Abstract
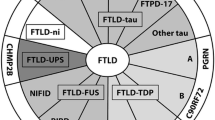
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is clinically, pathologically and genetically heterogeneous. Three major proteins are implicated in its pathogenesis. About half of cases are characterized by depositions of the microtubule associated protein, tau (FTLD-tau). In most of the remaining cases, deposits of the transactive response (TAR) DNA-binding protein with Mw of 43 kDa, known as TDP-43 (FTLD-TDP), are seen. Lastly, about 5–10 % of cases are characterized by abnormal accumulations of a third protein, fused in sarcoma (FTLD-FUS). Depending on the protein concerned, the signature accumulations can take the form of inclusion bodies (neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions and neuronal intranuclear inclusions) or dystrophic neurites, in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and subcortex. In some instances, glial cells are also affected by inclusion body formation. In motor neurone disease (MND), TDP-43 or FUS inclusions can present within motor neurons of the brain stem and spinal cord. This present paper attempts to critically examine the role of such proteins in the pathogenesis of FTLD and MND as to whether they might exert a direct pathogenetic effect (gain of function), or simply act as relatively innocent witnesses to a more fundamental loss of function effect. We conclude that although there is strong evidence for both gain and loss of function effects in respect of each of the proteins concerned, in reality, it is likely that each is a single face of either side of the coin, and that both will play separate, though complementary, roles in driving the damage which ultimately leads to the downfall of neurons and clinical expression of disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson MK, Stahlberg A, Arvidsson Y, Olofsson A, Semb H, Stenman G, Nilsson O, Aman P (2008) The multifunctional FUS, EWS and TAF15 proto-oncoproteins show cell type specific expression patterns and involvement in cell spreading and stress response. BMC Cell Biol 9:37
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Oda T (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:602–611
Armstrong RA, Ellis W, Hamilton RL, Mackenzie IR, Hedreen J, Gearing M, Montine T, Vonsattel JP, Head E, Lieberman AP, Cairns NJ (2010) Neuropathological heterogeneity in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy: a quantitative study of 94 cases using principal components analysis. J Neural Transm 117:227–239
Ayala YM, De Conti L, Avendano-Vasquez SE, Dhir A, Romano M, D’Ambrogio A, Tollervey J, Ule J, Baralle M, Buratti E, Baralle F (2011) TDP-43 regulates its mRNA levels through a negative feedback loop. EMBO 30:277–288
Baborie A, Griffiths TD, Jaros E, Richardson A, Ferrari R, Moreno J, Momeni P, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Duplessis D, Pal P, Rollinson S, Pickering-Brown SM, Thompson JC, Neary D, Snowden JS, Perry R, Mann DMA (2011) Pathological correlates of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in the elderly. Acta Neuropathol 12:365–373
Baker M, Mackenzie IRA, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick AD, Rollinson S, Cannon A, Dwosh E, Neary D, Melquist S, Richardson A, Dickson D, Eriksen J, Robinson T, Zehr C, Dickey CA, Crook R, McGowan E, Mann D, Boeve B, Feldman H, Hutton M (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442:916–919
Barmada SJ, Skibinski G, Korb E, Rao EJ, Wu JY, Finkbeiner S (2010) Cytoplasmic mislocalization of TDP-43 is toxic to neurons and enhanced by a mutation associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 30:639–649
Borroni B, Bonvicini C, Alberici A, Buratti E, Agosti C, Archetti S, Papetti A, Stuani C, Di Luca M, Gennarelli M, Padovani A (2009) Mutation within TARDBP leads to frontotemporal dementia without motor neuron disease. Hum Mutat 30:E974–E983
