Abstract.
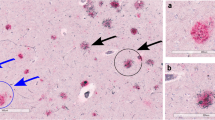
A comprehensive investigation of the incidence, distribution, progression and chemical composition of Aβ deposits in the brains of two young (5 years) and seven aged (25–30 years) rhesus monkeys was conducted to determine the similarity of this phenomenon to that in the human. The brains of the young rhesus were devoid of Aβ deposits. In contrast, Aβ deposits were observed within the cerebral cortex of all aged animals. In animals with mild Aβ burden, deposits were observed primarily in association cortical zones. In animals with moderate Aβ burden, many paralimbic cortical zones also contained Aβ deposits. Finally, in an animal with a heavy burden of Aβ, core limbic cortical zones were also involved. The primary sensory and motor cortices were relatively free of Aβ deposits. A higher proportion of plaques contained Aβ40 as compared with Aβ42. Aβ deposits contained a number of other constituents. Cholinesterases were present in nearly 50% of plaques and displayed the exact same biochemical characteristics as those in the human. Nearly 20% of Aβ deposits also contained apolipoprotein E and a smaller proportion contained heparin sulfate proteoglycans and α1-anti-chymotrypsin. The latter three chemicals were present in many compact plaques. These results indicate that the distribution, progression and chemical composition of plaques in the aged rhesus monkey display many similarities to those observed in the aged human and Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, despite some differences from the human, the aged rhesus may be a good model for studies of the pathological effects of Aβ in the primate brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sani, S., Traul, D., Klink, A. et al. Distribution, progression and chemical composition of cortical amyloid-β deposits in aged rhesus monkeys: similarities to the human. Acta Neuropathol 105, 145–156 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-002-0626-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-002-0626-5