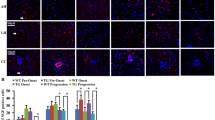
Abstract
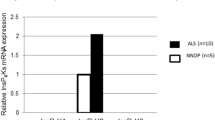
To clarify the trophic mechanism of residual anterior horn cells affected by sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (SALS) and familial ALS (FALS) with superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) mutations, we investigated the immunohistochemical expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a novel neurotrophic factor, and its receptor, c-Met. In normal subjects, immunoreactivity to both anti-HGF and anti-c-Met antibodies was observed in almost all anterior horn cells, whereas no significant immunoreactivity was observed in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Histologically, the number of spinal anterior horn cells in ALS patients decreased along with disease progression. Immunohistochemically, the number of neurons negative for HGF and c-Met increased with ALS disease progression. However, throughout the course of the disease, certain residual anterior horn cells co-expressed both HGF and c-Met with the same, or even stronger intensity in comparison with those of normal subjects, irrespective of the reduction in the number of immunopositive cells. Western blot analysis revealed that c-Met was induced in the spinal cord of a patient with SALS after a clinical course of 2.5 years, whereas the level decreased in a SALS patient after a clinical course of 11 years 5 months. These results suggest that the autocrine and/or paracrine trophic support of the HGF-c-Met system contributes to the attenuation of the degeneration of residual anterior horn cells in ALS, while disruption of the neuronal HGF-c-Met system at an advanced disease stage accelerates cellular degeneration and/or the process of cell death. In SOD1-mutated FALS patients, Lewy body-like hyaline inclusions (LBHIs) in some residual anterior horn cells exhibited co-aggregation of both HGF and c-Met, although the cytoplasmic staining intensity for HGF and c-Met in the LBHI-bearing neurons was either weak or negative. Such sequestration of HGF and c-Met in LBHIs may suggest partial disruption of the HGF-c-Met system, thereby contributing to the acceleration of neuronal degeneration in FALS patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendotti C, Tortarolo M, Suchak SK, Calvaresi N, Carvelli L, Bastone A, Rizzi M, Rattray M, Mennini T (2001) Transgenic SOD1 G93A mice develop reduced GLT-1 in spinal cord without alterations in cerebrospinal fluid glutamate levels. J Neurochem 79:737–746
Bruijn LI, Becher MW, Lee MK, Anderson KL, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Sisodia SS, Rothstein JD, Borchelt DR, Price DL, Cleveland DW (1997) ALS-linked SOD1 mutant G85R mediates damage to astrocytes and promotes rapidly progressive disease with SOD1-containing inclusions. Neuron 18:327–338
Charcot JM, Joffroy A (1869) Deux cas d'atrophie musculaire progressive avec lésions de la substance grise et des faisceaux antéro-latéraux de la moelle épinière. Arch Physiol (Paris) 2:744–760
Dawson VL, Brahmbhatt HP, Mong JA, Dawson TM (1994) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase causes delayed neurotoxicity in primary mixed neuronal-glial cortical cultures. Neuropharmacology 33:1425–1430
Desagher S, Glowinski J, Premont J (1996) Astrocytes protect neurons from hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J Neurosci 16:2553–2562
Ebens A, Brose K, Leonardo ED, Hanson MG Jr, Bladt F, Birchmeier C, Barres BA, Tessier-Lavigne M (1996) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is an axonal chemoattractant and a neurotrophic factor for spinal motor neurons. Neuron 17:1157–1172
Funakoshi H, Nakamura T (2001) Identification of HGF-like protein as a novel neurotrophic factor for avian dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:606–612
Funakoshi H, Nakamura T (2003) Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF): from diagnosis to clinical applications. Clin Chim Acta 327:1–23
Giordano S, Di Renzo MF, Narsimhan RP, Cooper CS, Rosa C, Comoglio PM (1989) Biosynthesis of the protein encoded by the c-met proto-oncogene. Oncogene 4:1383–1388
Hamanoue M, Takemoto N, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Nakajima K, Kohsaka S (1996) Neurotrophic effect of hepatocyte growth factor on central nervous system neurons in vitro. J Neurosci Res 43:554–564
Hirano A (1996) Neuropathology of ALS: an overview. Neurology 47:S63–S66
Honda S, Kagoshima M, Wanaka A, Tohyama M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (1995) Localization and functional coupling of HGF and c-Met/HGF receptor in rat brain: implication as neurotrophic factor. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 32:197–210
Howland DS, Liu J, She Y, Goad B, Maragakis NJ, Kim B, Erickson J, Kulik J, DeVito L, Psaltis G, DeGennaro LJ, Cleveland DW, Rothstein JD (2002) Focal loss of the glutamate transporter EAAT2 in a transgenic rat model of SOD1 mutant-mediated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1604–1609
Kato S, Shimoda M, Watanabe Y, Nakashima K, Takahashi K, Ohama E (1996) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with a two base pair deletion in superoxide dismutase 1 gene: multisystem degeneration with intracytoplasmic hyaline inclusions in astrocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1089–1101
Kato S, Hayashi H, Nakashima K, Nanba E, Kato M, Hirano A, Nakano I, Asayama K, Ohama E (1997) Pathological characterization of astrocytic hyaline inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Pathol 151:611–620
Kato S, Takikawa M, Nakashima K, Hirano A, Cleveland DW, Kusaka H, Shibata N, Kato M, Nakano I, Ohama E (2000) New consensus research on neuropathological aspects of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) gene mutations: inclusions containing SOD1 in neurons and astrocytes. ALS Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:163–184