Brellstaff J, Lashley T, Holton JL, Lees AJ, Rossor MN, Bandopadhyay R, Revesz T (2011) Transportin 1: a marker for FTLD-FUS. Acta Neuropathol 122:591–600
Brettschneider J, Van Deerlin VM, Robinson JL, Kwong L, Lee EB, Ali YO, Safren N, Monteiro MJ, Toledo JB, Elman L, McCluskey L, Irwin DJ, Grossman M, Molina-Porcel L, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Pattern of ubiquilin pathology in ALS and FTLD indicates presence of C9ORF72 hexanucleotide expansion. Acta Neuropathol 123:825–839
Buratti E, Baralle FE (2009) The molecular links between TDP-43 dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Adv Genet 66:1–34
Cairns NJ, Ghoshal N (2010) FUS: a new actor on the frontotemporal lobar degeneration stage. Neurology 74:354–356
Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Lee VM, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL 3rd, Schneider JA, Grinberg LT, Halliday G, Duyckaerts C, Lowe JS, Holm IE, Tolnay M, Okamoto K, Yokoo H, Murayama S, Woulfe J, Munoz DG, Dickson DW, Ince PG, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DM, Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (2007) Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 114:5–22
Cairns NJ, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Holm IE, Troost D, Hatanpaa KJ, Foong C, White CL 3rd, Schneider JA, Kretzschmar HA, Carter D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Paulsmeyer K, Strider J, Gitcho M, Goate AM, Morris JC, Mishra M, Kwong LK, Stieber A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Mackenzie IR (2007) TDP-43 in familial and sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin inclusions. Am J Pathol 171:227–240
Chen S, Townsend K, Goldberg TE, Davies P, Conejero-Goldberg C (2010) MAPT isoforms: differential transcriptional profiles related to 3R and 4R splice variants. J Alz Dis 22:1313–1329
Chen Y, Yang M, Deng J, Chen X, Ye Y, Zhu L, Liu J, Ye H, Shen Y, Li Y, Rao EJ, Fushimi K, Zhou X, Bigio EH, Mesulam M, Xu Q, Wu JY (2011) Expression of human FUS protein in Drosophila leads to progressive neurodegeneration. Protein Cell 2:477–486
Colombrita C, Zennaro E, Fallini C, Weber M, Sommacal A, Buratti E, Silani V, Ratti A (2009) TDP-43 is recruited to stress granules in conditions of oxidative insult. J Neurochem 111:1051–1061
Cook C, Gebdron TF, Scheffel K, Carlomagno Y, Dunmore J, Deture M, Petrucelli L (2012) Loss of HDAC6, a novel CHIP substrate, alleviates abnormal tau accumulation. Hum Mol Genet 21:2936–2945
Couthouis J, Hart MP, Shorter J, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Erion R, Oristano R, Liu AX, Ramos D, Jethava N, Hosangadi D, Epstein J, Chiang A, Diaz Z, Nakaya T, Ibrahim F, Kim HJ, Solski JA, Williams KL, Mojsilovic-Petrovic J, Ingre C, Boylan K, Graff-Radford NR, Dickson DW, Clay-Falcone D, Elman L, McCluskey L, Greene R, Kalb RG, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Ludolph A, Robberecht W, Andersen PM, Nicholson GA, Blair IP, King OD, Bonini NM, Van Deerlin V, Rademakers R, Mourelatos Z, Gitler AD (2011) A yeast functional screen predicts new candidate ALS disease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20881–20890
Cruts M, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Engelborghs S, Wils H, Pirici D, Rademakers R, Vandenberghe R, Dermaut B, Martin JJ, van Duijn C, Peeters K, Sciot R, Santens P, De Pooter T, Mattheijssens M, Van den Broeck M, Cuijt I, Vennekens K, De Deyn PP, Kumar-Singh S, Van Broeckhoven C (2006) Null mutations in progranulin cause ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Nature 442:920–924
Cushman M, Johnson BS, King OD, Gitler AD, Shorter J (2010) Prion-like disorders: blurring the divide between transmissibility and infectivity. J Cell Sci 123:1191–1201
