Abstract
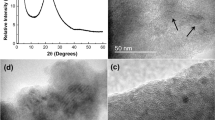
Organic/inorganic hybrids were prepared by catalytic hydrolysis and subsequent polycondensation of tetra-n-butyl titanate (TnBT) in shell layers grafted on core particles. The core particles were synthesized by emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization of styrene, N-n-butyl-N-2-methacryloyloxyethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium bromide (C4DMAEMA), and 2-chloropropionyloxyethyl methacrylate using 2,2′-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride as an initiator. The core diameters were controlled in the range of 70–550 nm by adjusting a C4DMAEMA feed concentration. The core–shell particles were prepared by surface-initiated activator generated electron transfer–atom transfer radical polymerization of 2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA). The sizes of core–shell particles were found to increase monotonically with an increase in a DMAEMA concentration. The hybrid particles were fabricated by adding TnBT into a water/ethanol dispersion of core–shell particles. The amounts of titania deposited increased in proportion to the grafted amounts of poly[2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] on the core particles. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the hollow titania particles obtained by heat treatment of hybrids have an anatase crystallographic phase.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrokhpay S (2009) A review of polymeric dispersant stabilisation of titania pigment. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 151:24–32
Farrokhpay S, Morris EG, Fornasiero D (2006) Titania pigment particles dispersion in water-based paint films. JCT Res 3:275–283
Ferroni M, Guidi V, Martinelli G (1996) Characterization of a nanosized TiO2 gas sensor. Nanostr Mater 7:709–718
Baratont MI, Merhari L (1998) Surface property control of semiconducting metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanostr Mater 10:699–713
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT Jr (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758
Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemann DW (1995) Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96
Levy B (1997) Photochemistry of nanostructured materials for energy applications. J Electroceram 1:239–272
Wang ZS, Kawauchi H, Kashima T, Arakawa H (2004) Significant influence of TiO2 photoelectrode morphology on the energy conversion efficiency of N719 dye-sensitized solar cell. Coord Chem Rev 248:1381–1389
Wu JM, Zhang TW (2005) Large-scale preparation of ordered titania nanorods with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Langmuir 21:6995–7002
Liu D, Yates MZ (2007) Fabrication of size-tunable TiO2 tubes using rod-shaped calcite templates. Langmuir 23:10333–10341
Yi DK, Yoo SJ, Kim DY (2002) Spin-on-based fabrication of titania nanowires using a sol–gel process. Nano Lett 2:1101–1104
Ao Y, Xu J, Fu D, Yuan C (2008) A simple method for the preparation of titania hollow sphere. Catal Comm 9:2574–2577
Song C, Yu W, Zhao B, Zhang H, Tang C, Sun K, Wua X, Dong L, Chen Y (2009) Efficient fabrication and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 hollow spheres. Catal Comm 10:650–654
Kondo Y, Yoshikawa H, Awaga K, Murayama M, Mori T, Sunada K, Bandow S, Iijima S (2008) Preparation, photocatalytic activities, and dye-sensitized solar-cell performance of submicron-scale TiO2 hollow spheres. Langmuir 24:547–550
Li H, Bian Z, Zhu J, Zhang D, Li G, Huo Y, Li H, Lu Y (2007) Mesoporous titania spheres with tunable chamber stucture and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Am Chem Soc 129:8406–8407
Imhof A (2001) Preparation and characterization of titania-coated polystyrene spheres and hollow titania shells. Langmuir 17:3579–3585
Cheng X, Chen M, Limin Wu L, Gu G (2006) Novel and facile method for the preparation of monodispersed titania hollow spheres. Langmuir 22:3858–3863
Caruso F, Shi X, Caruso RA, Susha A (2001) Hollow titania spheres from layered precursor deposition on sacrificial colloidal core particles. Adv Mater 13:740–744
Agrawal M, Pich A, Zafeiropoulos NE, Stamm M (2008) Fabrication of hollow titania microspheres with tailored shell thickness. Colloid Polym Sci 286:593–601
Yu J, Liu W, Yu H (2008) A One-Pot Approach to hierarchically nanoporous titania hollow microspheres with high photocatalytic activity. Cryst Growth Des 8:930–934
Yang HG, Zeng HC (2004) Preparation of hollow anatase TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J Phys Chem B 108:3492–3495
Wang XM, Xiao P (2005) Non-template synthesis of titania hollow spheres and their thermal stability. J Mater Res 20:796–800
Taniguchi T, Kashiwakura T, Inada T, Kunisada Y, Kasuya M, Kohri M, Nakahira T (2010) Preparation of organic/inorganic composites by deposition of silica onto shell layers of polystyrene (core)/poly[2-(N, N-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] (shell) particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 347:62–68
