Abstract
Purpose
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) contributes to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis by promoting vascular endothelial cell injury. Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenols (HLP), rich in flavonoids, have been shown to possess antioxidant and antiatherosclerotic activities. In this study, we examined the protective role of HLP and its main compound (−)-epicatechin gallate (ECG) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to ox-LDL in vitro.
Methods
In a model of ox-LDL-impaired HUVECs, assessments of cell viability, cytotoxicity, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and autophagy were detected. To highlight the mechanisms of the antiapoptotic effects of HLP and ECG, the expressions of molecular proteins were measured by Western blotting, real-time PCR, and so on.
Results
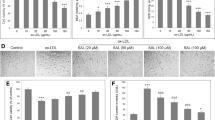
HLP or ECG improved the survival of HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced viability loss. In addition, HLP or ECG showed potential in reducing ox-LDL-dependent apoptosis. Next, the ox-LDL-induced formation of acidic vesicular organelles and upregulation of the autophagy-related genes were increased by HLP or ECG. The HLP-triggered autophagic flux was further confirmed by increasing the LC3-II level under the pretreatment of an autophagy inhibitor chloroquine. Molecular data indicated the autophagic effect of HLP or ECG might be mediated via class III PI3K/Beclin-1 and PTEN/class I PI3K/Akt cascade signaling, as demonstrated by the usage of a class III PI3K inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) and a PTEN inhibitor SF1670.
Conclusions
Our data imply that ECG-enriched HLP upregulates the autophagic pathway, which in turn led to reduce ox-LDL-induced HUVECs injury and apoptosis and provide a new mechanism for its antiatherosclerotic activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized LDL
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- LC3:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3
- Atg:
-
Autophagy-related genes
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- HLP:
-
Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenols
- ECG:
-
(−)-Epicatechin gallate
- CQ:
-
Chloroquine
- 3-MA:
-
3-Methyladenine
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-zyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- BrdU:
-
Bromodeoxyuridine
- DAPI:
-
4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TBS:
-
Tris-buffered saline
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- AO:
-
Acridine orange
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
References
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Xie Y, You SJ, Zhang YL, Han Q, Cao YJ, Xu XS, Yang YP, Li J, Liu CF (2011) Protective role of autophagy in AGE-induced early injury of human vascular endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep 4:459–464
Zhang YL, Cao YJ, Zhang X, Liu HH, Tong T, Xiao GD, Yang YP, Liu CF (2010) The autophagy-lysosome pathway: a novel mechanism involved in the processing of oxidized LDL in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:377–382
Durand E, Scoazec A, Lafont A, Boddaert J, Al Hajzen A, Addad F, Mirshahi M, Desnos M, Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2004) In vivo induction of endothelial apoptosis leads to vessel thrombosis and endothelial denudation: a clue to the understanding of the mechanisms of thrombotic plaque erosion. Circulation 109:2503–2506
Ulrich-Merzenich G, Zeitler H, Vetter H, Bhonde RR (2007) Protective effects of taurine on endothelial cells impaired by high glucose and oxidized low density lipoproteins. Eur J Nutr 46:431–438
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451:1069–1075
Martinet W, De Meyer GR (2009) Autophagy in atherosclerosis: a cell survival and death phenomenon with therapeutic potential. Circ Res 104:304–317
Yorimitsu T, Klionsky DJ (2005) Autophagy: molecular machinery for selfeating. Cell Death Differ 12:1542–1552
Sachdewa A, Nigam R, Khemani LD (2001) Hypoglycemic effect of Hibiscus rosa sinensis L. leaf extract in glucose and streptozotocin induced hyperglycemic rats. Indian J Exp Biol 39:284–286
Ochani PC, D’Mello P (2009) Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic activity of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. leaves and calyces extracts in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 47:276–282
Lin HH, Chan KC, Sheu JY, Hsuan SW, Wang CJ, Chen JH (2012) Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf induces apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem 132:880–891
Gosain S, Ircchiaya R, Sharma PC, Thareja S, Kalra A, Deep A, Bhardwaj TR (2010) Hypolipidemic effect of ethanolic extract from the leaves of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in hyperlipidemic rats. Acta Pol Pharm 67:179–184
Chen JH, Wang CJ, Wang CP, Sheu JY, Lin CL, Lin HH (2013) Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenolic extract inhibits LDL oxidation and foam cell formation involving up-regulation of LXRα/ABCA1 pathway. Food Chem 141:397–406