Davidson YS, Robinson AC, Hu Q, Mishra M, Baborie A, Jaros E, Perry RH, Cairns NJ, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Neary D, Snowden JS, Bigio EH, Mann DM (2012) Nuclear carrier and RNA binding proteins in frontotemporal lobar degeneration associated with fused in sarcoma (FUS) pathological changes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2012.01274.x
De Barreda EG, Dawson HN, Vitek MP, Avila J (2010) Tau deficiency leads to the upregulation of BAR-57, a protein involved in neuron-specific gene repression. FEBS Lett 584:2265–2270
DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Nicholson AM, Finch NA, Flynn H, Adamson J, Kouri N, Wojtas A, Sengdy P, Hsiung GY, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Josephs KA, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Wszolek ZK, Feldman H, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Dickson DW, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R (2011) Expanded GGGGCC Hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 72:245–256
Deng H-X, Chen W, Hong S-T, Boycott KM, Gorrie GH, Siddique N, Yang Y, Fecto F, Shi Y, Zhai H, Jiang H, Hirano M, Rampersaud E, Jansen GH, Donkervoort S, Bigio EH, Brooks BR, Ajroud K, Sufit RL, Haines JL, Mugnaini E, Pericak-Vance M, Siddique T (2011) Mutations in UBQLN2 cause dominant X-linked form of juvenile and adult-onset ALS and ALS/dementia. Nature 477:211–215
Dewey CM, Cenik B, Sephton CF, Johnson BA, Herz J, Yu G (2012) TDP-43 aggregation in neurodegeneration: are stress granules the key? Brain Res 1462:16–25
Dormann D, Rodde R, Edbauer D, Bentmann E, Fischer I, Hruscha A, Than ME, Mackenzie IR, Capell A, Scmid B, Neumann M, Haass C (2010) ALS-associated fused in sarcoma (FUS) mutations disrupt transportin-mediated nuclear import. EMBO J 29:2841–2857
Fuentealba RA, Udan M, Bell S, Wegorzewska I, Shao J, Diamond MI, Weihl CC, Baloh RH (2010) Interaction with polyglutamine aggregates reveals a Q/N-rich domain in TDP-43. J Biol Chem 285:26304–26314
Gao FB, Taylor JP (2012) RNA-binding proteins in neurological disease. Brain Res 1462:1–2
Gitcho MA, Baloh RH, Chakraverty S, Mayo K, Norton JB, Levitch D, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL 3rd, Bigio EH, Caselli R, Baker M, Al-Lozi MT, Morris JC, Pestronk A, Rademakers R, Goate AM, Cairns NJ (2008) TDP-43 A315T mutation in familial motor neuron disease. Ann Neurol 63:535–538
Guo W, Chen Y, Zhou X, Kar A, Ray P, Chen X, Rao EJ, Yang M, Ye H, Zhu L, Liu J, Zhang D, Buratti E, Baralle FE, Bigio EH, Mesulam M, Xu Q, Shen Y, Fushimi K, Wu JY (2011) An ALS-associated mutation affecting TDP-43 enhances protein aggregation, fibril formation and neurotoxicity. Nature Struct Mol Biol 18:822–830
Hoell JI, Larsson E, Runge S, Nusbaum JD, Duggimpudi S, Farazi TA, Hafner M, Borkhardt A, Sander C, Tuschl T (2011) RNA targets of wild-type and mutant FET family proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:1428–1431
Holm IE, Isaacs AM, Mackenzie IR (2009) Absence of FUS-immunoreactive pathology in frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 3 (FTD-3) caused by mutation in the CHMP2B gene. Acta Neuropathol 118:719–720
Huang C, Zhou H, Tong J, Chen H, Liu YJ, Wang D, Wei X, Xia XG (2011) FUS transgenic rats develop the phenotypes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. PLoS Genet 7:e1002011
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden M, Pickering-Brown SM, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaf E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski JQ, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd P, Hayward N, Kwok JBJ, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann DM, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutation in tau with inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Ito D, Seki M, Tsunoda Y, Uchiyama H, Suzuki N (2011) Nuclear transport impairment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutations in FUS/TLS. Ann Neurol 69:152–162