Taniguchi T, Inada T, Kashiwakura Murakami F, Kohri M, Nakahira T (2011) Preparation of polymer core–shell particles supporting gold nanoparticles. Coll Surf A 377:63–69
Taniguchi T, Obi S, Kamata Y, Kashiwakura T, Kasuya M, Ogawa T, Kohri M, Nakahira T (2012) Preparation of organic/inorganic hybrid and hollow particles by catalytic deposition of silica onto core/shell heterocoagulates modified with poly[2-(N, N-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate]. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:107–114
Queffelec J, Gaynor SG, Matyjaszewski K (2000) Optimization of atom transfer radical polymerization using Cu(I)/tris(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amine as a catalyst. Macromolecules 33:8629–8639
Nagai K, Ohishi Y, Inaba H, Kudo S (1985) Polymerization of surface-active monomers. I. Micellization and polymerization of higher alkyl salts of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate. J Polym Sci: Polym Chem Ed 23:1221–1230
Matyjaszewski K, Gaynor SG, Kulfan A, Podwika M (1997) Preparation of hyperbranched polyacrylates by atom transfer radical polymerization. 1. Acrylic AB* monomers in “living” radical polymerizations. Macromolecules 30:5192–5194
Taniguchi T, Ohashi T, Yamaguchi K, Nagai K (2000) Chemical immobilization of polymeric microspheres onto inorganic solid surfaces. Macromol Symp 151:529–534
Yamaguchi K, Taniguchi T, Kawaguchi S, Nagai K (2002) Immobilization of cationic polymer particles having active ester groups onto solid surfaces. Colloid Polym Sci 280:942–948
Taniguchi T, Kasuya M, Kunisada Y, Miyai T, Nagasawa H, Nakahira T (2009) Surface modification of polymer latex particles by AGET ATRP of a styrene derivative bearing a lactose residue. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 71:194–199
Ceska GW (1974) The effect of carboxylic monomers on surfactant-free emulsion copolymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 18:427–437
Ceska GW (1974) Carboxyl-stabilized emulsion polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 18:2493–2499
Ganachaud F, Sauzedde F, Elaïssari A, Pichot C (1997) Emulsifier-free emulsion copolymerization of styrene with two different amino-containing cationic monomers. I. Kinetic studies. J Appl Polym Sci 65:2315–2330
Sauzedde F, Ganachaud F, Elaïssari A, Pichot C (1997) Emulsifier-free emulsion copolymerization of styrene with two different amino-containing monomers: II. Surface and colloidal characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 65:2331–2342
Chu HH, Ou ED (2000) Emulsion polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and partition of monomer between particles and water phase. Polym Bull 44:337–344
Imroz Ali AM, Tauer K, Sedlak M (2005) Comparing emulsion polymerization of methacrylate monomers with different hydrophilicity. Polymer 46:1017–1023
Zheng G, Stöver HDH (2002) Grafting of polystyrene from narrow disperse polymer particles by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules 35:6828–6834
Polpanich D, Tangboriboonrat P, Elaïssari A (2005) The effect of acrylic acid amount on the colloidal properties of polystyrene latex. Colloid Polym Sci 280:152–159
Chen HJ, Wang L, Chiu WY (2007) Chelation and solvent effect on the preparation of titania colloids. Mater Chem Phys 101:12–19
Zhang T, Tian B, Kong J, Yang P, Liu B (2003) A sensitive mediator-free tyrosinase biosensor based on an inorganic–organic hybrid titania sol–gel matrix. Anal Chim Acta 489:199–206
Lee AS, Bütün V, Vamvakaki M, Armes SP, Pople JA, Gast AP (2002) Structure of pH-dependent block copolymer micelles: charge and ionic strength dependence. Macromolecules 35:8540–8551
Plunkett KN, Moore JS (2004) Patterned dual pH-responsive core–shell hydrogels with controllable swelling kinetics and volumes. Langmuir 20:6535–6537
Valtchev V (2002) Silicalite-1 hollow spheres and bodies with a regular system of macrocavities. Chem Mater 14:4371–4377
Zhang YB, Qian XF, Xi HA, Yin J, Zhu ZK (2003) Preparation of polystyrene core–mesoporous silica nanoparticles shell composite. Mater Lett 58:222–225
Seyedjamali H, Pirisedigh A (2011) Synthesis and morphology of new functional polyimide/titania nano hybrid materials. J Mater Sci 46:6744–6750
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Sekisui Chemical for TEM observation. We gratefully acknowledge Nippon Steel Chemical for providing some of the reagents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniguchi, T., Murakami, F., Kasuya, M. et al. Preparation of titania hollow particles with independently controlled void size and shell thickness by catalytic templating core–shell polymer particles. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 215–222 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2658-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2658-2