Abstract
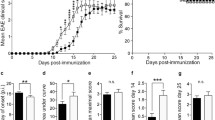
The role of B cells in autoimmune-mediated diseases of the peripheral nervous system was studied in experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN) in B cell deficient IgH0/0 C57BL/6J mice having been immunized with P0106–125 peptide. Compared to coisogenic IgH+/+ mice, onset of EAN was accelerated [100% disease incidence at day 9 post immunization (p.i.) vs. day 15 p.i.]. At day 9 p.i., numbers of P0106–125-specific interferon (IFN)-γ-producing CD4+ T cells were increased, while IL-10 mRNA and production were decreased in IgH0/0 mice. Beyond day 9 p.i., declining disease activity and a significant reduction of maximal disease activity were correlated with significantly reduced numbers of IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cells in IgH0/0 mice as compared with IgH+/+ mice. Correspondingly, neuropathology demonstrated only mild axonal damage, while demyelination and dying back axonopathy with spinal cord motor neuron apoptosis were absent. Thus, depending on the stage of EAN, B cells play a dual, i.e. suppressive and enhancing, role during induction and at height of EAN, respectively. The combined interaction of B cells as well as CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is required for the development of EAN.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboul-Enein F, Bauer J, Klein M, Schubart A, Flugel A, Ritter T, Kawakami N, Siedler F, Linington C, Wekerle H, Lassmann H, Bradl M (2004) Selective and antigen-dependent effects of myelin degeneration on central nervous system inflammation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:1284–1296
Archelos JJ, Roggenbuck K, Schneider-Schaulies J, Linington C, Toyka KV, Hartung HP (1993) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the extracellular domain of P0. J Neurosci Res 35:46–53
Archelos JJ, Roggenbuck K, Schneider-Schaulies J, Toyka KV, Hartung HP (1993) Detection and quantification of antibodies to the extracellular domain of P0 during experimental allergic neuritis. J Neurol Sci 117:197–205
Argall KG, Armati PJ, King NJ, Douglas MW (1991) The effects of West Nile virus on major histocompatibility complex class I and II molecule expression by Lewis rat Schwann cells in vitro. J Neuroimmunol 35:273–284
Bai XF, Zhu J, Zhang GX, Kaponides G, Hojeberg B, van der Meide PH, Link H (1997) IL-10 suppresses experimental autoimmune neuritis and down-regulates TH1-type immune responses. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 83:117–126
Benedetti L, Briani C, Grandis M, Vigo T, Gobbi M, Ghiglione E, Carpo M, Cocito D, Caporale CM, Sormani MP, Mancardi GL, Nobile-Orazio E, Schenone A (2007) Predictors of response to rituximab in patients with neuropathy and anti-myelin associated glycoprotein immunoglobulin M. J Peripher Nerv Syst 12:102–107
Bouaziz JD, Yanaba K, Tedder TF (2008) Regulatory B cells as inhibitors of immune responses and inflammation. Immunol Rev 224:201–214
Brunn A, Utermohlen O, Carstov M, Ruiz MS, Miletic H, Schluter D, Deckert M (2008) CD4 T cells mediate axonal damage and spinal cord motor neuron apoptosis in murine p0106–125-induced experimental autoimmune neuritis. Am J Pathol 173:93–105
Calida DM, Kremlev SG, Fujioka T, Hilliard B, Ventura E, Constantinescu CS, Lavi E, Rostami A (2000) Experimental allergic neuritis in the SJL/J mouse: induction of severe and reproducible disease with bovine peripheral nerve myelin and pertussis toxin with or without interleukin-12. J Neuroimmunol 107:1–7
Carmona A, Alonso JD, de las Heras M, Navarrete A (2006) Guillain-Barre syndrome in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and rituximab maintenance therapy. An association beyond anecdotal evidence? Clin Transl Oncol 8:764–766
Cross AH, Stark JL, Lauber J, Ramsbottom MJ, Lyons JA (2006) Rituximab reduces B cells and T cells in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 180:63–70
Dalakas MC, Rakocevic G, Salajegheh M, Dambrosia JM, Hahn AF, Raju R, McElroy B (2009) Placebo-controlled trial of rituximab in IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibody demyelinating neuropathy. Ann Neurol 65:286–293
Dass S, Vital EM, Emery P (2007) Development of psoriasis after B cell depletion with rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 56:2715–2718
Frericks M, Esser C (2008) A toolbox of novel murine house-keeping genes identified by meta-analysis of large scale gene expression profiles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779:830–837
Fujioka T, Purev E, Kremlev SG, Ventura ES, Rostami A (2000) Flow cytometric analysis of infiltrating cells in the peripheral nerves in experimental allergic neuritis. J Neuroimmunol 108:181–191
Goetz M, Atreya R, Ghalibafian M, Galle PR, Neurath MF (2007) Exacerbation of ulcerative colitis after rituximab salvage therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:1365–1368
Hafer-Macko CE, Sheikh KA, Li CY, Ho TW, Cornblath DR, McKhann GM, Asbury AK, Griffin JW (1996) Immune attack on the Schwann cell surface in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 39:625–635
Hill KE, Zollinger LV, Watt HE, Carlson NG, Rose JW (2004) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in chronic active multiple sclerosis plaques: distribution, cellular expression and association with myelin damage. J Neuroimmunol 151:171–179