Ke DK, Suchowerska AK, van der Hoven J, De Silva DM, Wu CW, van Eersel J, Ittner A, Ittner LM (2012) Lessons from tau-deficient mice. Int J Alz Dis. doi:10.1155/2012/873270
Kumar-Singh S (2011) Progranulin and TDP-43: mechanistic links and future directions. J Mol Neurosci 45:561–573
Kwiatkowski TJ, Bosco DA, LeClerc AL, Tamrazian E, Vanderburg CR, Russ C, Davis A, Gilchrist J, Kasarskis EJ, Munsat T, Valdmanis P, Rouleau GA, Hosler BA, Cortelli P, de Jong PA, Yoshinaga Y, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Yan J, Ticozzi N, Siddique T, Kenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Horvitz HR, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323:1205–1208
Lanson NA, Pandey UB (2012) FUS-related proteinopathies: lessons from animal models. Brain Res 1462:44–60
Lee EB, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:38–50
Li Y, Ray P, Rao E, Shi C, Guo W, Chen X, Woodruff EA III, Fushimi K, Wu JY (2010) A Drosophila model for TDP-43 proteinopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:3169–3174
Liu-Yesucevitz L, Bilqutay A, Zhang YJ, Vanderweyde T, Citro A, Mehta T, Zaarur N, McKee A, Bowser R, Sherman M, Petrucelli L, Wolozin B (2010) Tar DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) associates with stress granules: analysis of cultured cells and pathological brain tissue. PLoS ONE 5:e13250
Mackenzie IRA, Shi J, Shaw CL, Du Plessis D, Neary D, Snowden D, Mann DMA (2006) Dementia lacking distinctive histology (DLDH) revisited. Acta Neuropathol 112:551–559
Mackenzie IRA, Neumann M, Baborie A, Sampathu DM, Du Plessis D, Jaros E, Perry RH, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DMA, Lee VM-Y (2011) A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol 122:111–113
Mackenzie IRA, Munoz DG, Kusaka H, Yokota O, Ishihara K, Roeber S, Kretzschmar HA, Cairns NJ, Neumann M (2011) Distinct pathological subtypes of FTLD-FUS. Acta Neuropathol 121:207–218
McDonald KK, Aulas A, Destroismaisons L, Pickles S, Beleac E, Camu W, Rouleau GA, Vande Velde C (2011) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) regulates stress granule dynamics via differential regulation of G3BP and TOZ-1. Hum Mol Genet 20:1400–1410
Mori F, Tanji K, Odagiri S, Toyoshima Y, Yoshida M, Ikeda T, Sasaki H, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2012) Ubiquilin immunoreactivity in cytoplasmic and nuclear inclusions in synucleinopathies, polyglutamine diseases, and intranuclear inclusion body disease. Acta Neuropathol 124:149–151
Morris M, Maeda S, Vossel K, Mucke L (2011) The many faces of tau. Neuron 70:410–426
Mukherjee O, Pastor P, Cairns NJ, Chakraverty S, Kauwe JS, Shears S, Behrens MI, Budde J, Hinrichs AL, Norton J, Levitch D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Gitcho M, Tu PH, Tenenholz Grinberg L, Liscic RM, Armendariz J, Morris JC, Goate AM (2006) HDDD2 is a familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive, tau-negative inclusions caused by a missense mutation in the signal peptide of progranulin. Ann Neurol 60:314–322
Munoz DG, Neumann M, Kusaka H et al (2009) FUS pathology in basophilic inclusion body disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:617–627
Murray ME, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Rutherford NJ, Baker M, Duara R, Graff-Radford N, Wszolek ZK, Ferman TJ, Josephs KA, Boylan KB, Rademakers R, Dickson DW (2011) Clinical and neuropathological heterogeneity of c9FTD/ALS associated with hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72. Acta Neuropathol 122:673–690
Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DMA, Northen B, Goulding PJ, MacDermott N (1990) Frontal lobe dementia and motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:23–32
