Abstract
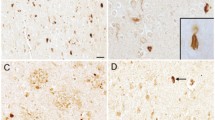
Emerging evidence has demonstrated the neuroprotection of estrogen in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The hippocampus, an important target of estrogen action, is severely affected in the Alzheimer process. The aim of present study was to detect the distribution of estrogen receptor-α (ER-α) and the relationship between ER-α-containing neurons and the pretangles stained by Alz-50 in the hippocampus of AD patients. The results showed that more than half of hippocampal neurons expressed ER-α. The number of cytoplasmic ER-α-positive neurons was significantly decreased in the CA1 and CA2 subfields of AD hippocampus, but the ratio of these ER-α-expressing neurons to the nucleolated neuronal profiles stained by thionin was not different between the two groups. Interestingly, the number of nuclear ER-α-staining neurons was also markedly decreased in the CA1 and CA2 subfields of AD hippocampus, and the percentage of these nuclear staining neurons was also significantly decreased in the same subfields. Furthermore, some double-labeled neurons containing ER-α and Alz-50 were found in AD patients. However, in these double-labeled neurons, ER-α was only located in the cytoplasm. Thus, we hypothesize that the nuclear ER-α may play more important roles of neuroprotection during the process of AD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthana S, Craft S, Baker LD, Raskind MA, Birnbaum RS, Lofgreen CP, Veith RC, Plymate SR (1999) Cognitive and neuroendocrine response to transdermal estrogen in postmenopausal women with Alzheimer's disease: results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind, pilot study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 24:657–677
Bachman DL, Wolf PA, Linn R, Knoefel JE, Cobb J, Belanger A, D'Agostino RB, White LR (1992) Prevalence of dementia and probable senile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Framingham study. Neurology 42:115–119
Birge SJ (1997) The role of estrogen in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 48:S36–S41
Blaustein JD (1992) Cytoplasmic estrogen receptors in rat brain: immunocytochemical evidence using three antibodies with distinct epitopes. Endocrinology 131:1336–1342
Blurton-Jones MM, Roberts JA, Tuszynski MH (1999) Estrogen receptor immunoreactivity in the adult primate brain: neuronal distribution and association with p75, trk, and choline acetyltransferase. J Comp Neurol 405:529–542
Clarke CH, Norfleet AM, Clarke MSF, Watson CS, Cunningham KA, Thomas ML (2000) Perimembrane localization of the estrogen receptor α protein in the neuronal processes of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroendocrinology 71:34–42
Donahue JE, Stopa EG, Chorsky RL, King JC, Schipper HM, Tobet SA, Blaustein JD, Reichlin S (2000) Cells containing immunoreactive estrogen receptor-α in the human basal forebrain. Brain Res 856:142–151
Doraiswamy PM, Bieber F, Kaiser L, Krishnan KR, Reuning SJ, Gulanski B (1997) The Alzheimer's disease assessment scale: patterns and predictors of baseline cognitive performance in multicenter Alzheimer's disease trials. Neurology 48:1511–1517
Fitzpatrick SL, Funkhouser JM, Sindoni DM, Stevis PS, Deecher DC, Bapat AR, Merchentaler I, Trail DE (1999) Expression of estrogen receptor-β protein in rodent ovary. Endocrinology 140:2581–2591
Gould E, Woolley CS, Frankfurt M, McEwen BS (1990) Gonadal steroids regulate dendritic spine density in hippocampal pyramidal cells in adulthood. J Neurosci 10:1286–1291
Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert J-M, Argos P, Chambon P (1986) Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to verb-A. Nature 320:134–139
Gronemeyer H (1991) Transcription activation by estrogen and progesterone receptors. Annu Rev Gene 25:89–123
Henderson VW (1997) The epidemiology of estrogen replacement therapy and Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 48:S27–S35
Henderson VW, Paganini-Hill A, Miller BL, Elble RJ, Reyes PF, Shoupe D, McCleary CA, Klein RA, Hake AM, Farlow MR (2000) Estrogen for Alzheimer's disease in women: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 54:295–301
Hu XY, Zhang HY, Qin S, Xu H, Swaab DF, Zhou JN (2002) Increased p75NTR expression in hippocampal neurons containing hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer patients. Exp Neurol 178:104–111
Ishunina TA, Swaab DF (2001) Increased expression of estrogen receptor α, and β in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:417–426
Ishunina TA, Kruijver FPM, Balesar R, Swaab DF (2000) Differential expression of estrogen receptor α, and β immunoreactivity in the human supraoptic nucleus in relation to sex and ageing. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3283–3291
Khatchaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Kruijver FPM, Balesar R, Espila AM, Unmehopa UA, Swaab DF (2002) Estrogen receptor-α distribution in the human hypothalamus in relation to sex and endocrine status. J Comp Neurol 454:115–139
Kumar V, Chambon P (1988) The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell 55:145–156
Liu RY, Zhou JN, Hoogendijk WJG, Heerikhuize JV, Kamphorst W, Unmehopa UA, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (2000) Decreased vasopressin gene expression in the biological clock of Alzheimer disease patients with and without depression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:314–322
Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R (1996) ERβ: identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett 392:49–53
Österlund MK, Gustafsson JA, Keller E, Hurd YL (2000) Estrogen receptor β (ERβ) messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression within the human forebrain: distinct distribution pattern to ERα mRNA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3840–3846
