Abstract
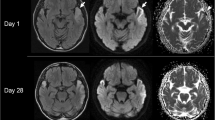
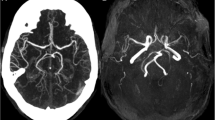
We describe the clinical and neuropathological findings of three unrelated autopsy cases of MELAS harboring the A3243G transition in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Using immunohistochemical techniques, we studied the expression of several subunits of the respiratory chain in various brain regions from the same cases. In all three cases there was a reduced immunocytochemical staining for mtDNA-encoded subunits of the respiratory chain, confirming the presence of a defective mitochondrial protein synthesis in this disease. Mitochondrial abnormalities were mostly confined to multiple areas of different size and shape, in agreement with the focal character of the brain pathology in MELAS, and were most prominent in the cerebral cortex, providing a morphological contribution to the explanation of the cognitive regression of the patients. Immunoreactivity for mtDNA-encoded subunits was reduced in the walls of many pial and intracerebral arterioles of different brain regions but there was no clear correlation between territories of affected vessels and distribution of the histological and immunohistochemical lesions. Cerebral focal lesions in MELAS might have a metabolic nature and several pathogenetic mechanisms might be involved in the genesis of stroke-like episodes when there is a local increased ATP demand.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amagasaki K, Shimizu T, Suzuki Y, Kakizawa T (2001) Focal hyperperfusion in a patient with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. J Neurosurg 94:133–136
Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, Bruijn MHL de, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreirer PH, Smith AJH, Staden R, Young IG (1981) Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290:457–465
Bedetti CD (1985) Immucytochemical demonstration of cytochrome c oxidase with an immunoperoxidase method. J Histochem Cytochem 33:446–452
Börner GV, Zeviani M, Tiranti V, Carrara F, Hoffmann S, Gerbitz KD, Lochmüller H, Pongratz D, Klopstock T, Melberg A, Holme E, Pääbo S (2000) Decreased aminoacylation of mutant tRNAs in MELAS but not MERRF patients. Hum Mol Genet 9:467–475
Brierley JB, Graham DI (1984) Hypoxia and vascular disorders of the central nervous system. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Arnold, London, pp 125–207
Chomyn A, Enriquez JA, Micol V, Fernandez-Silva P, Attardi G (2000) The mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episode syndrome-associated human mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) mutation causes aminoacylation deficiency and concomitant reduced association of mRNA with ribosomes. J Biol Chem 275:19198–19209
Ciafaloni E, Ricci E, Servidei S, Shanske S, Silvestri G, Manfredi G, Schon EA, DiMauro S (1991) Widespread tissue distribution of tRNALeu(UUR) mutation in the mitochondrial DNA of a patient with MELAS syndrome. Neurology 41:1663-1665
Ciafaloni E, Ricci E, Shanske S, Moraes CT, Silvestri G, Hirano M, Simonetti S, Angelici C, Donati MA, Garcia C, Martinuzzi A, Mosewich R, Servidei S, Zammarchi E, Bonilla E, De Vivo DC, Rowland LP, Schon EA, DiMauro S (1992) MELAS: clinical features, biochemistry, and molecular genetics. Ann Neurol 31:391–398
Dunbar DR, Moonie PA, Jacobs HT, Holt LJ (1995) Different cellular background confer a marked advantage to either mutant or wild-type mitochondrial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 992:6562–6566
Flierl A, Reichmann H, Seibel P (1997) Pathophysiology of the MELAS 3243 transition mutation. J Biol Chem 272:27189–27196
Gerbitz K-D, Van den Ouweland JMW, Maassen JA, Jaksch M (1995) Mitochondrial diabetes mellitus: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1271:253–260
Gonzalez-Halphen D, Lindorfer MA, Capaldi RA (1988) Subunit arrangement in beef heart complex III. Biochemistry 27:7021–7031
Goto Y-I, Nonaka I, Horai S (1990) A mutation in the tRNALeu(UUR) gene associated with the MELAS subgroup of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Nature 348:651–653
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Gropen TI, Prohovnik I, Tatemichi TK, Hirano M (1994) Cerebral hyperremia in MELAS. Stroke 25:1873–1876
Hao H, Morrison LE, Moraes CT (1999) Suppression of a mitochondrial tRNA gene mutation phenotype associated with changes in the nuclear background. Hum Mol Genet 8:1117–1124