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, Boone K, Miller BL, Cummings J, Benson DF (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Neumann M, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Boyer PJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CD, Taylor JP, Kretzschmar HA, Kimonis VE, Forman MS (2007) TDP-43 in the ubiquitin pathology of frontotemporal dementia with VCP gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:152–157
Neumann M, Roeber S, Kretzchmar HA, Rademakers R, Baker M, Mackenzie IRA (2009) Abundant FUS-immunoreactive pathology in neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:605–616
Neumann M, Rademakers R, Roeber S, Baker M, Kretzschmar HA, Mackenzie IRA (2009) A new subtype of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with FUS pathology. Brain 132:2922–2931
Neumann M, Bentmann M, Dormann D, Jawaid A, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Ansorge O, Roeber S, Kretzschmar HA, Munoz DG, Kusaka H, Yokota O, Ang LC, Bilbao J, Rademakers R, Haass C, Mackenzie IRA (2011) FET proteins TAF15 and EWS are selective markers that distinguish FTLD-FUS from ALS with FUS mutations. Brain 134:2595–2609
Nonaka T, Kametani F, Aiai T, Akiyama H, Hasegawa M (2009) Truncation and pathogenic mutations facilitate the formation of intracellular aggregates of TDP-43. Hum Mol Genet 18:3353–3364
Perez M, Santa-Maria I, de Barreda EG, Zhu X, Cuadris R, Cabrero JR, Sanchez-Madrid F, Dawson HN, Vitek MP, Perry G, MAM S, Avila J (2009) Tau-an inhibitor of deacetylase HDAC6 function. J Neurochem 109:1756–1766
Polymenidou M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Hutt KR, Huelga S, Moran J, Liang TY, Ling S-C, Sun E, Wancewicz E, Mazur C, Kordasiewicz H, Sedaghat Y, Donohue JP, Shiue L, Bennett CF, Yeo GW, Cleveland DW (2011) Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat Neurosci 14:459–468
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43:815–825
Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simón-Sánchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Laaksovirta H, Schymick JC, van Swieten J, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Mok K, Ryten M, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister J, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita V-M, Kaivorinne A-L, Holtta-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chio A, Restagno G, Borghero G, Sabatelli M, The ITALSGEN Consortium, Heckerman D, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rothstein J, Sendtner M, Drepper C, Eichler EE, Alkan C, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Dutra A, Pak E, Hardy J, Singleton A, Williams NM, Heutink P, Pickering-Brown S, Morris HR, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ (2011) A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia. Neuron 72:257–268
Rollinson S, Rizzu P, Sikkink S, Baker M, Halliwell N, Snowden J, Traynor B, Ruano D, Cairns N, Rohrer JD, Mead S, Collinge J, Rossor M, Akay E, Guerreiro R, Rademakers R, Morrison KE, Pastor P, Alonso E, Martinez-Lage P, Graf-Radford N, Neary D, Heutink P, Mann DMA, Van Swieten J, Pickering-Brown S (2009) Ubiquitin associated protein 1 is a risk factor for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurobiol Ageing 30:656–665
Rutherford NJ, Zhang Y-J, Baker M, Gass JM, Finch NA, Xu Y-F, Stewart H, Kelley BJ, Kuntz K, Crook RJP, Sreedharan J, Vance C, Sorenson E, Lippa C, Bigio EH, Geschwind DH, Knopman DS, Mitsumoto H, Petersen RC, Cashman NR, Hutton M, Shaw CE, Boylan KB, Boeve B, Graff-Radford NR, Wxzolek ZK, Caselli RJ, Dickson DW, Mackenzie IR, Petrucelli L, Rademakers R (2011) Novel mutations in TARDBP (TDP-43) in patients with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS Genet 4:e1000193
