and ICAM-1 in peripheral nerve of Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Neurol Sci 174:16–21
Rees JH, Vaughan RW, Kondeatis E, Hughes RA (1995) HLA-class II alleles in Guillain-Barre syndrome and Miller Fisher syndrome and their association with preceding Campylobacter jejuni infection. J Neuroimmunol 62:53–57
Regent A, Dib H, Ly KH, Agard C, Tamby MC, Tamas N, Weksler B, Federici C, Broussard C, Guillevin L, Mouthon L (2011) Identification of target antigens of anti-endothelial cell and anti-vascular smooth muscle cell antibodies in patients with giant cell arteritis: a proteomic approach. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R107. doi:10.1186/ar3388
Regent A, Lofek S, Dib H, Bussone G, Tamas N, Federici C, Broussard C, Guillevin L, Mouthon L (2014) Identification of target antigens of anti-endothelial cell antibodies in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: a proteomic approach. Clin Immunol 153:123–135. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2014.03.020
Rinaldi S (2013) Update on Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst 18:99–112. doi:10.1111/jns5.12020
Rizzuto N, Morbin M, Cavallaro T, Ferrari S, Fallahi M, Galiazzo Rizzuto S (1998) Focal lesions area feature of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Acta Neuropathol 96:603–609
Saida T, Saida K, Lisak RP, Brown MJ, Silberberg DH, Asbury AK (1982) In vivo demyelinating activity of sera from patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 11:69–75. doi:10.1002/ana.410110112
Sainaghi PP, Collimedaglia L, Alciato F, Leone MA, Naldi P, Molinari R, Monaco F, Avanzi GC (2010) The expression pattern of inflammatory mediators in cerebrospinal fluid differentiates Guillain–Barre syndrome from chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Cytokine 51:138–143. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2010.05.005
Sainaghi PP, Collimedaglia L, Alciato F, Leone MA, Puta E, Naldi P, Castello L, Monaco F, Avanzi GC (2008) Elevation of Gas6 protein concentration in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). J Neurol Sci 269:138–142. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.01.005
Salomon B, Rhee L, Bour-Jordan H, Hsin H, Montag A, Soliven B, Arcella J, Girvin AM, Padilla J, Miller SD, Bluestone JA (2001) Development of spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy in B7-2-deficient NOD mice. J Exp Med 194:677–684
Sarikcioglu L, Demirel BM, Demir N, Yildirim FB, Demirtop A, Oguz N (2008) Morphological and ultrastructural analysis of the watershed zones after stripping of the vasa nervorum. Int J Neurosci 118:1145–1155. doi:10.1080/00207450801898220
Schmidt B, Toyka KV, Kiefer R, Full J, Hartung HP, Pollard J (1996) Inflammatory infiltrates in sural nerve biopsies in Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 19:474–487. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199604)19:4<474:AID-MUS8>3.0.CO;2-9
Sessa G, Nemni R, Canal N, Marchisio PC (1997) Circulating fragments of myelin-associated alpha 6 beta 4 integrin in Guillain–Barre syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 80:115–120
Shimizu F, Sawai S, Sano Y, Beppu M, Misawa S, Nishihara H, Koga M, Kuwabara S, Kanda T (2014) Severity and patterns of blood–nerve barrier breakdown in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: correlations with clinical subtypes. PLoS One 9:e104205. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104205
Soliven B (2014) Animal models of autoimmune neuropathy. ILAR J 54:282–290. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilt054
Sommer C, Toyka K (2011) Nerve biopsy in chronic inflammatory neuropathies: in situ biomarkers. J Peripher Nerv Syst 16(Suppl 1):24–29. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2011.00301.x
Steck AJ, Kinter J, Renaud S (2011) Differential gene expression in nerve biopsies of inflammatory neuropathies. J Peripher Nerv Syst 16(Suppl 1):30–33. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2011.00302.x
Stevens A, Schabet M, Schott K, Wietholter H (1989) Role of endoneural cells in experimental allergic neuritis and characterisation of a resident phagocytic cell. Acta Neuropathol 77:412–419
Suzumura A, Sobue G, Sugimura K, Matsuoka Y, Sobue I (1985) Chronic experimental allergic neuritis (EAN) in juvenile guinea pigs: immunological comparison with acute EAN in adult guinea pigs. Acta Neurol Scand 71:364–372
Teener JW (2012) Miller Fisher’s syndrome. Semin Neurol 32:512–516. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1334470
Tumani H, Pfeifle M, Lehmensiek V, Rau D, Mogel H, Ludolph AC, Brettschneider J (2009) Candidate biomarkers of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP): proteome analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 214:109–112. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.06.012