Hayek T, Fuhrman B, Vaya J, Rosenblat M, Belinky P, Coleman R, Elis A, Aviram M (1997) Reduced progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice following consumption of red wine, or its polyphenols quercetin or catechin, is associated with reduced susceptibility of LDL to oxidation and aggregation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:2744–2752
Miura Y, Chiba T, Tomita I, Koizumi H, Miura S, Umegaki K, Hara Y, Ikeda M, Tomita T (2001) Tea catechins prevent the development of atherosclerosis in apoprotein E-deficient mice. J Nutr 131:27–32
Miura Y, Chiba T, Miura S, Tomita I, Umegaki K, Ikeda M, Tomita T (2000) Green tea polyphenols (flavan 3-ols) prevent oxidative modification of low density lipoproteins: an ex vivo study in humans. J Nutr Biochem 11:216–222
Havel RJ, Eder HA, Bragdon JH (1995) The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest 34:1345–1353
Das DK, Sato M, Ray PS, Maulik G, Engelman RM, Bertelli AA, Bertelli A (1999) Cardioprotection of red wine: role of polyphenolic antioxidants. Drugs Exp Clin Res 25:115–120
Alley MC, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Hursey ML, Czerwinski MJ, Fine DL, Abbott BJ, Mayo JG, Shoemaker RH, Boyd MR (1988) Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res 48:589–601
Madhok BM, Yeluri S, Perry SL, Hughes TA, Jayne DG (2010) Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Br J Cancer 102:1746–1752
Chao CL, Chang NC, Weng CS, Lee KR, Kao ST, Hsu JC, Ho FM (2011) Grape seed extract ameliorates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammatory status of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur J Nutr 50:401–409
Shvets E, Fass E, Elazar Z (2008) Utilizing flow cytometry to monitor autophagy in living mammalian cells. Autophagy 4:621–628
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B (2010) Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 140:313–326
Chen ML, Yi L, Jin X, Liang XY, Zhou Y, Zhang T, Xie Q, Zhou X, Chang H, Fu YJ, Zhu JD, Zhang QY, Mi MT (2013) Resveratrol attenuates vascular endothelial inflammation by inducing autophagy through the cAMP signaling pathway. Autophagy 9:2033–2045
Shiu SW, Wong Y, Tan KC (2012) Effect of advanced glycation end products on lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 expression in endothelial cells. J Atheroscler Thromb 19:1083–1092
Caro LH, Plomp PJ, Wolvetang EJ, Kerkhof C, Meijer AJ (1988) 3-Methyladenine, an inhibitor of autophagy, has multiple effects on metabolism. Eur J Biochem 175:325–329
Li Y, Prasad A, Jia Y, Roy SG, Loison F, Mondal S, Kocjan P, Silberstein LE, Ding S, Luo HR, Silberstein LE, Ding S, Luo HR (2011) Pretreatment with phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) inhibitor SF1670 augments the efficacy of granulocyte transfusion in a clinically relevant mouse model. Blood 117:6702–6713
Gaziano JM, Manson J, Buring JE, Hennekens CH (1992) Dietary antioxidants and cardiovascular disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 669:249–259
Yu YM, Wang ZH, Liu CH, Chen CS (2007) Ellagic acid inhibits IL-1beta-induced cell adhesion molecule expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Br J Nutr 97:692–698
Ludwig A, Lorenz M, Grimbo N, Steinle F, Meiners S, Bartsch C, Stangl K, Baumann G, Stangl V (2004) The tea flavonoid epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces cytokine-induced VCAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:659–665
Widlansky ME, Hamburg NM, Anter E, Holbrook M, Kahn DF, Elliott JG, Keane JF Jr, Vita JA (2007) Acute EGCG supplementation reverses endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Nutr 26:95–102
Kawai Y, Tanaka H, Murota K, Naito M, Terao J (2008) (−)-Epicatechin gallate accumulates in foamy macrophages in human atherosclerotic aorta: implication in the anti-atherosclerotic actions of tea catechins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:527–532
Zhen J, Villani TS, Guo Y, Qi Y, Chin K, Pan MH, Ho CT, Simon JE, Wu Q (2016) Phytochemistry, antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content and anti-inflammatory activity of Hibiscus sabdariffa leaves. Food Chem 190:673–680
Kim M, Choi SY, Lee P, Hur J (2015) Neochlorogenic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation and pro-inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells. Neurochem Res 40:1792–1798
Wu C, Luan H, Zhang X, Wang S, Zhang X, Sun X, Guo P (2014) Chlorogenic acid protects against atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice and promotes cholesterol efflux from RAW264.7 macrophages. PLoS One 9:e95452
Kleemann R, Verschuren L, Morrison M, Zadelaar S, van Erk MJ, Wielinga PY, Kooistra T (2011) Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-atherosclerotic effects of quercetin in human in vitro and in vivo models. Atherosclerosis 218:44–52
Kong L, Luo C, Li X, Zhou Y, He H (2013) The anti-inflammatory effect of kaempferol on early atherosclerosis in high cholesterol fed rabbits. Lipids Health Dis 12:115
