Summary
Background
Long-term consumption of imbalanced diets, poor in dietary fibres, resulted in the prevalence of several nutritional pathologies. However, low digestible carbohydrates (LDC) have many beneficial effects, especially on energy intake, digestive physiology, and mineral absorption.
Aim of the study
To determine the digestive effects of a LDC, called NUTRIOSE® FB, its metabolisable energy (ME) value, and its effects on mineral absorption in humans.
Methods
Ten healthy young men were fed for 31 d periods a maintenance diet supplemented with either dextrose or the LDC at a level of 100 g DM/d, in six equal doses per d according to a cross-over design. After a 20 d adaptation period, food intake was determined for 11 days using the duplicate meal method, and faeces and urine were collected for 10 d for further analyses.
Results
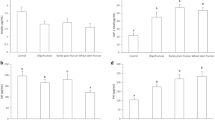
Ingestion of the LDC did not cause severe digestive disorders, except excessive gas emission, and flatulence and slight abdominal pain in some subjects for intakes above 50 g DM/d. Wet and dry stool outputs increased by 45 and 70%, respectively (P<0.02). In vitro enzymatic digestibility of the LDC was 15 (SD 1.5) %, and 9.2 (SD 8.3) % of the LDC was excreted in faeces (P<0.001). The ME value of the LDC was 14.1 (SD 2.3) kJ/g DM, that is 14 % less than the tabulated values of sucrose and starch. Its net energy value (NEV), estimated using three prediction equations, was 8.7, 8.9, and 11.4 kJ/g DM. Ingestion of the LDC significantly increased the relative apparent absorption of Mg, and Mg retention by 67% and 31 mg/d, respectively, tended to increase Ca apparent absorption (P=0.110) and Ca retention (P=0.059), but did not significantly alter Zn parameters.
Conclusion
NUTRIOSE® FB can be used as a “bulking” agent, and substituted up to 50 g/d for usual maltodextrins without causing digestive disorders in healthy subjects. It would reduce intestinal transit disorders and energy intake, and improve magnesium and calcium absorption and retention.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Livesey G (2002) Approaches to health via lowering of postprandial glycaemia. Brit J Nutr 88:741–744
Blundell JE, Burley VJ (1987) Satiation, satiety and the action of fibre on food intake. Int J Obesity 11(suppl.):9–25
Burton-Freeman B (2000) Dietary fiber and energy regulation. J Nutr 130:272–275
Cummings JH, Southgate DAT, Branch WJ, Houston H, Jenkins DJA, James WPT (1978) Colonic responses to dietary fibre from carrot, cabbage, apple, bran and guar gum. Lancet i:5–9
Scheppach W, Luehrs H, Menzel T (2001) Beneficial health effects of lowdigestible carbohydrate consumption. Brit J Nutr 85(Suppl. 1):S23–S30
Breuer RI, Buto SK, Christ ML, Bean J, Vernia P, Paoluzi P, Di Paolo MC, Caprilli R (1991) Rectal irrigation with short-chain fatty acid for distal ulcerative colitis. Preliminary report. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 36:185–187
Delzenne N, Aertssens J, Verplaetse H, Roccaro M, Roberfroid M (1995) Effect of fermentable fructo-oligosaccharides on mineral, nitrogen and energy digestive balance in the rat. Life Sci 57:1579–1587
Coudray C, Bellanger J, Castiglia-Delavaud C, Rémésy C, Vermorel M, Rayssiguier Y (1997) Effect of soluble or partly soluble dietary fibres supplementation on absorption and balance of calcium, magnesium, iron and zinc in healthy young men. Eur J Clin Nutr 51:375–380
Coudray C, Bellanger J, Vermorel M, Sinaud S, Wils D, Feillet-Coudray C, Brandolini M, Bouteloup-Demange C, Rayssiguier (2003) Effects of two polyol, low-digestible carbohydrates, LHBC and HPFL, on intestinal absorption and balance of calcium and magnesium in healthy young men. J Nutr 133:90–93
Tahiri M, Tressol JC, Arnaud J, Bornet F, Bouteloup-Demange C, Feillet-Coudray C, Ducros V, Pepin D, Brouns F, Rayssiguier Y, Roussel AM, Coudray C (2002) Effect of short chain fructooligosaccharides on intestinal absorption and status of calcium in postmenopausal women, A stable isotope study. Am J Clin Nutr 77:449–457
Tahiri M, Tressol JC, Arnaud J, Bornet F, Bouteloup-Demange C, Feillet-Coudray C, Ducros V, Pepin D, Brouns F, Rayssiguier AM, Coudray C (2001) Five-week intake of short-chain fructooligosaccharides increases intestinal absorption and status of magnesium in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 16:2152–2160
Wisker E, Knudsen KEB, Daniel M, Eggum BO, Feldheim W (1997) Energy values of non-starch polysaccharides: comparative studies in humans and rats. J Nutr 127:108–116
Baer DJ, Rumpler WV, Miles CW, Fahey GC Jr (1997) Dietary fiber decreases the metabolisable energy content and nutrient digestibility of mixed diets fed to humans. J Nutr 127:579–586
Castiglia-Delavaud C, Verdier E, Besle JM, Vernet J, Boirie Y, Beaufrère B, De Baynast R, Vermorel M (1998) Net energy value of non-starch polysaccharide isolates (sugarbeet fibre and commercial inulin) and their impact on nutrient digestive utilization in healthy human subjects. Brit J Nutr 80:343–352
Sinaud S, Montaurier C, Wils D, Vernet J, Brandolini M, Bouteloup-Demange C, Vermorel M (2002) Net energy value of two low-digestible carbohydrates, Lycasin® HBC and the hydrogenated fraction of Lycasin® HBC in healthy human subjects and their impact on nutrient digestive utilization. Brit J Nutr 87:131–139