Kato S, Nakashima K, Horiuchi S, Nagai R, Cleveland DW, Liu J, Hirano A, Takikawa M, Kato M, Nakano I, Sakoda S, Asayama K, Ohama E (2001) Formation of advanced glycation end-product-modified superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD1) is one of the mechanisms responsible for inclusions common to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients with SOD1 gene mutation, and transgenic mice expressing human SOD1 gene mutation. Neuropathology 21:67–81
Kato T, Hirano A, Kurland LT (1987) Asymmetric involvement of the spinal cord involving both large and small anterior horn cells in a case of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neuropathol 6:67–70
Kurland LT, Mulder DW (1955) Epidemiologic investigations of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. II. Familial aggregations indicative of dominant inheritance. Neurology 5:249–268
LoPachin RM Jr, Aschner M (1993) Glial-neuronal interactions: relevance to neurotoxic mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 118:141–158
Maina F, Klein R (1999) Hepatocyte growth factor, a versatile signal for developing neurons. Nat Neurosci 2:213–217
Maina F, Hilton MC, Andres R, Wyatt S, Klein R, Davies AM (1998) Multiple roles for hepatocyte growth factor in sympathetic neuron development. Neuron 20:835–846
Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (1997) HGF: its organotrophic role and therapeutic potential. Ciba Found Symp 212:198–211; discussion 211–214
Nakamura T, Nawa K, Ichihara A (1984) Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:1450–1459
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, Seki T, Shimonishi M, Sugimura A, Tashiro K, Shimizu S, Kazama T, Isemura M, Sato Y (1989) Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Immunohistochemical localization of heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycan in normal human skin with monoclonal antibodies: comparison with that of fibronectin. Nature 342:440–443
Nakano I, Hirano A, Kurland LT, Mulder DW, Holley PW, Saccomanno G (1984) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropathology of two brothers in American "C" family. Neurol Med (Tokyo) 20:458–471
Novak KD, Prevette D, Wang S, Gould TW, Oppenheim RW (2000) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is a neurotrophic survival factor for lumbar but not for other somatic motoneurons in the chick embryo. J Neurosci 20:326–337
Okura Y, Arimoto H, Tanuma N, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Yamashima T, Miyazawa T, Matsumoto Y (1999) Analysis of neurotrophic effects of hepatocyte growth factor in the adult hypoglossal nerve axotomy model. Eur J Neurosci 11:4139–4144
Park M, Dean M, Kaul K, Braun MJ, Gonda MA, Vande Woude G (1987) Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6379–6383
Rothstein JD, Martin LJ, Kuncl RW (1992) Decreased glutamate transport by the brain and spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 326:1464–1468
Rothstein JD, Van Kammen M, Levey AI, Martin LJ, Kuncl RW (1995) Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 38:73–84
Schmitt A, Asan E, Puschel B, Jons T, Kugler P (1996) Expression of the glutamate transporter GLT1 in neural cells of the rat central nervous system: non-radioactive in situ hybridization and comparative immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience 71:989–1004
Shibata N, Hirano A, Kobayashi M, Siddique T, Deng HX, Hung WY, Kato T, Asayama K (1996) Intense superoxide dismutase-1 immunoreactivity in intracytoplasmic hyaline inclusions of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with posterior column involvement. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:481–490
Silani V, Ciammola A, Pizzuti A, Cardin V, Scarlato G (1999) Motor neurone metabolism. J Neurol Sci 169:161–169
Sun W, Funakoshi H, Nakamura T (2002) Overexpression of HGF retards disease progression and prolongs life span in a transgenic mouse model of ALS. J Neurosci 22:6537-6548
Takahashi K, Nakamura H, Okada E (1972) Hereditary amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Histochemical and electron microscopic study of hyaline inclusions in motor neurons. Arch Neurol 27:292–299
Tower DB (1992) A century of neuronal and neuroglial interactions, and their pathological implications: an overview. Prog Brain Res 94:3–17
Trotti D, Rolfs A, Danbolt NC, Brown RH Jr, Hediger MA (1999) SOD1 mutants linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis selectively inactivate a glial glutamate transporter. Nat Neurosci 2:427–433
Van Bockstaele EJ, Colago EE (1996) Selective distribution of the NMDA-R1 glutamate receptor in astrocytes and presynaptic axon terminals in the nucleus locus coeruleus of the rat brain: an immunoelectron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 369:483–496
Yamamoto Y, Livet J, Pollock RA, Garces A, Arce V, de Lapeyriere O, Henderson CE (1997) Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF/SF) is a muscle-derived survival factor for a subpopulation of embryonic motoneurons. Development 124:2903–2913
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (c) (2) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology for Japan (S.K.: 13680821) and by a Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (S.K. and H.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, S., Funakoshi, H., Nakamura, T. et al. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met in the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord in the patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): immunohistochemical studies on sporadic ALS and familial ALS with superoxide dismutase 1 gene mutation. Acta Neuropathol 106, 112–120 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0708-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0708-z