Ubogu EE (2011) Chemokine receptors as specific anti-inflammatory targets in peripheral nerves. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 11:141–153
Ubogu EE (2012) Translational strategies in peripheral neuroinflammation and neurovascular repair. Transl Neurosci 3:373–383. doi:10.2478/s13380-012-0039-4
Ubogu EE (2013) Chemokine-dependent signaling pathways in the peripheral nervous system. Methods Mol Biol 1013:17–30. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-426-5_2
Ubogu EE (2013) The molecular and biophysical characterization of the human blood–nerve barrier: current concepts. J Vasc Res 50:289–303. doi:10.1159/000353293
Ubogu EE, Yosef N, Xia RH, Sheikh KA (2012) Behavioral, electrophysiological, and histopathological characterization of a severe murine chronic demyelinating polyneuritis model. J Peripher Nerv Syst 17:53–61. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2012.00375.x
Uceyler N, Devigili G, Toyka KV, Sommer C (2010) Skin biopsy as an additional diagnostic tool in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 120:109–116. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0662-5
van den Berg B, Walgaard C, Drenthen J, Fokke C, Jacobs BC, van Doorn PA (2014) Guillain-Barre syndrome: pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Nat Rev Neurol 10:469–482. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2014.121
van den Berg LH, Oey PL, Wokke JH, Veldman H, Wieneke GH, Notermans SH (1994) Features of the Guillain–Barre syndrome in mice following intraperitoneal injection of patient serum. J Neurol Sci 127:103–106
van Doorn PA, Schreuder GM, Vermeulen M, d’Amaro J, Brand A (1991) HLA antigens in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 32:133–139
Van Rhijn I, Van den Berg LH, Bosboom WM, Otten HG, Logtenberg T (2000) Expression of accessory molecules for T-cell activation in peripheral nerve of patients with CIDP and vasculitic neuropathy. Brain 123(Pt 10):2020–2029
Vedeler CA, Matre R, Nyland H (1988) Class and IgG subclass distribution of antibodies against peripheral nerve myelin in sera from patients with inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand 78:401–407
Vrancken AF, Gathier CS, Cats EA, Notermans NC, Collins MP (2011) The additional yield of combined nerve/muscle biopsy in vasculitic neuropathy. Eur J Neurol 18:49–58. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03041.x
Wakerley BR, Uncini A, Yuki N, Group GBSC, Group GBSC (2014) Guillain-Barre and Miller Fisher syndromes—new diagnostic classification. Nat Rev Neurol 10:537–544. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2014.138
Wang XK, Zhang HL, Meng FH, Chang M, Wang YZ, Jin T, Mix E, Zhu J (2013) Elevated levels of S100B, tau and pNFH in cerebrospinal fluid are correlated with subtypes of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Neurol Sci 34:655–661. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1092-z
Wilmshurst JM, Pohl KR, Vaughan RW, Hughes RA (1999) Familial Guillain–Barre syndrome. Eur J Neurol 6:499–503
Winer J, Hughes S, Cooper J, Ben-Smith A, Savage C (2002) gamma delta T cells infiltrating sensory nerve biopsies from patients with inflammatory neuropathy. J Neurol 249:616–621. doi:10.1007/s004150200072
Winer JB (2011) Guillain–Barre syndrome: clinical variants and their pathogenesis. J Neuroimmunol 231:70–72. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.09.017
Xia RH, Yosef N, Ubogu EE (2010) Selective expression and cellular localization of pro-inflammatory chemokine ligand/receptor pairs in the sciatic nerves of a severe murine experimental autoimmune neuritis model of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:388–398. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01092.x
Yalvac ME, Arnold WD, Hussain SR, Braganza C, Shontz KM, Clark KR, Walker CM, Ubogu EE, Mendell JR, Sahenk Z (2014) VIP-expressing dendritic cells protect against spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy. Mol Ther 22:1353–1363. doi:10.1038/mt.2014.77
Yamamoto M, Ito Y, Mitsuma N, Li M, Hattori N, Sobue G (2001) Pathology-related differential expression regulation of NGF, GDNF, CNTF, and IL-6 mRNAs in human vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 24:830–833
Yan WX, Archelos JJ, Hartung HP, Pollard JD (2001) P0 protein is a target antigen in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann Neurol 50:286–292
Yan WX, Taylor J, Andrias-Kauba S, Pollard JD (2000) Passive transfer of demyelination by serum or IgG from chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy patients. Ann Neurol 47:765–775