Van den Heuvel EGHM, Wils D, Pasman WJ, Bakker M, Lafay L, Saniez MH, Kardinaal AFW (2003) Short-term tolerance of different doses of NUTRIOSE®FB, a food dextrine, in adult men. Eur J Nutr (submitted)
ISO 5381 (1994) Starch hydrolysis products. Determination of water content. Modified Karl Fisher Method, October 1994
Prosky L, Asp NB, Furda I, De Vries JW, Schweizer TF, Harland BF (1985) Determination of total dietary fiber in foods and food products: collaborative study. J Assoc Analyt Chemists 68:677–679
Vernet J, Vermorel M (1993) Base de données pour le calcul des quantités d’éléments nutritifs ingérés dans les études de nutrition humaine (A database for calculating nutrient intakes in human nutrition studies). Cahiers des Techniques de L’INRA 31:51–76
SAS, (1996) version 6.12, Statistical Analysis systems Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA
Livesey G (2001b) Tolerance of low-digestible carbohydrates: a general view. Brit J Nutr 85(Suppl. 1):S7–S16
Marteau P, Flourié B (2001) Tolerance of low-digestible carbohydrates: symptomatology and methods. Brit J Nutr 85(Suppl. 1)S17–S21
Jouany JP,Lassalas B (2000) Effect of rumen protozoa on C and H distribution among the end products of fermentation. Repr Nutr Develop 40:210
Cherbut C, Bruley des Varannes S, Schnee M, Rival M, Galmiche JP, Delort-Laval J (1994) Involvement of small intestinal motility in blood glucose response to dietary fibre in man. Brit J Nutr 71:675–685
Zhang XZ, Meijer GW, Beynen AC (1990) Dietary maltitol causes increased serum and liver cholesterol concentrations in rats. Int J Vit Nutr Res 60:296–297
Tamura Y, Furuse M, Matauda S, Shimizu T, Okumura J (1991) Energy utilization of sorbose in comparison with maltitol in growing rats. J Agri Food Chem 39:732–735
Oku T, Kwon S (1988) Disaccharidase activity in rat cecum and colon with hyperplasia induced by maltitol or glucomannan. J Nutr Sci Vit 44:69–78
Yen JT, Nienaber JA, Hill DA, Pond WG (1989) Oxygen consumption by portal vein-drained organs and by whole animal in conscious growing swine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 190:393–398
Armstrong DG, Blaxter KL (1957) The heat increment of steam-volatile fatty acids in fasting sheep. Brit J Nutr 11:247–272
Krebs HA (1960) The cause of the specific dynamic action of foodstuffs. Arzneimittelforschung 10:369–373
Livesey G (1992) Energy values of dietary fibre and sugar alcohols for man. Nutr Res Reviews 5:61–84
Livesey G (2001a) A perspective on food energy standards for nutrition labelling. Brit J Nutr 85:271–287
Molis C, Flourié B, Ouarne F, Gailing MF, Lartigue S, Guibert A, Bornet F, Galmiche JP (1996) Digestion, excretion, and energy value of fructooligosaccharides in healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr 64:324–328
Rayssiguier Y, Remesy C (1977) Magnesium absorption in the caecum of rats related to volatile fatty acids production. Ann Rech Vét 8:105–110
Lopez WH, Coudray C, Bellanger J, Younes H, Demigne C, Remesy C (1998) Intestinal fermentation lessens the inhibitory effects of phytic acid on mineral utilisation in rats. J Nutr 128:1192–1198
Ohta A, Ohtsuki M, Baba S, Adachi T, Sakata T, Sakaguchi E (1995) Calcium and magnesium absorption from the colon and rectum are increased in rats fed fructo-oligosaccharides. J Nutr 125:2417–2424
Van den Heuvel EGHM, Muys T, van Dokkum W, Schaafsma G (1999) Oligofructose stimulates calcium absorption in adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr 69:544–548
Van den Heuvel EGHM, Schoterman MH, Muys T (2000) Transgalacto oligosaccharides stimulate calcium absorption in postmenopausal women. J Nutr 130:2938–2942
Van den Heuvel EGHM, Schaafsma G, Muys T, van Dokkum W (1998) Nondigestible oligosaccharides do not interfere with calcium and nonheme-iron absorption in young, healthy men. Am J Clin Nutr 67:445–451
Ducros V, Arnaud J, Tahiri M, Coudray C, Bornet F, Bouteloup-Demange C, Brouns F, Rayssiguier Y, Roussel AM (2003) Influence of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (sc-FOS) on apparent absorption and urinary excretion of Cu, Zn, and Se in healthy postmenopausal women. Submitted to Eur J Clin Nutr
Lutz T, Scharrer E (1991) Effect of short-chain fatty acids on calcium absorption by the rat colon. Exp Physiol 76:615–618
Brink EJ, Beynen AC (1992) Nutrition and magnesium absorption: a review. Prog Food Nutr Sci 16:125–162
Bronner F (1998) Calcium absorption—a paradigm for mineral absorption. J Nutr 128:917–920
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding The study was funded by the Roquette Frères company, which also supplied the experimental products.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermorel, M., Coudray, C., Wils, D. et al. Energy value of a low-digestible carbohydrate, NUTRIOSE® FB, and its impact on magnesium, calcium and zinc apparent absorption and retention in healthy young men. Eur J Nutr 43, 344–352 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0477-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0477-z