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Matsushita T, Fujimoto M, Hasegawa M, Komura K, Takehara K, Tedder TF, Sato S (2006) Inhibitory role of CD19 in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating cytokine response. Am J Pathol 168:812–821
Matsushita T, Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF (2008) Regulatory B cells inhibit EAE initiation in mice while other B cells promote disease progression. J Clin Invest 118:3420–3430
Miyamoto K, Miyake S, Schachner M, Yamamura T (2003) Heterozygous null mutation of myelin P0 protein enhances susceptibility to autoimmune neuritis targeting P0 peptide. Eur J Immunol 33:656–665
Pels H, Schulz H, Schlegel U, Engert A (2003) Treatment of CNS lymphoma with the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab: experience with two cases and review of the literature. Onkologie 26:351–354
Pilartz M, Jess T, Indefrei D, Schroder JM (2002) Adoptive transfer-experimental allergic neuritis in newborn Lewis rats results in inflammatory infiltrates, mast cell activation, and increased Ia expression with only minor nerve fiber degeneration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 104:513–524
Renaud S, Fuhr P, Gregor M, Schweikert K, Lorenz D, Daniels C, Deuschl G, Gratwohl A, Steck AJ (2006) High-dose rituximab and anti-MAG-associated polyneuropathy. Neurology 66:742–744
Rostami A, Burns JB, Brown MJ, Rosen J, Zweiman B, Lisak RP, Pleasure DE (1985) Transfer of experimental allergic neuritis with P2-reactive T-cell lines. Cell Immunol 91:354–361
Rostami A, Gregorian SK, Brown MJ, Pleasure DE (1990) Induction of severe experimental autoimmune neuritis with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the 53–78 amino acid sequence of the myelin P2 protein. J Neuroimmunol 30:145–151
Smith ME, Sadler RH, Dyer C, Benjamins JA, Yu AC (1990) Phagocytosis of peripheral nerve myelin in vitro: effect of antibody. J Neurosci Res 27:298–306
Taylor JM, Pollard JD (2001) Dominance of autoreactive T cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity or antibody-mediated demyelination results in distinct forms of experimental autoimmune neuritis in the Lewis rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:637–646
Terenghi F, Ardolino G, Nobile-Orazio E (2007) Guillain-Barre syndrome after combined CHOP and rituximab therapy in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Peripher Nerv Syst 12:142–143
Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Haas KM, Poe JC, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF (2008) A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 28:639–650
Zhang Z, Zhang ZY, Fauser U, Schluesener HJ (2008) FTY720 ameliorates experimental autoimmune neuritis by inhibition of lymphocyte and monocyte infiltration into peripheral nerves. Exp Neurol 210:681–690
Zhu J, Link H, Weerth S, Linington C, Mix E, Qiao J (1994) The B cell repertoire in experimental allergic neuritis involves multiple myelin proteins and GM1. J Neurol Sci 125:132–137
Zhu J, Nennesmo I, Deng GM, Levi M, Wahren B, Diab A, Mix E, Zhou JN, Ljunggren HG (1999) Induction of experimental autoimmune neuritis in CD4–8-C57BL/6J mice. J Neuroimmunol 94:196–203
Zhu J, Pelidou SH, Deretzi G, Levi M, Mix E, van der Meide P, Winblad B, Zou LP (2001) P0 glycoprotein peptides 56–71 and 180–199 dose-dependently induce acute and chronic experimental autoimmune neuritis in Lewis rats associated with epitope spreading. J Neuroimmunol 114:99–106
Zhu W, Mix E, Jin T, Adem A, Zhu J (2007) B cells play a cooperative role via CD40L-CD40 interaction in T cell-mediated experimental autoimmune neuritis in Lewis rats. Neurobiol Dis 25:642–648
Zhu Y, Bao L, Zhu S, Chen Z, van der Meide P, Nennesmo I, Winblad B, Ljunggren HG, Zhu J (2002) CD4 and CD8 T cells, but not B cells, are critical to the control of murine experimental autoimmune neuritis. Exp Neurol 177:314–320
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mariana Carstov, Elena Fischer, and Anja Tümmermann for expert technical assistance and Hartmut Stützer MD, MSc, Institute of Medical Statistics, Informatics, and Epidemiology, University Hospital of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, for helpful advice with statistical analysis. This study was supported by Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (P86/08 // A59/08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure
Dot plots of IL-10-expressing CD4+ T cells and F4/80+ macrophages in PLN and spleen of a P0106-125-immunized IgH0/0 mouse having received rat IgG, an immunized IgH+/+ mouse having received rat IgG and a non-immunized IgH+/+ mouse at d 9 (a), 15 (b), and 22 p.i. (c) including FSC SSC cytograms showing gating strategies (PPT 1,901 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunn, A., Utermöhlen, O., Sánchez-Ruiz, M. et al. Dual role of B cells with accelerated onset but reduced disease activity in P0106–125-induced experimental autoimmune neuritis of IgH0/0 mice. Acta Neuropathol 120, 667–681 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0724-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0724-8