Hasegawa H, Matsuoka T, Goto Y, Nonaka I (1991) Strongly succinate dehydrogenase-reactive blood vessels in muscle from patients with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Ann Neurol 29:601–605
Hirano M, Ricci E, Koenigsberger MR, Defendini R, Pavlakis SG, De Vivo DC, DiMauro S, Rowland LP (1992) MELAS: an original case and clinical criteria for diagnosis. Neuromuscul Disord 2:125–135
Isobs K, Ito S, Hosaka H, Iwamura Y, Kondo H, Kagawa Y, Hayashi J-I (1998) Nuclear recessive mutations of factors involved in mitochondrial translation are responsible for age-related respiration deficiency of human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 20:4601–4606
James AM, Sheard PW, Wei Y-H, Murphy MP (1999) Decreased ATP synthesis is phenotypically expressed during increased energy demand in fibroblasts containing mitochondrial tRNA mutations. Implications for neurodegenerative and mitochondrial DNA diseases. Eur J Biochem 259:462–469
Jenuth JP, Peterson AC, Shoubridge EA (1997) Tissue-specific selection for different mtDNA genotypes in heteropasmic mice. Nat Genet 16:93–96
King MP, Koga Y, Davidson M, Schon EA (1992) Defects in mitochondrial protein synthesis and respiratory chain activity segregate with the tRNALeu(UUR) mutation associated with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Mol Cell Biol 12:480–490
Kobayashi Y, Momoi MY, Tominaga K, Momoi T, Nihei K, Yanagisawa M, Kagawa Y, Ohta S (1990) A point mutation in the mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) gene in MELAS (mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173:816–822
Kristián T, Siesjö BK (1998) Calcium in ischemic cell death. Stroke 29:705–718
Lefai E, Vincent A, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Tanguy A, Alziari S (1997) Quantitative decrease of human cytochrome c oxidase during development: evidence for a post-transcriptional regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1318:191–201
Lombes A, Mendell JR, Nakase H, Barohn RJ, Bonilla E, Zeviani M, Yates AJ, Omerza J, Gales TL, Nakahara K, Rizzuto R, Engel KW, DiMauro S (1989) Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fibers with cytochrome oxidase deficiency: neuropathology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics. Ann Neurol 26:20–33
Macmillan C, Lach B, Shoubridge EA (1993) Variable distribution of mutant mitochondrial DNAs (tRNALeu[3243]) in tissues of symptomatic relatives with MELAS: the role of mitotic segregation. Neurology 43:1586–1590
Mariottini P, Chomyn A, Attardi G, Trovato D, Strong DD, Doolittle RF (1983) Antibodies against synthetic peptides reveal that unidentified reading frame A6L, overlapping the ATPase 6 gene, is expressed in human mitochondria. Cell 32:1269–1277
Martinuzzi A, Bartolomei L, Carrozzo R, Mostacciuolo M, Carbonin C, Toso V, Ciafaloni E, Shanske S, DiMauro S, Angelici C (1992) Correlation between clinical and molecular features in two MELAS families. J Neurol Sci 113:222–229
Matthews PM, Taivassalo T (1997) Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy to diagnosis and monitoring of mitochondrial disease. Ital J Neurol Sci 18:341–351
Matthews PM, Andermann F, Silver K, Karpati G, Arnold DL (1993) Proton MR spectroscopic characterization of differences in regional brain metabolic abnormalities in mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Neurology 43:2484–2490
Mirabella M, Di Giovanni S, Silvestri G, Tonali P, Servidei S (2000) Apoptosis in mitochondrial encephalomyopathies with mitochondrial DNA mutations: a potential pathogenetic mechanism. Brain 123:93–104
Miyamoto A, Oki J, Takahashi S, Itoh J, Kusunoki Y, Cho K (1997) Serial imaging in MELAS. Neuroradiology 39:427–430
Molnár MJ, Valikovics A, Molnár S, Trón L, Diószeghy P, Mechler F, Gulyás B (2000) Cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in mitochondrial disorders. Neurology 55:544–548
Moraes CT, Schon EA, DiMauro S (1991) Mitochondrial diseases: toward a rational classification. In: Appel SH (eds) Current neurology, vol 11. Mosby-Year Book, St Louis, pp 83–120
Moraes CT, Ricci E, Bonilla E, DiMauro S, Schon EA (1992) The mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) mutation in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes (MELAS): genetic, biochemical, and morphological correlations in skeletal muscle. Am J Hum Genet 50:934–949
Moraes CT, Ciacci F, Silvestri G, Shanske S, Sciacco M, Hirano M, Schon EA, Bonilla E, DiMauro S (1993) Atypical presentations associated with the MELAS mutation at position 3243 of human mitochondrial DNA. Neuromuscul Disord 1:43–50