Sasyama H, Shimamura M, Tokuda T, Azuma Y, Yoshida T, Mizuno T, Nakagawa M, Fujikake N, Nagai Y, Yamaguchi M (2012) Knockdown of the Drosophila fused in sarcoma (FUS) homologue causes deficient locomotive behavior and shortening of motoneuron terminal branches. PLoS ONE 7:e39483
Seelaar H, Klijnsma KY, de Koning I, van der Lugt A, Chiu WZ, Azmani A, Rozemuller AJM, Van Swieten JC (2010) Frequency of ubiquitin and FUS-positive, TDP-43-negative frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Neurol 257:747–753
Sennvik K, Boekhoorn K, Lasrado R, Terwel D, Verhaeghe S, Korr H, Schmitz C, Tomiyama T, Mori H, Krugers H, Joels M, Ramakers GJ, Lucassen PJ, Van Leuven F (2007) Tau-4R suppresses proliferation and promotes neuronal differentiation in the hippocampus of tau knockin/knockout mice. FASEB J 21:2149–2161
Shi J, Shaw CL, Richardson AMT, Bailey K, Tian J, Varma AR, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DMA (2005) Histopathological changes underlying frontotemporal lobar degeneration with clinicopathological correlation. Acta Neuropathol 110:501–512
Skibinski G, Parkinson NJ, Brown JM, Chakrabarti L, Lloyd SL, Hummerich H, Nielsen JE, Hodges JR, Spillantini MG, Thusgaard T, Brandner S, Brun A, Rossor MN, Gade A, Johannsen P, Sørensen SA, Gydesen S, Fisher EM, Collinge J (2005) Mutations in the endosomal ESCRTIII-complex subunit CHMP2B in frontotemporal dementia. Nat Genet 37:806–808
Snowden JS, Neary D, Mann DMA (2004) Autopsy proven frontotemporal dementia, due to microvacuolar-type histology, with onset at 21 years of age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1337–1339
Snowden JS, Hu Q, Rollinson S, Halliwell N, Robinson A, Davidson YS, Momeni P, Baborie A, Griffiths TD, Jaros E, Perry RH, Richardson A, Neary D, Pickering-Brown SM, Mann DMA (2011) The most common form of FTLD-FUS (aFTLD-U) is associated with a distinct clinical form of frontotemporal dementia, but not related to mutations in the FUS gene. Acta Neuropathol 122:99–110
Snowden JS, Snowden JS, Rollinson S, Thompson JC, Harris J, Stopford CL, Richardson A, Jones M, Gerhard A, Davidson Y, Robinson A, Gibbons L, Hu Q, Halliwell N, DuPlessis D, Neary D, Mann DMA, Pickering-Brown S (2011) Distinct clinical characteristics in patients with frontotemporal dementia and C9ORF72 mutations: a study of demographics, neurology, behaviour, cognition, and histopathology. Brain 135:693–708
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multisystem tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:7737–7741
Sreedharan J, Blair IP, Tripathi VB, Hu X, Vance C, Rogelj B, Ackerley S, Durnall JC, Williams KL, Buratti E, Baralle F, de Belleroche J, Mitchell JD, Leigh PN, Al-Chalabi A, Miller CC, Nicholson G, Shaw CE (2008) TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 319:1668–1672
Stallings NR, Puttaparthi K, Luther CM, Burns DK, Elliott JL (2010) Progressive motor weakness in transgenic mice expressing human TDP-43. Neurobiol Dis 40:404–414
Strong MJ, Grace GM, Freedman M, Lomen-Hoerth C, Woolley S, Goldstein LH, Murphy J, Shoesmith C, Rosenfeld J, Leigh PN, Bruijn L, Ince P, Figlewicz D (2009) Consensus criteria for the diagnosis of frontotemporal cognitive and behavioural syndromes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10:131–146
Tan AY, Manley JL (2009) The TET family of proteins: functions and roles in disease. J Mol Cell Biol 1:82–92
Tsai KJ, Yang CH, Fang YH, Cho KH, Chien WL, Wang WT, Wu TW, Lin CP, Fu WM, Shen CK (2010) Elevated expression of TDP-43 in the forebrain of mice is sufficient to cause neurological and pathological phenotypes mimicking FTLD-U. J Exp Med 207:1661–1673
Vaccaro A, Tauffenberger A, Aggad D, Rouleau G, Drapeau P, Parker JA (2012) Mutant TDP-43 and FUS cause age-dependent paralysis and neurodegeneration in C. elegans. PLoS One 7:e31321