Österlund MK, Keller E, Hurd YL (2000) The human forebrain has discrete estrogen receptor α messenger RNA expression: high levels in the amygdaloid complex. Neuroscience 95:333–342
Paganini-Hill A, Henderson VW (1996) Estrogen replacement therapy and risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Intern Med 156:2213–2217
Pike CJ (1999) Estrogen modulates neuronal Bcl-xL expression and β-amyloid-induced apoptosis: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 72:1552–1563
Register TC, Shively CA, Lewis CE (1998) Expression of estrogen receptor α and β transcripts in female monkey hippocampus and hypothalamus. Brain Res 788:320–322
Rosene DL, Van Hoesen GW (1987) The hippocampal formation of the primate brain: a review of some comparative aspects of cytoarchitecture and connections. In: Jones EG, Peters A (eds) Cerebral cortex. Plenum Press, New York, pp 345–456
Saji S, Jensen EV, Nilsson S, Rylander T, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2000) Estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the rodent mammary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:337–342
Salehi A, Van de Nes JAP, Hofman MA, Gonatas NK, Swaab DF (1995) Early cytoskeletal changes as shown by Alz-50 are not accompanied by decreased neuronal activity. Brain Res 678:29–39
Savaskan E, Olivieri G, Meie F, Ravid R, Müller-Spahn F (2001) Hippocampal estrogen β-receptor immunoreactivity is increased in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 908:113–119
Seshadri S, Zornberg GL, Derby LE, Myers MW, Jick H, Drachman DA (2001) Postmenopausal estrogen replacement therapy and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 58:435–440
Shughrue PJ, Lane MV, Merchenthaler I (1997) Comparative distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha and –beta mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 388:507–525
Singer CA, Figueroa-Masot XA, Batchelor RH, Dorsa DM (1999) The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates estrogen neuroprotection after glutamate toxicity in primary cortical neurons. J Neurosci 19:2455–2463
Solum DT, Handa RJ (2001) Localization of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in pyramidal neurons of the developing rat hippocampus. Dev Brain Res 128:165–175
Stone DJ, Rozovsky I, Morgan TE, Anderson CP, Finch CE (1998) Increased synaptic sprouting in response to estrogen via an apolipoprotein E-dependent mechanism: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 18:3180–3185
Su JD, Qiu J, Zhong YP, Chen YZ (2001) Expression of estrogen receptors-alpha and –beta immunoreactivity in the cultured neonatal suprachiasmatic nucleus: with special attention to GABAergic neurons. Neuroreport 12:1955–1959
Swaab DF, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Kremer HPH, Ravid R, Van de Nes JA (1992) Tau and ubiquitin in the human hypothalamus in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 590:239–249
Tang MX, Jacobs D, Stern Y, Marder K, Schofield P, Gurland B, Andrews H, Mayeux R (1996) Effect of oestrogen during menopause on risk and age at onset of Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 348:429–432
Taylor AH, Al-Azzawi F (2000) Immunolocalisation of oestrogen receptor beta in human tissues. J Mol Endocrinol 24:145–155
Tranque PA, Suarez I, Olmas G, Fernandez B, Garcia-Segura LM (1987) Estradiol-induced redistribution of glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Brain Res 406:348–351
Van de Nes JA, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Swaab DF (1998) Comparison of beta-protein/A4 deposits and Alz-50-stained cytoskeletal changes in the hypothalamus and adjoining areas of Alzheimer's disease patients: amorphic plaques and cytoskeletal changes occur independently. Acta Neuropathol 96:129–138
Wang PN, Liao SQ, Liu RS, Liu CY, Chao HT, Lu SR, Yu HY, Wang SJ, Liu HC (2000) Effects of estrogen on cognition, mood, and cerebral blood flow in AD, a controlled study. Neurology 54:2061–2066
Wolozin BL, Pruchnicki A, Dickson DW, Davies P (1986) A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science 232:648–650
Woolley CS, McEwen BS (1992) Estradiol mediates fluctuation in hippocampal synapse density during the estrous cycle in the adult rat. J Neurosci 12:2549–2554
Working Group (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer's Disease. Neurobiol Aging 18 (Suppl 4):S1–S2
Xu H, Gouras GK, Greenfield JP, Vincent B, Naslund J, Mazzarelli L, Fried G, Jovanovic JN, Seeger M, Relkin NR, Liao F, Checler F, Buxbaum JD, Chait BT, Thinakaran G, Sisodia SS, Wang R, Greengard P, Gandy S (1998) Estrogen reduces neuronal generation of Alzheimer β-amyloid peptide. Nat Med 4:447–451
Zandi PP, Carlson MC, Plassman BL, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Mayer LS, Steffens DC, Breitner JC (2002) Hormone replacement therapy and incidence of Alzheimer disease in older women: the Cache County Study. JAMA 288:2123–2129
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Netherlands Brain Bank for the brain material, and to Ms. Hong-Yue Ju and Huai-Yu Zhang for experimental help. This project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30070826), the National Key Project for Basic Science of China (G1999054007), the KNAW 02CDP014, the Innovation Project of Science Academy of China (KSCX2-SW-217), and the International Cooperation Project of China (2001CB711101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, XY., Qin, S., Lu, YP. et al. Decreased estrogen receptor-α expression in hippocampal neurons in relation to hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer patients. Acta Neuropathol 106, 213–220 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0720-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0720-3