Abstract
Purpose
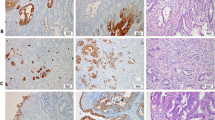
S100A4, a multifunctional protein, has been linked to the invasive growth and metastases of several human cancers. This study investigated the association between S100A4 and overall survival and other clinicopathological features in patients with stage C colonic cancer.
Methods
Clinical and pathological data were obtained from a prospective hospital registry of 409 patients who had a resection for stage C colonic cancer. Tissue microarrays for immunohistochemistry were constructed from archived tissue. S100A4 staining intensity and percentage of stained cells were assessed in nuclei and cytoplasm for both the central part of the tumour and at the advancing front. Overall survival was analysed by the Kaplan–Meier method and Cox regression.
Results
Only a high percentage of cells with S100A4 cytoplasmic staining in frontal tissue was associated with poor survival (hazard ratio, 1.6; 95 % CI 1.1–2.2; p = 0.008) after adjustment for other prognostic variables. There was no association between frontal cytoplasmic S100A4 expression and any of 13 other clinicopathological variables.
Conclusions
High expression of S100A4 in cytoplasm at the advancing front of stage C colonic tumours indicates a poor prognosis. Whether S100A4 can predict response to adjuvant chemotherapy remains to be investigated in a randomised clinical trial.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mazzucchelli L (2002) Protein S100A4: too long overlooked by pathologists? Am J Pathol 160:7–13
Garrett SC, Varney KM, Webber DJ (2006) S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J Biol Chem 281:677–680
Boye K, Mælandsmo M (2010) S100A4 and metastasis: a small actor playing many roles. Am J Pathol 176:528–535
Takenaga K, Nakanishi H, Wada K, Suzuki M, Matsuzaki O, Matasuura A, Endo H (1997) Increased expression of S100A4, a metastasis-associated gene in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 3:2309–2316
Bronckart Y, Decaestecker C, Nagy N, Harper L, Schäfer BW, Salmon I, Pochet R, Kiss R, Heizman CW (2001) Development and progression of malignancy in human colon tissues and correlated with expression of specific Ca2+-binding S100 proteins. Histol Histopathol 16:707–712
Taylor S, Herrington S, Prime W, Rudland PS, Barraclough R (2002) S100A4 (p9Ka) protein in colon carcinoma and liver metastases: association with carcinoma cells and T-lymphocytes. Br J Cancer 86:409–416
Flatmark K, Pedersen KB, Nesland JM, Rasmussen K, Aamodt G, Mikalsen S-O, Bjørnland K, Fodstad Ø, Mælandsmo GM (2003) Nuclear localization of the metastasis-related protein S100A4 correlates with tumour stage in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 200:589–595
Kim JH, Kim CN, Kim SY, Lee JS, Cho D, Kim JW, Yoon SY (2009) Enhanced S100A4 protein expression is clinicopathologically significant to metastatic potential and p53 dysfunction in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 22:41–47
Gongoll S, Peters G, Mengel M, Piso P, Klempnauer J, Kreipe H, Von Wasielewski R (2002) Prognostic significance of calcium-binding protein S100A4 in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 123:1478–1484
Cho YG, Kim CJ, Nam SW, Yoon SH, Lee SH, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Park WS (2005) Overexpression of S100A4 is closely associated with progression of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 11:4852–4856
Hemandas AK, Salto-Tellez M, Maricar SH, Leong AFPK, Leow CK (2006) Metastasis-associated protein S100A4—a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 93:498–503
Wang HY, Zhang JY, Cui JT, Tan XH, Li WM, Gu J, Lu YY (2010) Expression status of S100A14 and S100A4 correlates with metastatic potential and clinical outcome in colorectal cancer after surgery. Oncol Rep 23:45–52
Boye K, Nesland JM, Sandstad B et al (2010) Nuclear S100A4 is a novel prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 46:2919–2925
NIH Consensus Conference (1990) Adjuvant therapy for patients with colon and rectal cancer. JAMA 264:1444–1450
Andre T, Boni C, Navaro M et al (2009) Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluourouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol 27:3109–3116
Twelves C, Wong A, Nowacki MP et al (2005) Capecitabine as adjuvant treatment for stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med 352:2696–2704
Andre T, Colin P, Louvet C (2003) Semimonthly versus monthly regimen of fluorouracil and leucovorin administered for 24 or 36 weeks as adjuvant therapy in stage II and III colon cancer: results of a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 21:2896–2903
Newland RC, Chapuis PH, Pheils MT, Macpherson JG (1981) The relationship of survival to staging and grading of colorectal carcinoma. A prospective study of 503 cases. Cancer 47:1424–1429
Newland RC, Chapuis PH, Smyth EJ (1987) The prognostic value of substaging in colorectal carcinoma. A prospective study of 1117 cases with standardized pathology. Cancer 60:852–857
Bokey EL, Chapuis PH, Dent OF, Mander BJ, Bissett IP, Newland RC (2003) Surgical technique in patients having a curative resection for colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 46:860–866
Davis NC, Newland RC (1983) Terminology and classification of colorectal adenocarcinoma: the Australian Clinico-pathological Staging System. Aust NZ J Surg 53:211–221
Chan C, Jankova L, Fung CL-S, Clarke C, Robertson G, Chapuis PH, Bokey L, Lin BPC, Dent OF, Clarke S (2010) Fascin expression predicts survival after potentially curative resection of node-positive colon cancer. Am J Surg Pathol 34:656–666
Fung CL-S, Chan C, Jankova L, Dent OF, Robertson G, Molloy M, Bokey L, Chapuis PH, Lin BPC, Clarke SJ (2010) Clinicopathological correlates and prognostic significance of maspin expression in 450 patients after potentially curative resection of node-positive colonic cancer. Histopathology 56:319–330
Fielding LP, Arsenault PA, Chapuis PH, Gathright B, Hardcastle JD, Hermanek P, Jass JR, Newland RC (1991) Clinicopathological staging for colorectal cancer: an international documentation (IDS) and an international comprehensive anatomical terminology (ICAT). J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:325–344
Zlobec I, Lugli A (2009) Invasive front of colorectal cancer: dynamic interface of pro-/anti-tumor factors. World J Gastroenterol 15:5895–5906
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ronald C. Newland who examined and reported on over 90 % of the surgical specimens and reviewed the remainder before 2001. The authors also thank Gael Sinclair for her work in entering patient data and maintaining the database. This work was funded by a Cancer Institute New South Wales Translational Program Grant for Colorectal Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kho, P.S.S., Jankova, L., Fung, C.LS. et al. Overexpression of protein S100A4 is independently associated with overall survival in stage C colonic cancer but only in cytoplasm at the advancing tumour front. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 1409–1417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1469-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1469-8