Morita K, Ono S, Fukunaga M, Yasuda T, Higashi Y, Terao A, Morita R (1989) Increased accumulation of N-isopropyl-p-(123I)-iodoamphetamine in two cases with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with lactic acidosis and strokelike episodes (MELAS). Neuroradiology 31:358–361
Ohama E, Ohara S, Ikuta F, Tanaka K, Nishizawa M, Miyatake T (1987) Mitochondrial angiopathy in cerebral blood vessels of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:226–233
Ozawa M, Nonaka I, Goto Y (1998) Single muscle fiber analysis in patients with 3243 mutation in mitochondrial DNA: comparison with the phenotype and the proportion of mutant genome. J Neurol Sci 159:170–175
Pavlakis SG, Phillips PC, DiMauro S, De Vivo DC, Rowland LP (1984) Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol 16:481–488
Pavlakis SG, Kingsley PB, Kaplan GP, Stacpoole PW, O'Shea M, Lustbader D (1998) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy use in monitoring MELAS treatment. Arch Neurol 55:849–852
Peng NJ, Liu RS, Li JY, Tsay DG, Kong KW, Kwok CG, Strauss HW (2000) Increased crebral blood flow in MELAS shown by Tc-99m HMPAO brain SPECT. Neuroradiology 42:26–29
Rothman SM (2000) Mutations of the mitochondrial genome: clinical overview and possible pathophysiology of cell damage. Biochem Soc Symp 66:111–122
Sakuta R, Nonaka I (1989) Vascular involvement in mitochondrial myopathy. Ann Neurol 25:594–601
Silvestri G, Bertini E, Servidei S, Rana M, Zachara E, Ricci E, Tonali P (1997) Maternally inherited cardiomyopathy: a new phenotype associated with the A to G at nt 3243 of mitochondrial DNA (MELAS mutation). Muscle Nerve 20:221–225
Silvestri G, Rana M, Odoardi F, Modoni A, Paris E, Papacci M, Tonali P, Servidei S (2000) Single-fiber PCR in MELAS3243 patients: correlations between intratissue distribution and phenotypic expression of the mtDNAA3243G genotype. Am J Med Genet 94:201–206
Sparaco M, Bonilla E, DiMauro S, Powers JM (1993) Neuropathology of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies due to mitochondrial DNA defects. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:1–10
Sparaco M, Schon EA, DiMauro S, Bonilla E (1995) Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers (MERRF): an immunohistochemical study of the brain. Brain Pathol 5:125–133
Tokunaga M, Mita S, Sakuta R, Nonaka I, Araki S (1993) Increased mitochondrial DNA in blood vessels and ragged-red fibers in mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS). Ann Neurol 33:275–280
Tokunaga M, Mita S, Murakami T, Kumamoto T, Uchino M, Nonaka I Ando M (1994) Single muscle fiber analysis of mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS). Ann Neurol 35:413–419
Tritschler HJ, Bonilla E, Lombes A, Andreatta F, Servirei S, Schneyder B, Miranda AF, Schon EA, Kadenbach B, DiMauro S (1991) Differential diagnosis of fatal and benign cytochrome c oxidase-deficient myopathies of infancy: an immunohistochemical approach. Neurology 41:300–305
Wallace DC (2001) Mitochondrial defects in neurodegenerative diseases. MRDD Res Rev 7:158–166
Watahiki Y, Tomiyama M, Nagata K, Shishido F, Kobayashi Y, Komatsu K, Goto A, Takada G (1988) Positron emission tomographic study in patients with MELAS. No To Hattatsu 20:404–411
Wong A, Cortopassi G (1997) mtDNA mutations confer cellular sensitivity to oxidant stress that is partially rescued by calcium depletion and cyclosporin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 239:139–145
Zhang J, Yoneda M, Naruse K, Borgeld H-JW, Gong J-S, Obata S, Tanaka M, Yagi K (1998) Peroxide production and apoptosis in cultured cells carrying mtDNA mutation causing encephalomyopathy. Biochem Mol Biol Int 46:71–79
Zhou L, Chomyn A, Attardi G, Miller CA (1997) Myoclonus epilepsy and ragged-red fibers (MEERF) syndrome: selective vulnerability of CNS neurons does not correlate with the level of mitochondrial tRNALys mutation in individual neuronal isolates. J Neurosci 17:7746–7753
Zupanc ML, Moraes CT, Shanske S, Langman CB, Ciafaloni E, DiMauro S (1991) Deletion of mitochondrial DNA in patients with combined features of Kearns-Sayre and MELAS syndromes. Ann Neurol 29:680–683
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant M.U.R.S.T. 60% to N.R., A.F. 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sparaco, M., Simonati, A., Cavallaro, T. et al. MELAS: clinical phenotype and morphological brain abnormalities. Acta Neuropathol 106, 202–212 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0716-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0716-z