Abstract
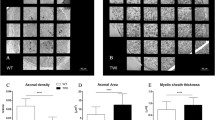
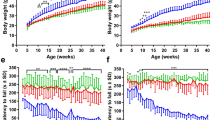
The aromatic γ-diketone 1,2-diacetylbenzene (1,2-DAB), the putative active metabolite of the organic solvent 1,2-diethylbenzene, forms blue-colored polymeric protein adducts and induces the formation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-like giant, intraspinal neurofilamentous axonal swellings in Sprague Dawley rats. The pathogenetic mechanism of this neuropathy has yet to be understood. We assessed whether these pathological changes are also seen in the C57BL/6 mouse, the animal of choice for toxicogenomic studies. Mice were treated intraperitoneally with 30, 35, 50, or 70 mg/kg 1,2-DAB or its inactive isomer 1,3-DAB per day (or on alternate days) for up to 43 days. Animals treated with 30 or 35 mg/kg per day 1,2-DAB, but not with 1,3-DAB, developed muscle spasms and progressive weakness, most prominently in hind limbs. Light microscopy revealed swollen axons in spinal anterior horns and proximal ventral roots, and to a lesser extent in dorsal root ganglia of 1,2-DAB-treated animals. Ultrastructural examination of swollen axons revealed clumps of maloriented 10-nm neurofilaments. Sciatic nerves showed clustering of axonal microtubules and other organelles. These findings are qualitatively comparable to those reported in rats treated with 1,2-DAB and represent a suitable phenotype with which to explore molecular mechanisms of proximal, giant neurofilamentous axonopathy using proteomic and genomic technologies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Chalabi A, Miller CC (2003) Neurofilaments and neurological disease. Bioessays 25:346–355
Anthony DC, Boekelheide K, Anderson CW, Graham DG (1983) The effect of 3,4-dimethyl substitution on the neurotoxicity of 2,5-hexanedione. II. Dimethyl substitution accelerates pyrrole formation and protein crosslinking. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 71:372–382
Anthony DC, Boekelheide K, Graham DG (1983) The effect of 3,4-dimethyl substitution on the neurotoxicity of 2,5-hexanedione. I. Accelerated clinical neuropathy is accompanied by more proximal axonal swellings. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 71:362–371
Anthony DC, Giangaspero F, Graham DG (1983) The spatio-temporal pattern of the axonopathy associated with the neurotoxicity of 3,4-dimethyl-2,5-hexanedione in the rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:548–560
Boekelheide K, Fleming SL, Allio T, Embree-Ku ME, Hall SJ, Johnson KJ, Kwon EJ, Patel SR, Rasoulpour RJ, Schoenfeld HA, Thompson S (2003) 2,5-Hexanedione-induced testicular injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:125–147
Delisle MB, Carpenter S (1984) Neurofibrillary axonal swellings and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 63:241–250
Gold BG (2000) β,β’-Iminodipropionitrile. In: Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (eds) Experimental and Clinical Neurotoxicology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 678–680
Griffin JW, Parhad I, Gold B, Price DL, Hoffman PN, Fahnestock K (1985) Axonal transport of neurofilament proteins in IDPN neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 6:43–53
Hirano A, Donnenfeld H, Sasaki S, Nakano I (1984) Fine structural observations of neurofilamentous changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:461–470
Kim MS, Sabri MI, Miller VH, Kayton RJ, Dixon DA, Spencer PS (2001) 1,2-Diacetylbenzene, the neurotoxic metabolite of a chromogenic aromatic solvent, induces proximal axonopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177:121–131
Kim MS, Hashemi SB, Spencer PS, Sabri MI (2002) Amino acid and protein targets of 1,2-diacetylbenzene, a potent aromatic gamma-diketone that induces proximal neurofilamentous axonopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 183:55–65
Lehning EJ, Jortner BS, Fox JH, Arezzo JC, Kitano T, LoPachin RM (2000) γ-Diketone peripheral neuropathy. I. Quantitative morphometric analyses of axonal atrophy and swelling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 165:127–140
LoPachin RM, Jortner BS, Reid ML, Das S (2003) γ-Diketone central neuropathy: quantitative morphometric analysis of axons in rat spinal cord white matter regions and nerve roots. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 193:29–46
Monaco S, Wongmongkolrit T, Shearson CM, Patton A, Schaetzle B, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P, Sayre LM (1990) Giant axonopathy characterized by intermediate location of axonal enlargements and acceleration of neurofilament transport. Brain Res 519:73–81
Okamoto K, Hirai S, Shoji M, Senoh Y, Yamazaki T (1990) Axonal swellings in the corticospinal tracts in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 80:222–226
Politis MJ, Pellegrino RG, Spencer PS (1980) Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. V. Axonal neurofilaments accumulate at sites of 2,5-hexanedione application: evidence for nerve fibre dysfunction in experimental hexacarbon neuropathy. J Neurocytol 9:505–516
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (1977) Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. III. The evolution of experimental peripheral giant axonal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 36:276–299
Spencer PS, Kim MS, Sabri MI (2002) Aromatic as well as aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent axonopathy. Int J Hyg Environ Health 205:131–136
Zagoren JC, Politis MJ, Spencer PS (1983) Rapid reorganization of the axonal cytoskeleton induced by a gamma diketone. Brain Res 270:162–164
Zhan CG, Dixon DA, Sabri MI, Kim MS, Spencer PS (2002) Theoretical determination of chromophores in the chromogenic effects of aromatic neurotoxicants. J Am Chem Soc 124:2744–2752
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by PHS grants P42ES10338, U19ES11384, the Oregon Worker Benefit Fund, and a grant from the International Brain Research Organization to D.D. Tshala-Katumbay. The technical expertise of Dan Austin is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tshala-Katumbay, D.D., Palmer, V.S., Kayton, R.J. et al. A new murine model of giant proximal axonopathy. Acta Neuropathol 109, 405–410 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0982-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0982-z