Abstract
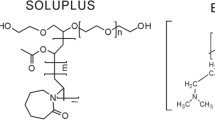
Eudragit® E/HCl salt (E–SD) displays a good antireprecipitation effect on solid dispersion formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs. To elucidate the mechanism underlying the antireprecipitation effect of E–SD, a study on supersaturation was conducted using a dissolution test method with test fluids at varying pH and ionic strength values. Both pH and ionic strength of the test fluid were shown to influence the antireprecipitation effect of E–SD; a strong antireprecipitation effect was observed at a neutral pH (pH 6∼7) and an ionic strength of 0.1 to 1.0. To investigate E–SD in its dissolved state in each test fluid, fluorescence measurement using pyrene as a probe molecule and dynamic light-scattering (DLS) measurement were conducted. The total fluorescence intensity of pyrene increased with increasing E–SD concentrations. Further, small nanoparticles were observed using DLS measurement. These results suggest that E–SD may form a micelle-like structure in the dissolved test fluid.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishikawa T, Watanabe Y, Utoguchi N, Matsumoto M (1999) Preparation and evaluation of tablets rapidly disintegrating in saliva containing bitter-taste-masked granules by the compression method. Chem Pharm Bull 47:1451–1454
Kayumba PC, Huyghebaert N, Cordella C, Ntawukuliryayo JD, Vervaet C, Remon JP (2007) Quinine sulphate pellets for flexible pediatric drug dosing: formulation development and evaluation of taste-masking efficiency using the electronic tongue. Eur J Pharm Biopharam 66:460–465
Khan S, Kataria P, Nakhat P, Yeole P (2007) Taste masking of ondansetron hydrochloride by polymer carrier system and formulation of rapid-disintegrating tablets. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 8:E1–E7
Haware RV, Chaudhari PD, Parakh SR, Bauer-Brandl A (2008) Development of a melting tablet containing promethazine HCl against motion sickness. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 9:1006–1015
Shah PP, Mashru RC, Rane YM, Thakkar A (2008) Design and optimization of mefloquine hydrochloride microparticles for bitter taste masking. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 9:377–389
Randale SA, Dabhi CS, Tekade AR, Belgamwar VS, Gattani SG, Surana SJ (2010) Rapidly disintegrating tablets containing taste masked metoclopramide hydrochloride prepared by extrusion-precipitation method. Chem Pharm Bull 58:443–448
Rao VM, Engh K, Qiu Y (2003) Design of pH-independent controlled release matrix tablets for acidic drugs. Int J Pharm 252:81–86
Obeidat WM, Znait AA, Sallam AA (2008) Novel combination of anionic and cationic polymethacrylate polymers for sustained release tablet preparation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34:650–660
Obeidat WM, Abuznait AH, Sallam AA (2010) Sustained release tablets containing soluble polymethacrylates: comparison with tableted polymethacrylate IPEC polymers. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 11:54–63
Katsuma M, Watanabe S, Kawai H, Takemura S, Masuda Y, Fukui M (2002) Studies on lactulose formulations for colon-specific drug delivery. Int J Pharm 249:33–43
Li J, Yang L, Ferguson SM, Hudson TJ, Watanabe S, Katsuma M, Fix JA (2002) In vitro evaluation of dissolution behavior for a colon-specific drug delivery system (CODES™) in multi-pH media using United States pharmacopeia apparatus II and III. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 3:1–9
Yang L, Watanabe S, Li J, Chu JS, Katsuma M, Yokohama S, Fix JA (2003) Effects of colonic lactulose availability on the timing of drug release onset in vitro from a unique colon-specific drug delivery system (CODES™). Pharm Res 20:429–434
Katsuma M, Watanabe S, Takemura S, Sako K, Sawada T, Masuda Y, Nakamura K, Fukui M, Connor AL, Wilding IR (2004) Scintigraphic evaluation of a novel colon-targeted delivery system (CODES™) in healthy volunteers. J Pharm Sci 93:1287–1299
Katsuma M, Watanabe S, Kawai H, Takemura S, Sako K (2006) Effects of absorption promoters on insulin absorption through colon-targeted delivery. Int J Pharm 307:156–162
Six K, Verreck G, Peeters J, Brewster M, Mooter GV (2004) Increased physical stability and improved dissolution properties of itraconazole, a class II drug, by solid dispersions that combined fast- and slow-dissolving polymers. J Pharm Sci 93:124–131
Six K, Daems T, Hoon J, Hecken AV, Depre M, Bouche MP, Prinsen P, Verreck G, Peeters J, Brewster ME, Mooter GV (2005) Clinical study of solid dispersions of itraconazole prepared by hot-stage extrusion. Eur J Pharm Sci 24:179–186