Steinberg D, Lewis A (1997) Conner memorial lecture. Oxidative modification of LDL and atherogenesis. Circulation 95:1062–1071
Chen J, Mehta JL, Haider N, Zhang X, Narula J, Li D (2004) Role of caspases in Ox-LDL-induced apoptotic cascade in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Circ Res 94:370–376
Park HJ, Zhang Y, Georgescu SP, Johnson KL, Kong D, Galper JB (2006) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells offer new insights into the relationship between lipid metabolism and angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev 2:93–102
Morselli E, Maiuri MC, Markaki M, Megalou E, Pasparaki A, Palikaras K, Criollo A, Galluzzi L, Malik SA, Vitale I, Michaud M, Madeo F, Tavernarakis N, Kroemer G (2010) Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin-1-dependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis 1:e10
Jeong YJ, Choi YJ, Kwon HM, Kang SW, Park HS, Lee M, Kang YH (2005) Differential inhibition of oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells treated with different flavonoids. Br J Nutr 93:581–591
Babich H, Schuck AG, Weisburg JH, Zuckerbraun HL (2011) Research strategies in the study of the pro-oxidant nature of polyphenol nutraceuticals. J Toxicol 2011:467305
Chiu LC, Wan JM (1999) Induction of apoptosis in HL-60 cells by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is associated with downregulation of bcl-2 expression. Cancer Lett 145:17–27
Chan FL, Choi HL, Chen ZY, Chan PS, Huang Y (2000) Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by a flavonoid, baicalin. Cancer Lett 160:219–228
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D, Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM, Das DK (2010) Cardioprotection by resveratrol: a novel mechanism via autophagy involving the mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res 86:103–112
Chen Q, Ganapathy S, Singh KP, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2010) Resveratrol induces growth arrest and apoptosis through activation of FOXO transcription factors in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 5:e15288
Chiu CT, Hsuan SW, Lin HH, Hsu CC, Chou FP, Chen JH (2015) Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenolic extract induces human melanoma cell death, apoptosis, and autophagy. J Food Sci 80:H649–H658
Kim HS, Quon MJ, Kim JA (2014) New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate. Redox Biol 2:187–195
Pallauf K, Rimbach G (2013) Autophagy, polyphenols and healthy ageing. Ageing Res Rev 12:237–252
Zhang Y, Yang ND, Zhou F, Shen T, Duan T, Zhou J, Shi Y, Zhu XQ, Shen HM (2012) (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces non-apoptotic cell death in human cancer cells via ROS-mediated lysosomal membrane permeabilization. PLoS One 7:e46749
Li W, Zhu S, Li J, Assa A, Jundoria A, Xu J, Fan S, Eissa NT, Tracey KJ, Sama AE, Wang H (2011) EGCG stimulates autophagy and reduces cytoplasmic HMGB1 levels in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 81:1152–1163
Kim HS, Montana V, Jang HJ, Parpura V, Kim JA (2013) Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) stimulates autophagy in vascular endothelial cells: a potential role for reducing lipid accumulation. J Biol Chem 288:22693–22705
Buttke TM, Sandstrom PA (1994) Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today 15:7–10
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306:990–995
Guo H, Chen Y, Liao L, Wu W (2013) Resveratrol protects HUVECs from oxidized-LDL induced oxidative damage by autophagy upregulation via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 27:189–198
Petiot A, Ogier-Denis E, Blommaart EF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P (2000) Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinases are involved in signaling pathways that control macroautophagy in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem 275:992–998
Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Ogier-Denis E (2001) The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol Chem 276:35243–35246
Cao C, Subhawong T, Albert JM, Kim KW, Geng L, Sekhar KR, Gi YJ, Lu B (2006) Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin or apoptotic pathway induces autophagy and radiosensitizes PTEN null prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:10040–10047
Wu X, Senechal K, Neshat MS, Whang YE, Sawyers CL (1998) The PTEN/MMAC1 tumor suppressor phosphatase functions as a negative regulator of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15587–15591
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grant from the National Science Council (NSC99-2632-B-040-001-MY3), Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JH., Lee, MS., Wang, CP. et al. Autophagic effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenols and epicatechin gallate (ECG) against oxidized LDL-induced injury of human endothelial cells. Eur J Nutr 56, 1963–1981 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1239-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1239-4