Abstract
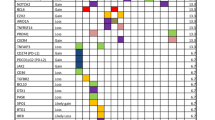
Primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL), the intracerebral subgroup of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), shows evidence for aberrant activation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway. In order to identify potential activators of the NF-κB complex, we analyzed the CARD11 and TNFAIP3 genes for the presence of somatic mutations and TNFAIP3 for aberrant promoter methylation in PCNSL. We also compared PCNSL to spinal DLBCL, because CARD11 and TNFAIP3 mutations have been described in systemic DLBCL. CARD11 mutations, located in the coiled-coil region, which may activate NF-κB, were detected in 16% (5/32) of PCNSL, while TNFAIP3 mutations were detected in 3% (1/32) of PCNSL. In PCNSL, all CARD11 mutations were heterozygous, in-frame, induced amino acid exchanges, and presumably led to activation of this oncogene. Spinal DLBCL harbored mutations of CARD11 and TNFAIP3 in 10% (1/10) and 20% (2/10) of cases, respectively. In both PCNSL and spinal DLBCL, mutations in CARD11 and TNFAIP3 were mutually exclusive. TNFAIP3 was unmethylated in all PCNSLs (30/30) and spinal DLBCLs (10/10). We conclude that mutations of the oncogene CARD11 may contribute to NF-κB activation and thereby play a role in the pathogenesis of PCNSL, while, in contrast to systemic DLBCL, inactivation of TNFAIP3 either by mutation or methylation seems to be of minor significance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG et al (2004) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 5:1052–1060
Chanudet E, Huang Y, Ichimura K et al (2010) A20 is targeted by promoter methylation, deletion and inactivating mutation in MALT lymphoma. Leukemia 24:483–487
Compagno M, Lim WK, Grunn A et al (2009) Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 459:717–721
Courts C, Montesinos-Rongen M, Martin-Subero JI et al (2007) Transcriptional profiling of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway identifies a subgroup of primary lymphoma of the central nervous system with low BCL10 expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:230–237
Davis RE, Brown KD, Siebenlist U, Staudt LM (2001) Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 194:1861–1874
De Valck D, Heyninck K, Van Criekinge W, Contreras R, Beyaert R, Fiers W (1996) A20, an inhibitor of cell death, self-associates by its zinc finger domain. FEBS Lett 384:61–64
Deckert M, Paulus W (2007) Malignant lymphomas. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) WHO classification of tumors pathology & genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IRAC, Lyon, pp 188–192
Egawa T, Albrecht B, Favier B et al (2003) Requirement for CARMA1 in antigen receptor-induced NF-kappa B activation and lymphocyte proliferation. Curr Biol 13:1252–1258
Hara H, Wada T, Bakal C et al (2003) The MAGUK family protein CARD11 is essential for lymphocyte activation. Immunity 18:763–775
Jun JE, Wilson LE, Vinuesa CG et al (2003) Identifying the MAGUK protein Carma-1 as a central regulator of humoral immune responses and atopy by genome-wide mouse mutagenesis. Immunity 18:751–762
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I et al (2009) Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature 459:712–716
Kluin P, Deckert M, Ferry JA (2008) Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the CNS. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon, pp 240–241
Lam KP, Kuhn R, Rajewsky K (1997) In vivo ablation of surface immunoglobulin on mature B cells by inducible gene targeting results in rapid cell death. Cell 90:1073–1083
Lenz G, Davis RE, Ngo VN et al (2008) Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science 319:1676–1679
Miranda RN, Glantz LK, Myint MA et al (1996) Stage IE non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma involving the dura: a clinicopathologic study of five cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 120:254–260
Montesinos-Rongen M, Brunn A, Bentink S et al (2008) Gene expression profiling suggests primary central nervous system lymphomas to be derived from a late germinal center B cell. Leukemia 22:400–405
Montesinos-Rongen M, Küppers R, Schlüter D et al (1999) Primary central nervous system lymphomas are derived from germinal-center B cells and show a preferential usage of the V4-34 gene segment. Am J Pathol 155:2077–2086
Montesinos-Rongen M, Siebert R, Deckert M (2009) Primary lymphoma of the central nervous system: just DLBCL or not? Blood 113:7–10
Montesinos-Rongen M, Van Roost D, Schaller C, Wiestler OD, Deckert M (2004) Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous system are targeted by aberrant somatic hypermutation. Blood 103:1869–1875
Montesinos-Rongen M, Zühlke-Jenisch R, Gesk S et al (2002) Interphase cytogenetic analysis of lymphoma-associated chromosomal breakpoints in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:926–933
Newton K, Dixit VM (2003) Mice lacking the CARD of CARMA1 exhibit defective B lymphocyte development and impaired proliferation of their B and T lymphocytes. Curr Biol 13:1247–1251
Novak U, Rinaldi A, Kwee I et al (2009) The NF-{kappa}B negative regulator TNFAIP3 (A20) is inactivated by somatic mutations and genomic deletions in marginal zone lymphomas. Blood 113:4918–4921
Richter J, Ammerpohl O, Martin-Subero JI et al (2009) Array-based DNA methylation profiling of primary lymphomas of the central nervous system. BMC Cancer 9:455
Rickert CH, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Simon R, Paulus W (1999) Chromosomal imbalances in primary lymphomas of the central nervous system. Am J Pathol 155:1445–1451
Schmitz R, Hansmann ML, Bohle V et al (2009) TNFAIP3 (A20) is a tumor suppressor gene in Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. J Exp Med 206:981–989
Schumacher MA, Schmitz R, Brune V et al (2010) Mutations in the genes coding for the NF-kappaB regulating factors IkappaBalpha and A20 are uncommon in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica 95:153–157
Srinivasan L, Sasaki Y, Calado DP et al (2009) PI3 kinase signals BCR-dependent mature B cell survival. Cell 139:573–586
Thompsett AR, Ellison DW, Stevenson FK, Zhu D (1999) V(H) gene sequences from primary central nervous system lymphomas indicate derivation from highly mutated germinal center B cells with ongoing mutational activity. Blood 94:1738–1746
Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H et al (2004) De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 430:694–699
Acknowledgments
The excellent technical assistance of Hatice Önder, Elena Fischer, and Reina Zühlke is very much appreciated. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Krebshilfe/Dr. Mildred Scheel-Stiftung für Krebsforschung (Grant no.: 107733), the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung (2005.168.2) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (De 485/9-1).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montesinos-Rongen, M., Schmitz, R., Brunn, A. et al. Mutations of CARD11 but not TNFAIP3 may activate the NF-κB pathway in primary CNS lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol 120, 529–535 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0709-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0709-7