Yang Y, Liu S, Qin Z, Cui Y, Qin Y, Bai S (2009) Alteration of cystatin C levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Guillain–Barre Syndrome by a proteomical approach. Mol Biol Rep 36:677–682. doi:10.1007/s11033-008-9228-1
Yang YR, Liu SL, Qin ZY, Liu FJ, Qin YJ, Bai SM, Chen ZY (2008) Comparative proteomics analysis of cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:737–744. doi:10.1007/s10571-007-9257-7
Yano K, Gale D, Massberg S, Cheruvu PK, Monahan-Earley R, Morgan ES, Haig D, von Andrian UH, Dvorak AM, Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity is an evolutionarily conserved feature of the endothelium. Blood 109:613–615. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-026401
Yosef N, Ubogu EE (2012) alpha(M)beta(2)-integrin-intercellular adhesion molecule-1 interactions drive the flow-dependent trafficking of Guillain–Barre syndrome patient derived mononuclear leukocytes at the blood–nerve barrier in vitro. J Cell Physiol 227:3857–3875. doi:10.1002/jcp.24100
Yosef N, Xia RH, Ubogu EE (2010) Development and characterization of a novel human in vitro blood–nerve barrier model using primary endoneurial endothelial cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:82–97. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181c84a9a
Yuan F, Yosef N, Lakshmana Reddy C, Huang A, Chiang SC, Tithi HR, Ubogu EE (2014) CCR2 gene deletion and pharmacologic blockade ameliorate a severe murine experimental autoimmune neuritis model of Guillain–Barre syndrome. PLoS One 9:e90463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090463
Yuki N, Hartung HP (2012) Guillain–Barre syndrome. N Engl J Med 366:2294–2304. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1114525
Zhang HL, Zhang XM, Mao XJ, Deng H, Li HF, Press R, Fredrikson S, Zhu J (2012) Altered cerebrospinal fluid index of prealbumin, fibrinogen, and haptoglobin in patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand 125:129–135. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2011.01511.x
Zhang HL, Zheng XY, Zhu J (2013) Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokines in Guillain–Barre syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24:443–453. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.005
Zou LP, Pelidou SH, Abbas N, Deretzi G, Mix E, Schaltzbeerg M, Winblad B, Zhu J (1999) Dynamics of production of MIP-1alpha, MCP-1 and MIP-2 and potential role of neutralization of these chemokines in the regulation of immune responses during experimental autoimmune neuritis in Lewis rats. J Neuroimmunol 98:168–175
Zweiman B, Rostami A, Lisak RP, Moskovitz AR, Pleasure DE (1983) Immune reactions to P2 protein in human inflammatory demyelinative neuropathies. Neurology 33:234–237
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to past and current employees of the Shin J Oh Muscle and Nerve Histopathology Lab, the University of Alabama at Birmingham for generating histopathology slides from which digital photomicrographs are shown, and current and past members and collaborators of the Neuromuscular Immunopathology Research Laboratory (NIRL) for digital photomicrographs and videos depicting inflammation in murine models and in vitro leukocyte trafficking. Work in the NIRL is currently supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R21 NS078226 (2012-2015), R01 NS075212 (2012-2017) and a Creative and Novel Ideas in HIV Research subaward P30 AI27767 (2012-2015), as well as institutional support from the Department of Neurology, the University of Alabama at Birmingham (2013-). The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 22070 kb) Supplementary Video 1. Pathogenic leukocyte trafficking at the human BNB in vitro. Peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (200,000/mL) from an untreated AIDP patient were infused over a cytokine-treated monolayer of primary human endoneurial endothelial cells (that form the BNB) at a linear velocity of 1 mm/s, mimicking estimated capillary flow rates in vivo. The multi-step paradigm is demonstrated with leukocytes (phase bright) rolling on the endothelial monolayer surface, followed by arrest, firm adhesion and some transmigration (change from phase bright to phase dark) during this 20 min epoch (compressed to 10X normal frame rate). Clusters of leukocytes aggregate at sites of intercellular junctions, presumably at sites of high chemokine presentation by specific glycosaminoglycans, and migrate via the paracellular route in this model system. Frame size 650 μm × 870 μm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ubogu, E.E. Inflammatory neuropathies: pathology, molecular markers and targets for specific therapeutic intervention. Acta Neuropathol 130, 445–468 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1466-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1466-4