Vance C, Rogelj B, Hortobágyi T, De Vos KJ, Nishimura AL, Sreedharan J, Hu X, Smith B, Ruddy D, Wright P, Ganesalingam J, Williams KL, Tripathi V, Al-Saraj S, Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN, Blair IP, Nicholson G, de Belleroche J, Gallo JM, Miller CC, Shaw CE (2009) Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 323:1208–1211
Wang JW, Brent JR, Tomilnson A, Shneider NA, McCabe BD (2011) The ALS-associated proteins FUS and TDP-43 function together to affect Drosophila locomotion and life span. J Clin Invest 121:4118–4126
Watts GD, Wymer J, Kovach MJ, Mehta SG, Mumm S, Darvish D, Pestronk A, Whyte MP, Kimonis VE (2004) Inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia is caused by mutant valosin-containing protein. Nat Genet 36:377–381
Wegorzewska I, Baloh RH (2011) TDP-43-based animal models of neurodegeneration: new insights into ALS pathology and pathophysiology. Neurodegener Dis 8:262–274
Wegorzewska I, Bell S, Cairns NJ, Miller TM, Baloh RH (2009) TDP-43 mutant transgenic mice develop features of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18809–18814
Wils H, Kleinberger G, Janssens J, Pereson S, Joris G, Cuijt I, Smits V, Groote CC, Van Broeckhoven C, Kumar-Singh S (2010) TDP-43 transgenic mice develop spastic paralysis and neuronal inclusions characteristic of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:3858–3863
Xu Y-F, Gendron TF, Zhang Y-J, Lin W-L, D’Alton S, Sheng H, Casey MC, Tong J, Knight J, Yu X, Rademakers R, Boylan K, Hutton M, McGowan E, Dickson DW, Lewis J, Petrucelli L (2010) Wild-type human TDP-43 expression causes TDP-43 phosphorylation, mitochondrial aggregation, motor deficits, and early mortality in transgenic mice. J Neurosci 30:10851–10859
Xu Z (2012) Does a loss of TDP-43 function cause neurodegeneration? Mol Neurodegener 7:27
Yang C, Tan W, Whittle C, Qiu L, Cao L, Akbarian S, Xu Z (2010) The C-terminal TDP-43 fragments have a high aggregation propensity and harm neurons by a dominant-negative mechanism. PLoS ONE 5:e15878
Zhou H, Huang C, Chen H, Wang D, Landel CP, Xia PY, Bowser R, Liu YJ, Xia XG (2010) Transgenic rat model of neurodegeneration caused by mutation in the TDP gene. PLoS Genet 6:e1000887
Zinszner H, Sok J, Immanuel D, Yin Y, Ron D (1997) TLS (FUS) binds RNA in vivo and engages in nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling. J Cell Sci 110:1741–1750
Acknowledgments
This work was presented at a Round Table Discussion Session at the 8th International Conference on Frontotemporal Dementias, held in Manchester, UK, 6–8 September 2012, and was supported by Springer. GH receives a NHMRC Senior Principal Research Fellowship 630434. EHB is supported by National Institute on Aging grant (P30 AG13854). NJC is supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (P50 AG05681 and P01 AG03991), the Hope Center for Neurological Disorders, and the Charles F. and Joanne Knight Alzheimer’s Disease Research Centre. MN is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (31003A-132864 and CRSII3-136222), the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (01GI1005B), and the Hans and Ilse Breuer Foundation. IRM is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Grants (179009 and 74580), and the Pacific Alzheimer’s Research Foundation Center Grant (C06-01). DMAM is supported by grants from the Wellcome Trust and Medical Research Council, and the Manchester Brain Bank receives funding from Alzheimers Research UK and Alzheimers Society through the Brains for Dementia Research Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halliday, G., Bigio, E.H., Cairns, N.J. et al. Mechanisms of disease in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: gain of function versus loss of function effects. Acta Neuropathol 124, 373–382 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1030-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1030-4