Ye G, Wang S, Heng PWS, Chen L, Wang C (2007) Development and optimization of solid dispersion containing pellets of itraconazole prepared by high shear pelletization. Int J Pharm 337:80–87
Goddeeris C, Willems T, Houthoofd K, Martens JA, Mooter GV (2008) Dissolution enhancement of the anti-HIV drug UC 781 by formulation in a ternary solid dispersion with TPGS 1000 and Eudragit E100. Eur J Pharm Biopharam 70:861–868
Janssens S, Zeure AD, Paudel A, Humbeeck JV, Rombaut P, Mooter GV (2010) Influence of preparation methods on solid state supersaturation of amorphous solid dispersions: a case study with itraconazole and Eudragit E100. Pharm Res 27:775–785
Brouwers J, Brewster ME, Augustijns P (2009) Supersaturating drug delivery system: solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J Pharm Sci 98:2549–2572
Yoshida T, Yoshihara K, Umejima H, Kurimoto I (2008) Aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymer E for maintaining solubility of poorly water-soluble drug. PCT Int Appl Patent WO 2008081829
Yoshida T, Kurimoto I, Yoshihara K, Umejima H, Ito N, Watanabe S, Sako K, Kikuchi A (2012) Aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymers for improving the solubility of tacrolimus. I: evaluation of solid dispersion formulations. Int J Pharm 428:18–24
Konno T, Watanabe J, Ishihara K (2003) Enhanced solubility of paclitaxel using water-soluble and biocompatible 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers. J Biomed Mater Res 65A:209–214
Eisele J, Haynes G, Rosamilia T (2011) Characterisation and toxicological behaviour of basic methacrylate copolymer for GRAS evaluation. Regul Toxicol Pharm 61:32–43
Chono K, Katsumata K, Kontani T, Kobayashi M, Sudo K, Yokota T, Konno K, Shimizu Y, Suzuki H (2010) ASP2151, a novel helicase–primase inhibitor, possesses antiviral activity against varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplexvirus types 1 and 2. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:1733–1741
Alasino RV, Leonhard V, Bianco ID, Beltramo DM (2012) Eudragit E100 surface activity and lipid interactions. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 91:84–89
Kalyanasundaram K, Thomas JK (1976) Environmental effects of vibronic band intensities in pyrene monomer fluorescence and their application in studies of micellar systems. J Amer Chem Soc 99:2039–2044
Winnik FM, Regismond STA (1996) Fluorescence methods in the study of the interactions of surfactants with polymers. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 118:1–39
Wilhelm M, Zhao CL, Wang Y, Xu R, Winnik MA (1991) Poly(styrene-ethylene oxide) block copolymer micelle formation in water: a fluorescence probe study. Macromolecules 24:1033–1040
Kwon G, Naito M, Yokoyama M, Okano T, Sakurai Y, Kataoka K (1993) Micelles based on AB block copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(β-benzyl l-aspartate). Langmuir 9:945–949
Kim IS, Jeong YI, Cho CS, Kim SH (2000) Thermo-responsive self-assembled polymeric micelles for drug delivery in vitro. Int J Pharm 205:165–172
Chou DK, Krishnamurthy R, Randolph TW, Carpenter JF, Manning MC (2005) Effects of Tween 20® and Tween 80® on the stability of albutropin during agitation. J Pharm Sci 94:1368–1381
Villalobos AP, Gunturi SR, Heavner GA (2005) Interaction of polysorbate 80 with erythropoietin: a case study in protein–surfactant interactions. Pharm Res 22:1186–1194
Fournier D, Hoogenboom R, Thijs HML, Paulus RM, Schubert US (2007) Tunable pH- and temperature-sensitive copolymer libraries by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer copolymerizations of methacrylates. Macromolecules 40:915–920
Nurmi L, Peng H, Seppala J, Haddleton DM, Blakey I, Whittaker AK (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of partly fluorinated polyelectrolytes as components in 19F MRI-detectable nanoparticles. Polym Chem 1:1039–1047
Adler M, Pasch H, Meier C, Senger R, Koban HG, Augenstein M, Reinhold G (2005) Molar mass characterization of hydrophilic copolymers, 2 size exclusion chromatography of cationic (meth)acrylate copolymers. e-Polymers, no. 057
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, T., Kurimoto, I., Umejima, H. et al. Effects of dissolved state of aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymer E/HCl on solubility enhancement effect for poorly water-soluble drugs. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 1191–1199 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2848-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2848-y